Through the article, TMSA and Sire2.0 Those things
Author:Nobeli Maritime Network Time:2022.06.20
This article will explain in detail what TMSA is, what is Sire2.0, and the relationship between TMSA and Sire2.0. After deep reading, how TMSA runs through Sire2.0's future inspection, it is no longer difficult.

TMSA Introduction
TMSA refers to the abbreviation of self -assessment of oil tankers. A tool developed by OCIMF in 2004 to help ship operators/managers conduct self -assessment and self -improvement of the safety management system based on the guidelines provided. Essence TMSA encourages operators to self -assess the key performance indicators (KPI) and corresponding best practice (BPG) to identify the gap between the company's safety management and the requirements of TMSA, and continuously improve the security management system (SMS), plus add Safety production investment such as large personnel, equipment, and training improves the management level of ships and shore in order to reach the ultimate goal of zero casualties, zero accidents, zero pollution, and reduction of emissions.
The initial purpose of TMSA development is to be the "best practical guide" of the liquid cargo ship industry to improve the safety management performance of ship operators. However, as an effective measurement tool that integrates existing industry guides based on ISM rules, integrates existing industry guidelines, and supplemented by the best practice and procedure instance, TMSA enables operators to evaluate their safety management system perfection and management status, and to all types for all types The ship operators and even related industries have reference value and huge attractiveness.
In accordance with the principle of the development of the system, TMSA guides the shipping company to explore the best management methods and methods suitable for itself, and then achieve the purpose of management improvement. TMSA not only focuses on the integrity and operability of the security management system (SMS), but also pays attention to the methods of passing personnel training, risk identification and evaluation, operation permits, labor protection, approval procedures, target indicators formulation and implementation, regular review and other methods to achieve achievement Personnel safety, environmental protection, and good purpose of ship/equipment maintenance.
Effectively improving management is not only a complete procedure, but also essential to include the promise of the highest leadership and the action of implementing commitments. The company's vision, mission, and values, the company's long -term and short -term target indicators systems and implementation. The highest management should provide sufficient resources and personnel to ensure that the ship is properly managed. The management system should include at least related procedures, instructions, and management requirements to ensure investigation of incidents, accidents and typical hidden dangers, to identify the root causes, formulate corrections and preventive measures, and learn lessons from it. A proper system, process or tool should be established to analyze risks to ensure that all personnel involved are clear risks and prevention and control measures, and improve the approval process.
TMSA characteristic
Tracking and improving performance
Article 12 of the benchmark ISM rules, that is, the company's verification, review and evaluation, requiring the company to review, and verifying the security and pollution prevention measures to meet the safety management system (SMS). The ISM rule also requires enterprises to regularly evaluate the effectiveness of SMS. To this end, TMSA provides the company with a platform that can measure SMS integrity, effectiveness and operability.
TMSA aims to help companies continue to improve SMS through regular self -assessment. And follow the following cycle:
● Plan: Effective strategy needs to formulate clear goals, policies, processes, and clarify roles and responsibilities. TMSA provides a guidelines for the operator of the ship operator, which helps the goal to formulate;
● Action: In order to allow the company to improve the goals, there must be consistent and effective implementation plans. Management should convey clear plans to all employees, and then determine the priority order and improvement goals of the improvement process.
● Measures: Article 12 of the ISM rule requires the company to evaluate the safety management system established and conducts regular internal review to evaluate the management performance and the abide by the existing procedures. A procedure should be checked and measured the progress of the organization in SMS sustainable improvement to achieve excellent security and environmental requirements.
● Improvement: In order to continue to improve, the company must evaluate its performance and determine the implementation of the relevant goals to maintain the development of the continuous improvement process. The results of the assessment can provide input items for the improvement plan to achieve management level spiral. The plan should be consent from employees and focuses on the long -term goals and goals that are most conducive to operators. This part of the continuous improvement cycle combines action with the process goals, and ensures regular review and update personal improvement plans.
This procedure is a supplement to the quality rules of the industry, which aims to encourage continuous improvement. It also provides a means to show its operator to show its means of commitment to safety and environmental excellent performance.
Measure SMS performance
TMSA divides the status of the company's security management system into four key stages or levels. Level 1 and level 2 are usually called lower stages, involving the establishment and inspection of the company's rules and regulations, procedures, and standards; level 3 measurement whether the regular evaluation work is comprehensive and whether the implementation is in place; level 4, introduce third -party evaluation or based on based on a third -party assessment or based on the basis Technical means to verify the implementation of the first three stages of the first three stages, and verify whether the management meets the requirements. The higher level is based on the lower level, and each stage should be completed in turn. If the lower stage requirements are not effectively handled, the assumptions made at the high stage are not reliable, and they are more like the air tower.
