The Japanese GDP, which is less than 4 trillion, may fall back 30 years ago!How is "lost time" cause?
Author:Daily Economic News Time:2022.09.19
After the asset bubble ruptured in the 1990s, the Japanese economy had stagnated for a long time. Asset prices (such as housing prices and stock prices) also fell for many years after this crisis.
Affected by this, the scale of Japan's GDP was also greatly affected. According to the Nikkei News, the Japanese GDP, which is denominated in the US dollar, is shrinking. If calculated by $ 1 against 140 yen, it is expected that the Japanese nominal GDP in 2022 will be lower than 4 trillion US dollars (about 56.6 trillion yen) for the first time in 30 years, which is basically the same as the fourth position in Germany.
Not only that, the average Japanese -pricing index for the US dollar has fallen by 20%this year, and Japan's salary also returned 30 years ago, which reduced Japan's purchasing power and talent attractiveness. The analysis pointed out that, based on industries with high value -added, the economic structure of rising wages and strengthening currencies has become a top priority in Japan.
The retrogression of Japan's GDP is directly related to the depreciation of the yen since this year. Although the Japanese authorities have expressed concern about the recent "over -" fluctuations in the yen, Derrick Halpeni, head of the global market research director of Mitsubishi Ninja Financial Group, believes in the comment email sent to the reporter of "Daily Economic News" considers , Kuroda Kuroda Kuroda Kuroda, the governor of the Bank of Japan, is unlikely to change the policy position before the end of the term of April next year. Given that the US dollar will go further, the US dollar will continue to rise against the yen, at least it will break through the recent high point, which may even be a high point in August 1998.
"Lost 30 years"?
"Nikkei News" quoted the prediction of the OECD (OECD) that Japan's nominal GDP this year was 553 trillion yen. If it is converted to $ 140 for $ 1 to US dollars, it is $ 3.9 trillion, which will be the first time that this economic indicator of Japan has been lower than 4 trillion US dollars since 1992. If the yen continues to depreciate or hovers low, it may fall below $ 4 trillion this year and next year.
That is to say, the Japanese economy, which is denominated by the US dollar, has returned to the bubble economic collapse in the 1990s. From the 1990s to the present, global GDP has increased by 4 times, and Japan's proportion has once exceeded 15 %, and it has now shrunk to nearly 4 %. Japan exceeded 6 trillion US dollars in 2012, about 7.5 % higher than Germany, but it is currently flat.
Not only is the GDP denominated in the US dollar, the average salary of Japan is also gone backwards -if it is calculated at a exchange rate of 140 yen, the current average annual salary of the Japanese is 30,000 US dollars, and it is back to the level around 1990. This means that the attraction of work in Japan is gradually declining for foreign labor.
In addition, the soaring energy prices this year also caused a heavy blow to Japan's depreciation of currency. As a representative indicator of crude oil futures, the US dollar VI Curdote futures increased by 13 % compared with the end of last year. The crude oil futures (the most active settlement month in the transaction) of the Tokyo Commodity Exchange, which are priced at the yen, rose 33 %, which was even greater.
"Daily Economic News" reporter also noticed that in the past yen's depreciation cycle, foreign investment has often bet on the growth of Japanese companies and buy Japanese stocks. However, the situation is completely opposite during the current yen devaluation cycle.
Data show that foreign capital sold 2.7 trillion yen in Japanese stocks from January to August 2022. From January to August 2013, the Bank of Japan launched large -scale currency loose and the yen quickly depreciated. During this period, foreign capital purchased more than 9.1 trillion yen.
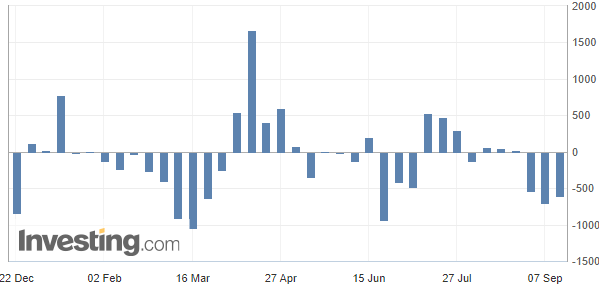
Since the beginning of this year, the inflow and outflow of the Japanese stock market (picture source: British love)
In addition, in terms of US dollars, the average Nikkei index has fallen by 23 % this year, and it is expected to create the largest annual decline since 2008's global financial crisis (42 %). For overseas investors, the value of Japanese assets is decreasing.
It is undeniable that the Japanese economy has indeed performed very well, and it is quite good in income distribution. However, since 1990, the economic growth of Japan has stalled. In the following time, "the decade" or "lost twenty years lost" was often hung by people.
