Liu Libo/Yang Yuyan, etc.
Author:Institute of Geological Earth Time:2022.06.16


Today we are increasingly relying on navigation positioning, wireless communication and other technologies, and the requirements for the stability and accuracy of these technologies are getting higher and higher. Therefore, it is urgent to further understand the spatial structure characteristics of the ionization layer. The ionization layer of the Earth has a complex space structure with latitude and longitude changes. These space structures have greatly challenged how to accurately describe the status of the ionization layer, which also has an important impact on navigation positioning, radio communication, satellite remote sensing and other technologies. Observation materials such as the total electronic content of ionizing layers (TEC) and electronic density profiles are assumed that the local level is uniform during the counter -discrimination process. When the existence of space structure, it will undoubtedly seriously affect the accuracy of the electrical ionization information from the detection data extraction.
In the past, research focused on vertical structure and latitude structure, and the understanding of the longitudinal structure mainly focused on large -scale structures. A variety of plasma parameters show a wave -like structure in the equator and low latitudes, and also shows significant differences in the sector in the middle and latitudes. However, we do not understand the characteristics of smaller -scale ionization layer spatial structure.
Researcher Liu Libo, a key laboratory at the Institute of Geology and Earth Physics of the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, studied the TEC data of the GNSS receiver detection network of the GNSS receiver in my set up, and studied the ionizing layer at night and strong gradient events. They discovered the more finely ionizing layer spatial structure characteristics. In the comparison verification verification with GIM and other global ionization products, it put forward suggestions for improving the ability to describe these data products.
Research uses the TEC data that uses the unique synchronous track satellite (GEO) signal unique to the Beidou navigation system. Compared with the traditional GPS TEC, time information is intertwined with space information, the GEO satellite is static relative to the ground, and it can provide pure time and space information. The analysis results showed that the incident of the electrical off -layer night reinforcement occurred within the very limited period of longitude and latitude. The maximum extension range was about 17 ° × 25 ° (longitude × latitude), showing a very significant evolution characteristics of the longitude and latitude (Figure 1 (Figure 1 1 (Figure 1 1 To.
For the two -year TEC data analysis of the GDGZ station, there are four types of longitude gradients, accompanied by significant daily changes. Analysis of a significant strong gradient event, it is found that these strong gradient structures mainly appear in the latitude range of low latitude stenosis in the northern hemisphere, and there is a strong hemisphere asymmetric feature (Figure 2).

Figure 1 The absolute TEC changing diagram and relative TEC change diagram of 110 ° e (a) and 21 ° n (b) during the night enhancement incident

Figure 2 TEC gradient value distribution diagram in the two events. The size of the triangle represents the size of the longitude gradient, and the color represents the direction of the durability gradient. The position represents the center point of the signal range received by each receiver
Compared with analysis of the TEC products released by each institution, it is found that the data products of each institution can not show the structure that enhances at night. Data products of most institutions are difficult to present these significant longitude gradient structures (Figure 3). Therefore, time and space resolution needs to be improved to improve the depiction of the horizontal structure of the ionization layer and its time evolution.
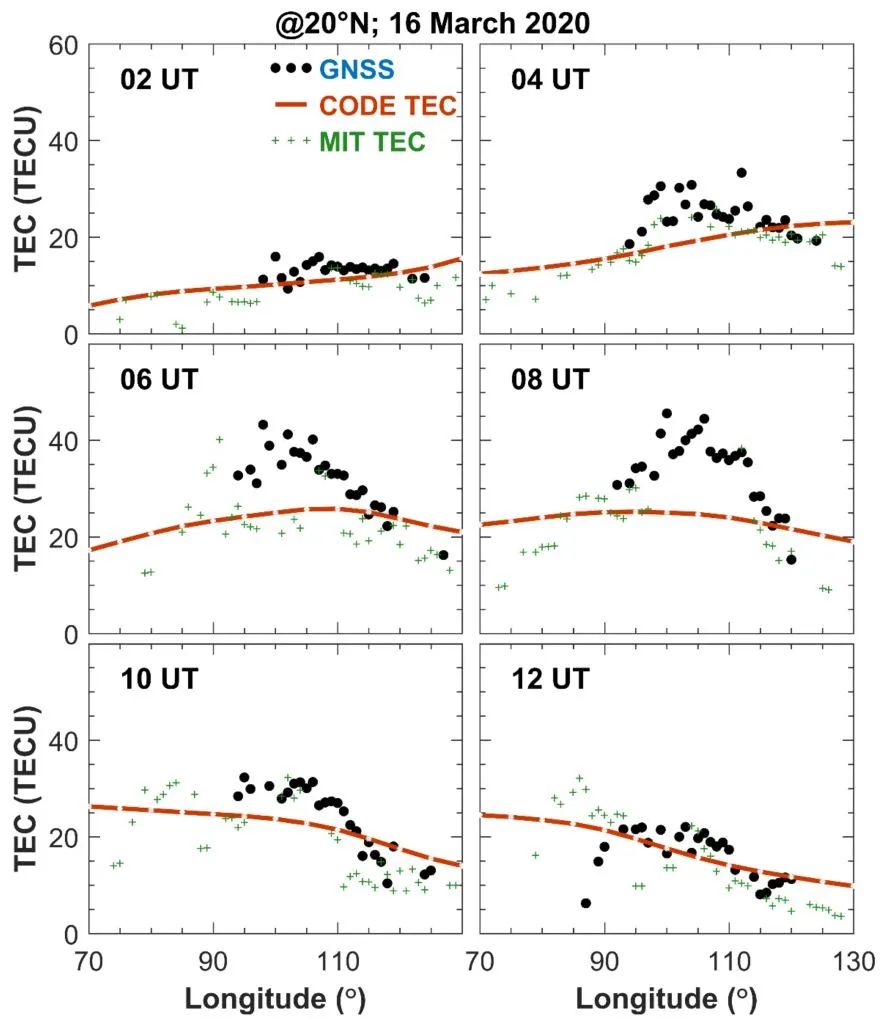
Figure 3 TEC observation values (black dots), CODE's GIM TEC (orange dotted line), and MIT TEC (green plus number) longitudinal changes
The research results were published on the international academic journal Remote Sensing. The study was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42030202), the National Key R & D Plan (2017YFE0131400), the National Natural Science Foundation (42174204), and the noon engineering project.
1.Yang Y, Liu L, Zhao X, Xie H, Chen Y, Le H, Zhang R, Tariq M A, Li W. Ionospheric Nighttime Enhancements at Low Latitudes Challenge Performance of the Global Ionospheric Maps[J].Remote Sensing, 2022 , 14 (5): 1088. Doi: 10.3390/RS14051088.
2.Liu L, Yang Y, Le H, Chen Y, Zhang R, Zhang H, Sun W, Li G. Unexpected Regional Zonal Structures in Low Latitude Ionosphere Call for a High Longitudinal Resolution of the Global Ionospheric Maps[J].Remote Sensing, 2022, 14 (10): 2315. Doi: 10.3390/RS14102315.

Beautiful editor: Chen Feifei
School pair: Wanpeng
- END -
49 -year -old Luo Yonghao, quietly bid farewell to the Internet!

Luo Yonghao, the first net celebrity, just retired from the net!From Lao Luo quote...
The Eye of the Secret Realm · The Calendar of Human Friends | Captain Bee Eagle: Bird's Nest, Love Honeycomb

The wild boar goes down the mountain! Monkey Paper to my balcony! The news of wild...