The TMSA system contains all relevant elements and provides a architecture to assist Shipo and the operator to evaluate the performance of the safety management system with appropriate tools, thereby measuring and improving it as unqualified or weak aspects. At the same time, TMSA pays great attention to the application of statistical analysis, encouraging ship operators to discover typical and common problems through statistical analysis, summarize good practices and promote the use, identify the root causes and development trends of defects, learn lessons, formulate effective prevention and control and control measure. TMSA provides a "standard" that is recommended to operate according to key performance indicators and refer to the best practices provided by referring to the lack of procedures and systems, the implementation of procedural guidelines, fleet inspection and review, and external audit 4 steps (four levels) (four levels) Increase requirements step by step. Starting from the improvement of the system and documents, strictly implement relevant regulations and self -monitor and inspection, invite or receive external reviews and advanced software and hardware, management concepts/culture. Gradually improve the target indicators that can be quantified within the set time, take targeted measures and track the implementation, and review and revise the target indicators if necessary.
The TMSA score is also the ruler of the management level of Da oil company in the management level of leasing ships and evaluating ship companies. Only by continuously improving and improving the management system according to the requirements of KPI and BPG provided by TMSA, and improving management levels, can we win more opportunities in the market.
TMSA composition
TMSA is divided into 13 key elements, 19 points, and 268 KPIs and several BPG compositions. Each element is divided into four levels. As a ruler for measuring the management level of the company, the higher the level, the higher the corresponding requirements. Among them, L1-75 KPI, L2-72, L3-62, L4-59.
The 14th element-human factors, counting 22 KPIs, which are about to be included in it. In the future, you may meet you with TMSA 4. The addition of human factors reflects that OCIMF's development concept of integrating human factors into the development of the industry is increasingly improved and implemented.
Sire2.0 Introduction
Sire2.0 was launched by OCIMF in 2020. It is a inspection guide different from the previous VIQ structure. It has been greatly adjusted from the aspects of questionnaire structure, inspection tools, evidence collection, and inspection implementation. Due to the continuous development of the industry, the risks they face have also changed, and a more complex and fine risk judgment and management tools have been formed. In this context, it is necessary to further strengthen the original inspection procedure and ensure that it can pass the strengthening inspection to play a real role in today and future marine environmental protection. Sire2.0 pays more attention to the accuracy, high quality, reliability and adaptability of the report to ensure that the report can accurately describe the management and verification of key safety operation risks on the ship, and develop a group of objective integrity inspectors. Human factors, industry changes, regulatory structure updates and technological progress.
Characteristic
Sire2.0 check program is a way to strengthen inspection. Risk -based methods, more comprehensive inspection mechanisms, stronger inspection tools, strengthen process management and more pragmatic inspection reports. By improving the standards of ship equipment, procedures and human factors, the control of ship safety systems and processes is further improved. Through strengthening process management, providing greater transparency and control channels for relevant parties that directly or indirectly participate in the inspection process, and use OCIMF executable and verified rules.
Questionnaire
The Sire2.0 questionnaire includes the following functional blocks. The script preparation is very detailed.
● Question summary (Short Question Text): Questionnaire theme, what to check;
● Ship type: applicable ship type;
● Reorganized check -in sequence: Focus on the parts that are concerned about or the inspection method taken;
● Publications: Conventions, specifications, industry guidelines involved in questionnaires;
● Purpose: Through the purpose of the questionnaire and the purpose and what you want to confirm;
● Industry guidelines: Conventions, communication, specifications, industry guidelines such as questionnaires, such as SOLAS, TMSA, ISM CODE, ISGOTT, COWSP, IACS, UK MCA, etc. (as applicable);
● Inspection guide: the inspection guide refined according to industry guidelines;
● It is recommended that the inspector's actions: the procedures that should be verified, the test equipment, the candidate inquiries, etc.;
● Evidence required: For the above inspection and confirmation, the evidence that the ship should provide;
● Potential evidence of negative observation items: places where defects may occur.
Questionnaire
● Whether the captain and senior crew are familiar with ... the program/purpose/operation/test ...
● Whether the captain and driver are familiar with ... program/purpose/operation/test ...