The former Vice President of the Bank of Japan and Professor Waseda University Ruoda Takamoto, the book of "Stagging and Abe Economics: The lesson of Japan", even directly referred to the period since the 1990s as the "big stagnation". Ruodian Masako believes that the economic argument caused by the long -term stagnation of the Japanese economy has also become an important part of its itself, and it is these controversy that leads to the confusion of Japan's policy. During this period Bad, weaker in response to the economic crisis.
Regarding why Japan has experienced a 30 -year economic stagnation and cannot be "up", the chief economist of Nomura Securities Richard C. KOO has previously given, and the current explanation of the current popularity is "asset liabilities. Balance Sheet Recession, that is, after the economic crisis, due to the decline in asset prices, the asset -liability statement of Japanese companies was greatly destroyed. At this time In such an environment, the main goal of Japanese companies is no longer expanding the balance sheet, but how to make the balance sheet safely. Even the unprecedented currency looseness cannot change the cautious attitude of Japanese consumers and enterprises for expenditure.
Will the Japanese central bank intervene?
The retrogression of Japan's GDP, which is denominated in the US dollar, is directly related to the depreciation of the yen this year.
Since the beginning of this year, due to the differences in the United States and Japan's currency policy, the yen has continued to depreciate. From the beginning of the year to the present, the yen exchange rate has depreciated by nearly 25%. Market currency. Over the past year, the US dollar is against the yen trend (picture source: British is financial affairs)

On September 14, the yen's exchange rate against the US dollar fell to nearly 1 USD against 144.9 yen, and forced the 145 mark. Subsequently, the Bank of Japan conducted a "Currency Rate Check". After the news was released, the yen exchange rate rose rapidly, rebounding from a low point in the past 24 years.
The "exchange rate inspection" mechanism is equivalent to the preparation phase of the yen. The Bank of Japan asked market participants to ask market participants to move the exchange rate movement and request major commercial banks in Japan to provide the central bank with the details of foreign exchange transactions to prepare for intervention in the foreign exchange market. Japanese decision -making officials also reiterated on the same day that they have prepared "necessary actions" for the severe fluctuations of the Japanese yen.
However, the reporter of "Daily Economic News" noticed that since Japan's long -term shrinkage in April 1995, the Bank of Japan has only conducted actual intervention on the yen.
From November 1997 to June 1998, the Bank of Japan sold a total of 4.2 trillion yen in 11 times. On June 16, 1998, the dollar reached 146.78 against the dollar, a record high. The Prime Minister of Japan subsequently issued a statement that he promised to restore the health of the Japanese banking industry and boost domestic demand. In the four trading days from June 16th to 19th, 1998, the dollar fell from 146.78 to 133.69, a decrease of 9%. To 143.36.
Japan's largest financial institution, the global market research director of Mitsubishi Japan, Derek Halpenny, said in a comment email sent to the reporter of "Daily Economic News" that last week, to the US dollar to Japan to Japan The meta exchange rate is a very important week. Earlier, the market has been the most clear warning to Tokyo, that is, Japan's tolerance for the devaluation of the yen has reached the limit. The Minister of Finance and the Deputy Minister in charge of international affairs (the top official in charge of foreign exchange policies) of Kanda Real people's remarks on Wednesday reflected their concerns about the "excessive" fluctuations of the yen. However, he also pointed out that although the influence of oral intervention (on the yen exchange rate) in Japan, if there is no fundamental support, the impact of oral intervention will fade.
This week, the global market has ushered in the "Super Central Bank Week". In addition to the focus of the global market, the Fed will announce the interest rate resolution, more than 10 central banks including Japan and the British Bank will also announce interest rate resolutions. The trend of Yuan and British pounds attract market attention.
In this regard, Halpeni pointed out in an email that this week's fundamentals for the yen exchange rate are also very important. He is very confident that the Fed will continue to maintain an eagle position this week.
"Our views believe that the Fed will raise interest rates at least 75 basis points this week, or even 100 basis points, and the Fed's" dot matrix chart "may continue to pass the eagle information. At the same time, we also believe that the Bank of Japan will not change its position. Given that the Japanese government expressed concerns about the weak yen last week, political pressure is accumulating. The central bank's 'has no choice' and can only continue to relax the monetary policy. We agree with the basic point of view of inflation, that is, Kuroda Dongyan is unlikely to change the policy position before the end of the term of April next year. "Halpeni added.
"Therefore, given that the US dollar will further rise, the US dollar will continue to rise against the yen, at least it will break through the recent high, and it may even be a high point in August 1998." Halpenney pointed out that "the rapid and sudden exchange rate Fluctuations may still lead to Japanese intervention, but the example of 1998 shows that this may not be enough to change the general trend of exchange rates. "
Daily Economic News
- END -
These 3 areas of Shanghai are classified as the epidemic high school risk area
The Office of the Leading Group of the Municipal New Crown Pneumonia Epidemic Even...
"Cang Lan Jue" has exceeded 10,000; the world's second courtyard line or bankruptcy | entertainment in a week

Hello everyone, another new week, let's review the entertainment news that might m...