● Whether the captain, senior crew and ordinary crew are familiar ... the program/purpose/operation/test ...
● Whether the senior crew is familiar with ...
● Whether the driver and the deck of the deck are familiar with ...
● Whether the equipment/system is satisfied ... requirements, whether it is satisfactory ...
● Whether the chief of the turbine and the motorcycle is familiar ...
In short, the request for the captain and senior crew should be very high, and the company's procedures related to questionnaires should be familiar with the operation and testing of various related equipment/systems, clearing the maintenance cycle, and providing relevant records. Ordinary crew members are often required to demonstrate or answer the questions of inspectors on the spot. Sire2.0 Questionnaire and TMSA KPI benchmark
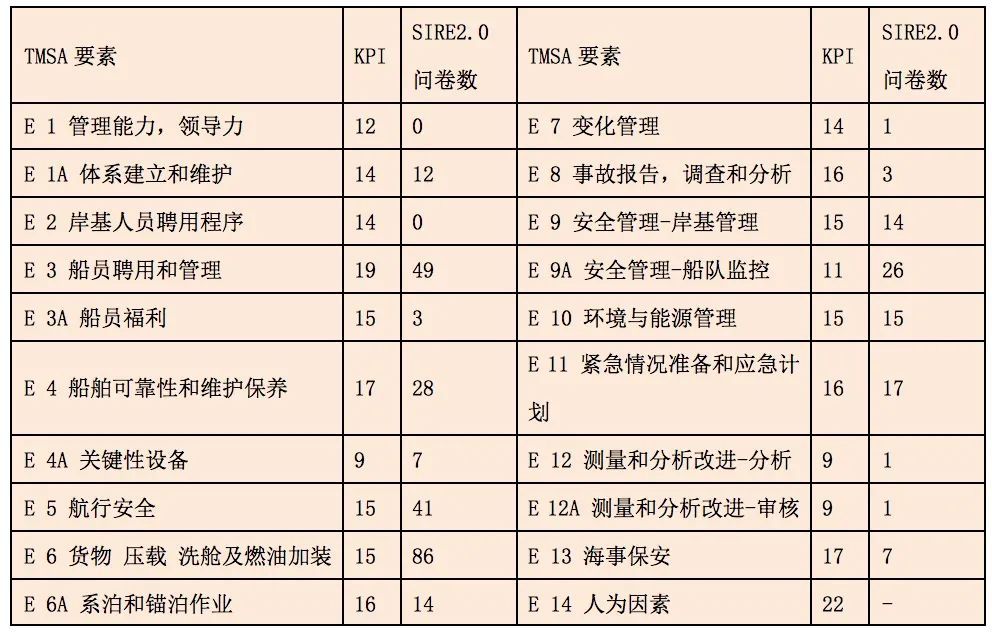
Sire2.0 Different from the previous VIQ questionnaire, the TMSA for shore -based management self -assessment requires throughout the Sire2.0 questionnaire. Except for the first element "management capabilities and leadership", all other elements have more or less questionnaires. Level (Level) 1, that is, L1 involves Sire2.0 questionnaires (excluding OBO) 252, L2 corresponds to 56, level 3 corresponds to 7, and level 4 corresponds to 8.

TMSA elements correspond to the questionnaire distribution of Sire2.0
Note 1: E is an Element abbreviation, which refers to each element in TMSA, the same below
Note 2: E7-E14 will be listed in WeChat tomorrow.
领E1 & 1A leadership and security management system (SMS)
The first element clarifies the fact that the supreme leadership commitment is the basis of the construction of the safety management system. Excellent leadership is the cornerstone of the company's healthy development. It also outlines the responsibility of the company's management establishment and maintaining dynamic SMS to promote health, safety, safety, and Excellence in the field of security and environment (HSSE). The ship safety management system should include a clear, concise and documentary procedure to determine the role, responsibilities and responsibilities of all shore and maritime staff.
E1 has no corresponding questionnaire.
体 Element 1A Safety Management System Construction
Corresponding to 12 questionnaires of Sire2.0, including L1-9, L2-3. in:
L1, Chapter 2 includes 3 articles that the Captain system review, SMS written in working languages, and 3 articles that crew can use smooth communication requirements in work language; Chapter 3 document document, about the requirements of working language on board; Personnel receives 1 training, and 4 iced operations in Chapter 12.
L2, Chapter 2 The crew is familiar with the job responsibilities stipulated in SMS; Chapter 4 Airlines Equipment (suitable for the operation of the sea platform); Chapter 5 is familiar with MSDS/SDS such as cargo oil, fuel, paint and chemicals on board.
The employment and management of the 2 shore members
To some extent, by introducing and continuing to revise the STCW Convention, the assessment mechanism of controlling seafarers' qualifications and certificate issuance has been resolved. Similar methods and appointments of ship management employment qualifications and appointments have also taken similar methods. A formal pre -duty program recognition whether the applicant is suitable for shore -based positions. The selection process should ensure that the candidate's physical health, strong technical ability, and appropriate qualifications and experience, can hold the positions they are applying for.
Evaluation, training, sustainable development and long -term planning should be part of the management and management system. Emphasizing the continuity of personnel, the retirement rate and development space of employees are the key factor to ensure effective commitment and positive coastal management culture. The training record should include the training experience of each employee to ensure that they understand the latest development in the industry in a timely manner.
This element has no questionnaire in Sire2.0.
E3 & 3A crew employment management and benefits
The ability, initiative, health, and well -being of crew members are the key factor to ensure the safe and effective operation of any ship. Before recruitment, the company needs to determine the accuracy of the applicant's qualifications, background and experience. For the pre -employed medical examination for the crew, the certified medical examination report reduces the claim for subsequent medical care and repatriation expenses.
The company's response to the regular assessment procedures for the crew can help identify people who work well in the team, and can be used to ensure that the crew gets the goal of sustaining their own and the company's continuous career plan.
Through continuous evaluation to determine and correct the weaknesses of capabilities, and encourage and cultivate promotion candidates. In the case of using crew agencies, we should conduct regular reviews in response to these intermediaries to ensure that their company procedures can be reflected in the operation practice. It should provide sufficient resources to ensure that the personal needs and well -being of the crew are met.
聘E3 crew hiring and management
累计49个SIRE2.0问卷,第3章3.3船员培训系列4条;3.5 船员熟悉程序系列问卷3条;5.2固定式消防系统系列问卷15条;5.3便携式灭火设备系统问卷6条;5.6固定式和4 questionnaires of the portable gas detection system; Chapter 8; Chapter 10 Question 3 questionnaires.
Grade distribution in TMSA:
L1-40, involving two forced training of crew members, and 38 crews include contractors familiar with their responsibilities procedures;
L2-2, which are the statutory foreign training and the quality of the crew of the crew;
L4-1, carry out the requirements for the behavior of crew.
福E3A crew welfare
Article 3 is the questionnaire of Chapter 3, including: 3.1.3 to satisfy or exceed the duty standards promised by the minimum and company, and ensure the continuity of daily operations when hand transfer; And tracking; 3.4.2 Prevent alcoholic drug abuse and unbelievable spot checks.
E4 & 4A ship reliability and maintenance, including key equipment
Improve and good maintenance and maintenance procedures are important for ensuring the safety, efficient and reliable operation of the ship. The ISM rule requires additional control measures for the preparation of mechanical, electrical and other faults that may cause dangerous situations. This "key equipment" can include but not limited to the main promotion system, steering gear and cargo loading and unloading equipment. Effective plan maintenance system (PMS), including defect reports and closing procedures, will help keep ship equipment in a good state. The effective work order management system should also ensure that appropriate spare parts are provided for timely completion of the plan.
The crew and the designated person in charge should maintain close work communication to ensure that the information is unblocked, and the required support can be provided in time. The competent personnel should visit the ship regularly, including checking with the ship and passing the inspection of close ship relations. Procedures for stopping services (such as dock repair) should be formulated, and inspection and test requirements after repair should be considered and evaluated by the inheritor.
靠E4 ship reliability and maintenance
Corresponding to 23 questionnaires. in:
L1-16 questionnaires, including Chapter 2 3, Chapter 5 1, Chapter 8 (including oil tankers, chemicals, oily ships, gas ships), Chapter 10 5. The content of the questionnaire mainly includes:
● Chapter 2-Management crew is familiar with the equipment fault reporting system. The shore base notified some faults and the competent authorities and applied for inspection, temporary certificates and exemptions.
● Chapter 5-5.9.2 Risk assessment of spare parts for the minimum spare parts of the deck of the deck;
● Chapter 8-Deep wells pump blowing, cargo and carrier valve test, liquid level measurement system verification, cargo hose inspection and use and testing, independent cargo compartment inspection and maintenance and grounding procedures during cargo operations;
● Chapter 10-Sea Water System Status, the alarm, testing and operating procedures and demonstrations of the cabin sewage system, the PMS system is familiar and the spare parts list is consistent with the actual situation, the hot surface splattered layout and regular inspection, the machine oil fog concentration alarm and the curved abduction Various security measures such as box high temperature alarms are normal.
L2-8, including Chapter 2 5, Chapter 5 1, Chapter 8 2. The questionnaire includes: Senior crew members are familiar with the maintenance requirements of the statutory certificate of the ship and the major ship -level memo of the ship; the captain of the captain is familiar with the ESP program and the cabin coating file; The detection procedures for liquid leakage between the cargo cabin, fuel cabin, carrier cabin, air compartment and coffin; familiar with the double -layer shell double -layer bottom space combustible gas detection procedure, etc.
Article 2-2, 2.3.5 of Sire2.0-about 15 years or above ship CAP inspection, 10.4.2 oil, hydraulic oil slip oil and abnormal indicators;
Article L4-1, 3.2.6 Appropriate qualified personnel implementation of the turbine review.
设E4A Key Equipment
Article L1-7 corresponds to the requirements of "4A.1.4 with procedures to record key equipment and system tests of non-continuous use". They are:
● Chapter 5 Familiar with the maintenance and testing of emergency fire pumps and emergency lighting systems;
● Chapter 10 5 questionnaires include the requirements of the procedures, maintenance, testing and recording of emergency generators, emergency batteries, emergency air compressors, water dense doors, and hydraulic power units.
✍E5 navigation safety
The captain has the final responsibility for the safety navigation of the ship, but the company has the obligation to establish and maintain the navigation procedures for ensuring the safety of the ship. Related requirements for publications such as "Driver Procedure Guide" should be met and ensure that the navigation technology that is suitable for navigation situations should be fully implemented.
The best approach to implementing the industry will include regular navigation reviews, and personnel with appropriate qualifications and experience will be carried out during sailing. The company's review should conduct independent comprehensive navigation reviews with appropriate qualifications, and use this as the benchmark.
Involved 41 questionnaires. 33 of them, 2, L3-3, L4-3.
L1 Chapter 4 (including 2 shuttle tankers), Chapter 10 and 12. In the defects of Chapter 4, 15 voyage equipment is familiar with 15 related questionnaires; 7 questionnaires such as UKC, Navigation Plan, Night Airlines commands; 4 driving stations and cabin teams manages 4; 1 radio communication; 3 DP operations. Chapter 10, before use and key voyage, including host, steering gear, power station and other key equipment and system testing. Chapter 12, the driver's ice navigation training.
Article 3, including Chapter 3, the appropriate qualified person implements static navigation review; Chapter 4 VDR/S-VDR data download test.
Article 2, the company's qualified maritime supervisor implements dynamic navigation review according to the PiQ questionnaire; Chapter 12, the qualifications of polar navigators.
Article L4-3 is a sailing review by a qualified third party; a remote navigation review of VDR & ECDIS is performed by a qualified third-party implementation; BTM training.
货E6 & 6A cargo, pressure load, laundering, fuel oil installation, wandering and anchor operation
The purpose of TMSA's 6th and 6a is to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the operation of ships related to goods, refueling and moisturizing. To this end, the company needs to formulate a comprehensive comprehensive procedure covering all aspects of application. In addition, all relevant personnel should understand and apply these procedures. The new promotion of senior crew members should actively participate in the preparation and process implementation of the planning of goods, refueling and moving operations as part of its personal development plan. Before the crew is responsible for cargo and pressure, it should receive appropriate training, which may include using computer training or simulator training on the shore. Polish operations often cause personal injury. Incidents are often caused by bad practices and lack of initiative. A sound company's moisture procedure should reflect the "anchor, tie, and drag -trailer operation" in COSWP. You can also refer to other related best practices in the industry.
载E6 cargo, pressure load and fuel installation operation
Including chemicals, oily ships, gas vessels and shuttles, involve 86 Sire questionnaires, of which:
L1-67, including 42 oil tankers, chemicals and oil ships; 24 gas vessels; 1 shuttle tanker, of which:
● Chapter 5 Safety Management 4, including the familiarity of the processing procedure of the cargo oil into the double shell space and the time available for related equipment; Familiar with breathing equipment (disabled filtration) use procedures;
● Chapter 80, of which:
There are 6 oil tankers, including COW; the lazy gas system and cargo cabin inertia are familiar; familiar with the procedures for separating individual cargo compartment from the common breathable system; the driver is familiar with the procedure of the laundering plan and records containing volatile gas cargo;
包括 8 chemicals, including inertia operation; P & A manual; cargo inhibitors operation; appropriate installation certificate; volatility and toxic cargo washing procedures; not compatible with the separation and management of goods; SCBA and other safety equipment;
Twenty -one oily ships, including the operation test (including oxygen meter) and maintenance of the lazy/nitrogen generator; the high and high test of the cargo compartment; the non -inertial cabin and the sampling static prevention; Avoid electrostatic accumulation; emergency cutting (ESD) and emergency stop testing; the operation of the cargo compartment air -breathable system; the lazy gas system stops the valve maintenance; P/V valve maintenance and testing.
L2-16 questionnaires. in:
● Chapter 2, 1 pressure -load water management plan and record;
● Chapter 4 During the operation of the cargo operation, use the risk of non -home -type communication equipment;
● Chapter 6, 1 operation of BMWS;
● 37 questionnaires in Chapter 8 and 5 oil tanks, including familiar cargo and pressure -loading plan, familiar SSSCL, shipping stability management during the operation period or sailing stage, pipeline valves and breathable/disability before the cargo operation. Check, etc. 1 oily ship;
● 10 chapters (cabin and steering room), familiar with the requirements for fuel installation/sampling procedures.
Article L3-1, 8.3.22 (oil ship) Captain and senior crew members are familiar with the procedures for mixed operation management on board, and the procedure meets the requirements.
Article 3 of L4-2, including the questionnaire, includes: the company's qualified personnel implement comprehensive cargo review; senior crew members of the deck should participate in the coil-based organization of the cargo simulator training covering the routine and emergency operation of the shore organization.
E6A mooring and anchor operation
Corresponding to 14 questionnaires, 13 of which are Chapter 9 (Tie) questionnaire, of which:
L1-2, familiar with the procedures and operations of the brake testing of the Pebu Cable Machine, provides records; familiar with the dangerous rebound zone during the operation of the cable machine and during the operation;
L2-10, including: 3 articles management of moisture equipment; 3 operations of STS; 2 single-point berths; 1 part of the anchor and shuttle tanker; each;
L3-1, the safety management of the moist and anchor team;
Article L4-1, comprehensive review of Poor anchor operation.
问Sire2.0 questionnaire and TMSA KPI benchmark
Sire2.0 Different from the previous VIQ questionnaire, the TMSA for shore -based management self -assessment requires throughout the Sire2.0 questionnaire. Except for the first element "management capabilities and leadership", all other elements have more or less questionnaires. Level (Level) 1, that is, L1 involves Sire2.0 questionnaires (excluding OBO) 252, L2 corresponds to 56, level 3 corresponds to 7, and level 4 corresponds to 8.
TMSA elements correspond to the questionnaire distribution of Sire2.0
Note: E is an Element abbreviation, which refers to each element in TMSA, the same below

OE7 change management MOC
Any changes in the organization or on the ship may bring additional risks. It should be evaluated for changes on the impact of the process and tasks to determine the most affected scope. Proper risk assessment helps to control the implementation process.
Technical changes may need to provide revised drawings, as well as the amendments to the operation manual and technical files. Record the required changes and effectively connect with the control of the ship related documents. In this way, important controlling documents should be maintained and maintained. All the changes that have been implemented should be reviewed regularly to evaluate the results of these changes and measure the level of planning goals.

Correspondingly, the questionnaire L1-1, 2.5.1 Class-grade community or legal inspection requires the effects of changes in the ship structure, machinery and equipment. 、E8 accident report, investigation and analysis
All accidents/events can be prevented. Therefore, the company needs to report, investigate and analyze procedures that must be reported, investigated and analyzed to prevent re -occurrence. The accident survey needs to dig in depth the real reason, eliminate hidden dangers from the source, and prevent the measures to prevent repeated accidents and report the fleet.
Emphasized crew members and shores participating in the accident must receive the company and third -party professional training. The training plan should include appropriate re -training and become part of the personal training plan. It is necessary to ensure the results of the accident information and analysis and experience in the fleet, and organize the crew to discuss during the training exercise of the Kishiki Safety Commission and the ship on board.
Corresponding to Article L1-3:
● Chapter 4 DP positioning questionnaire.
● Chapter 5: 5.7.1 Report and investigate the incidents/accidents on the ship. Incidents and above incidents should issue investigation reports to summarize experience lessons; 5.7.2 Familiar with the accident and danger report procedures, and investigate and close.
安全E9 & 9A safety management
TMSA aims to strengthen the implementation of the spirit of ISM Code and establish a proactive security culture on the ship. The implementation of the monitoring safety management system requires shore -based managers to review the work practice on board. The risk assessment completed on the ship shall be reviewed by the qualified personnel of the shore base and introduce a unified risk assessment standard in the entire fleet. Potential risks should be found through Near Miss reports to promote the development of safe culture on board.
Best practice includes centralized security awareness publicity activities, management procedures for third -party contractors, and hiring safety trainers for boarding training, promoting company values and security culture.
基 Element 9-shore base monitoring
Corresponding to Chapter 5, 14 questions, including L1-5, L2-9. in:
Article L1-5, the relevant procedures of work permit (PTW) are familiar, risk assessment, control measures, etc., including: closed places, thermal work operations, high-altitude operations, out-of-off operations, and electrical equipment operations.
Article L2-9 includes: lifeboat release and abandoned ship exercises; personnel implementation and rescue emergency response plans; identification and isolation of dangerous energy; risk assessment and risk re-evaluation corresponding to responsibilities; at the same time of operation (SIMOPS); fixing the water diversion board device; The side ladder is fixed and maintained; the safety channel control and the mobile boarding of the wheel ladder during the berth period;
船 Element 9A-fleet monitoring
Corresponding to 26 Sire2.0 questionnaires, of which L1-25, L2-1:
● Chapter 4 Communication equipment and programs, including Epirb, SART and VHF use, maintenance, testing;
● Chapter 5 8 questionnaires related to the life equipment; the "monthly safety meeting", "special safety meeting" in safety management and 1 "work plan" required for shore base approval; 7 security inspections in each region; 1 equipment;
● Chapter 10 4, including: front insulation pads of power distribution board; insulation monitoring; oxygen acetylene facilities; safety management of welding equipment; 1 use of stop cards.
源EE10 environment and energy management
The basis of effective environmental measures is to systematically identify, evaluate, and minimize the sources of ocean and atmospheric pollution, and deal with the environment responsible for the environment that may be destructive. The requirements of the anti -pollution convention and/or the state and region restrictions are mentioned in the corporate agreement, and it should be supplemented by regular review of necessary actions to ensure current and future compliance. Long -term environmental plans should be maintained, reviewed and updated regularly. The environmental management plan should include the energy efficiency and fuel management practices of the entire team. Ship recycling shall follow the principles of harmless environment.
L1-14, Chapter 6 11. include:
● Chapter 2 VOC Management Plan and SEEMP Management Plan 2 legal management plan questionnaires;
● Chapter 6 Six questionnaires in the anti -pollution record book; including the water discharge of water in the pump cabin or the leakage of the accident;
● Chapter 8 1, familiar with the VAPOUR vapor recycling system inspection, testing and operation.
Article 10: Chapter 10, the fuel conversion operation procedure of the cabin management crew is maintained.
备E11 emergency preparation and emergency plan
The company should establish a set of emergency response systems on board and the company's emergency situation. The system needs to conduct regular reliability tests to ensure that it can respond quickly and deal with accidents. At the same time, a comprehensive exercise plan should be formulated to test the response to all predictable emergencies. The training of the Kishi Emergency Group is part of the training plan.
The incident/accident management plan must consider the company's 24 -hour emergency response good approach, and the shore emergency personnel should be able to obtain the resources and personnel required to deal with the accident. The contact information of the company's relevant personnel and external personnel should be kept and available at any time. Regular emergency drills and exercises that can be reflected in the trading area of ships and fleets and the characteristics of ship types should be performed. The purpose of the drill and exercise is to test the effectiveness of mobilizing external personnel and resources.
The designated group members should receive media training that is compatible with their roles to ensure control of information passed to the press. Establishing relationships with media professionals should be established and supported by the company if necessary. Clarify the necessity of business continuity and recovery after major events. L1-17, the questionnaire involved includes:
● Chapter 4, the crew is familiar with the sending and receiving procedures of the danger information, security and emergency information, and the GMDSS operation instructions are posted 1.
● Chapter 5, 5.1 Emergency Plan and Exercise Series 14 Questionnaires;
● Chapter 6, remove 1 procedure related facilities for pollutants such as oil spill, chemicals and other pollutants;
● Chapter 9, Emergency Dragon Program and 1 Emergency Dragon Equipment.
AE12 & 12A measurement, analysis and improvement
The most important feature of any effective security management system (SMS) is the continuous improvement of dynamic dynamics. The operator must work hard to ensure that their system files and program files are used in daily management and operation. The validity of the relevant procedures, manuals, and notes should be reviewed and evaluated regularly to ensure that the nature of the work that is ongoing is accurately reflected.
The shore basis should regularly conduct internal trials of the ship, verify the compliance of relevant activities, and track the follow -up operations to verify the operation of the system. When reviewing all ships and the internal interior of the system, standard inspection formats that meet the requirements of the industry's best practices shall be adopted.
The person responsible for the review should have appropriate experience and receive formal internal trial training. The audit records should be preserved for the follow -up review of the management department, and the implementation of the audit according to the plan. Evaluate the validity and correction state of the proposed correction measures in the previous review, and there should be a corresponding fileization program.
The analysis of the review results and the ability of the operator to meet the requirements of ISM, and the verification of newly revised regulatory regulatory regulatory compliance should be part of the regular management review of SMS.
Each of L1-2, 12 and 12A, is 2.2.1 in charge of the ship of 2.2.1 every 6 months, and internal trials of 2.2.2 ships.
✍E13 Maritime Safety
The safety situation at sea is a dynamic process of continuous change. In order to monitor and manage these changes, ship operators need an effective safety management system. The system should be able to identify security threats in all trading areas, and reduce the risks constituted to the lowest level by joining the escort fleet, hiring armed security, taking Harden Ship, and changing routes.
If necessary, contact external experts to provide support to deal with the defined security threat. The company should provide security and monitoring facilities to the ship, and consider installing and testing security equipment on existing ships and new ships. Security management should include internal trial plans.
Implementation of network security procedures/plans. The procedure should include threat recognition of the ship and company terminal, network, general guidance and control equipment. The procedure should also include guidance to measures for cyber security and measures to respond to cyber attack threats.
Corresponding to 7 questionnaires, including L1-3, L2-4. in:
In L1, Chapter 5, the captain and security officers are familiar with the ship security plan, and verify the effectiveness of the security plan for the ship through the exercise; Chapter 7, familiar with the regional security report requirements, familiar with SSAS operations and test regularly; familiar with and implement the company's network security Risk management procedures.
L2 is the seventh chapter of the questionnaire, including: all the sections in the voyage plan should include the information of the security threat; the ship strengthening measures and the ship enhancement plan of the ship when the ship enters the area where the security risk is risky; Effective implementation; SSO training and evidence collection and security records during Hong Kong.
素EE14 Factors
Human factors are the physiological, psychological and social characteristics that affect the interaction between people and equipment, systems, processes, other individuals and work teams. Human errors still occur in the interaction with conditions, systems and/or others. The impact of properly handling human factors to reduce human errors, thereby reducing accidents, increasing reliability and productivity, helping companies and leadership teams to identify and control the conditions and systems of people's behavior and decision -making, and promote the safety and excellence of all operations.
Summary
In the Sire2.0 questionnaire, the TMSA corresponds to the L1 and L2 questionnaires, which are concentrated in the crew's familiarity with related procedures, the operation, testing, and maintenance of related equipment and systems. Can meet the inspection requirements. Pay attention to 15 related questionnaires of L3 and L4, including Chapter 3, 10 questionnaires related to crew training, 5 other chapters.
Article L3-7, including: CAP inspection, dynamic navigation review, newly promoted the captain's operation of ship training, special operations of cargo, moisturizing operation procedures and safety supervision, burning oil test and trend analysis, etc., which requires relevant evidence for ships;
Article 3, all in Chapter 3, including the examination and evaluation of third-party comprehensive navigation review, such as carving review, fuel installation review, VDR remote review, turbine review, crew behavior ability evaluation, and third-party comprehensive navigation review. The guidelines are not yet perfect, and some reviews of ship operators still feel that they cannot start. It is necessary to invest more funds for the company and provide relevant training for the Kishiki supervisor to implement it smoothly.
Originally on: Chinese Ship Inspection
Author: Fu Xingxing

- END -
State Grid Changfeng County Power Supply Company: Fansing Electricity Assisting Companies to relieve the difficulties

We will seriously consider the power consumption solution you provide. This will n...
Help the Sichuan Dazhou Market Supervision and Administration Bureau through the "Cloud Exhibition Hall" live broadcast and bring goods

Cover reporter Luo Xuan Photography ReportOn June 17, the Dazhou Market Supervisio...