[Scientific Research Progress] The joint team of Shanghai Observatory and Shanghai Jiaotong University of China and Shanghai Jiaotong University has made important progress in the structural research of the fairy landline (M31)
Author:Shanghai Observatory of China Time:2022.08.06

Recently, the joint research team of the Shanghai Astronomical Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Shanghai Jiaotong University has made important progress in the structural research of the fairy landline (M31). The research team proposes a new idea of searching the ropper in the interstellar gas observation data, so that the M31 galaxy is an independent evidence of a rotary galaxy rather than the Putong vortex galaxy, and uses fluid dynamics to simulate and reproduce the turbulence in the gas in the gas. The main observation characteristics. Related research results are recently published in the international astronomical journal "The Astrophysical Journal". The research results were selected as research highlights by the NOVA website of the American Society (AAS) on July 25, and reported on the website headline with the title of "A Bar in the Bar in The Andromeda Galaxy" (Figure 1). The website selects about five papers every week from the many astronomical journals published by the American Astronomical Society as research on the highlights of the study and shared with the astronomical community.

Figure 1. Research results were selected as research highlights by the NOVA website of the American Society (AAS) on July 25. The topic of "A Bar in the Bar in The Andromeda Galaxy" was reported on the website headline.
The vortex galaxy is divided into two types: normal vortex galaxy and stick galaxy. The stick of the galaxy center is a long strip structure composed of a star. It is the most important internal cause of the long -term slow transformation of the driving rotor galaxy. M31 is the recent vortex galaxy from our closest. For a long time, astronomers have been trying to determine the M31 galaxy form, so as to give it the position of the famous Hubble galaxy classification. However, because the direction of M31 is almost a side of the galaxy compared to our sight direction, it is difficult to determine the structural characteristics inside the galaxy image directly. Prior to this, astronomers proposed that the M31 may include a galaxy stick based on the distortion of the brightness lines such as the stars, but this phenomenon may not only be generated by the stick, or it can be generated by an unwanted ellipse -shaped nuclear ball [1] [1] [1] [1] 2] [3] [4]. Gas observation data also implies that M31 may have sticks, such as significant gas periac motion, twisted zero -speed lines, etc. But other mechanisms, such as the process of co -consistency with another galaxy -can also lead to similar features. Therefore, as a galaxy with a significant classic nuclear ball component [5], there is still a lot of controversy for whether the M31 is a stick galaxy, and determining that the internal structure of the M31 will better understand the structure evolution of our near neighboring galaxy for astronomers Provide huge help.
To solve this problem, the research team proposed a new idea of searching the ropper in the interstellar gas observation data, so that the M31 galaxy is an independent evidence of a rotary galaxy instead of the Putong vortex galaxy, and uses fluid dynamics to simulate the weight. The main observation characteristics of the ripples in the gas are now.
When the rotor galaxy's rod driver flows in the interstellar medium, it will cause a wave of waves. This thrilling wave will produce one of the most significant features of the rotal galaxy -on the Leading Side side, it will form a pair of dust belt, which is similar to that of the stick. Professor Shen Jun, Shanghai Jiaotong University, said: "The thrills will show a sharp speed jump characteristics on the position-view-version diagram. And this severe speed jump characteristics can be viewed by the points spectral spectrometer by the points field spectrum. (Integral Field Unit, IFU) capture and distinguish. If these rosewave features conform to the law of the rotal galaxy, you can clearly prove that there is a stick in the M31 galaxy. "
Based on this idea, the research team uses the latest points of viewing spectrometer Virus-W to the observation data of M31 China Electric Oxygen Gased [OIII], combined with the data of neutral hydrogen atomic gas (Hi), extract vertical on the galaxy disk Different positions in the main axis-see the speed chart, and finally identify the M31 galaxy [OIII] and Hi data through the edge detection algorithm (Figure 2).
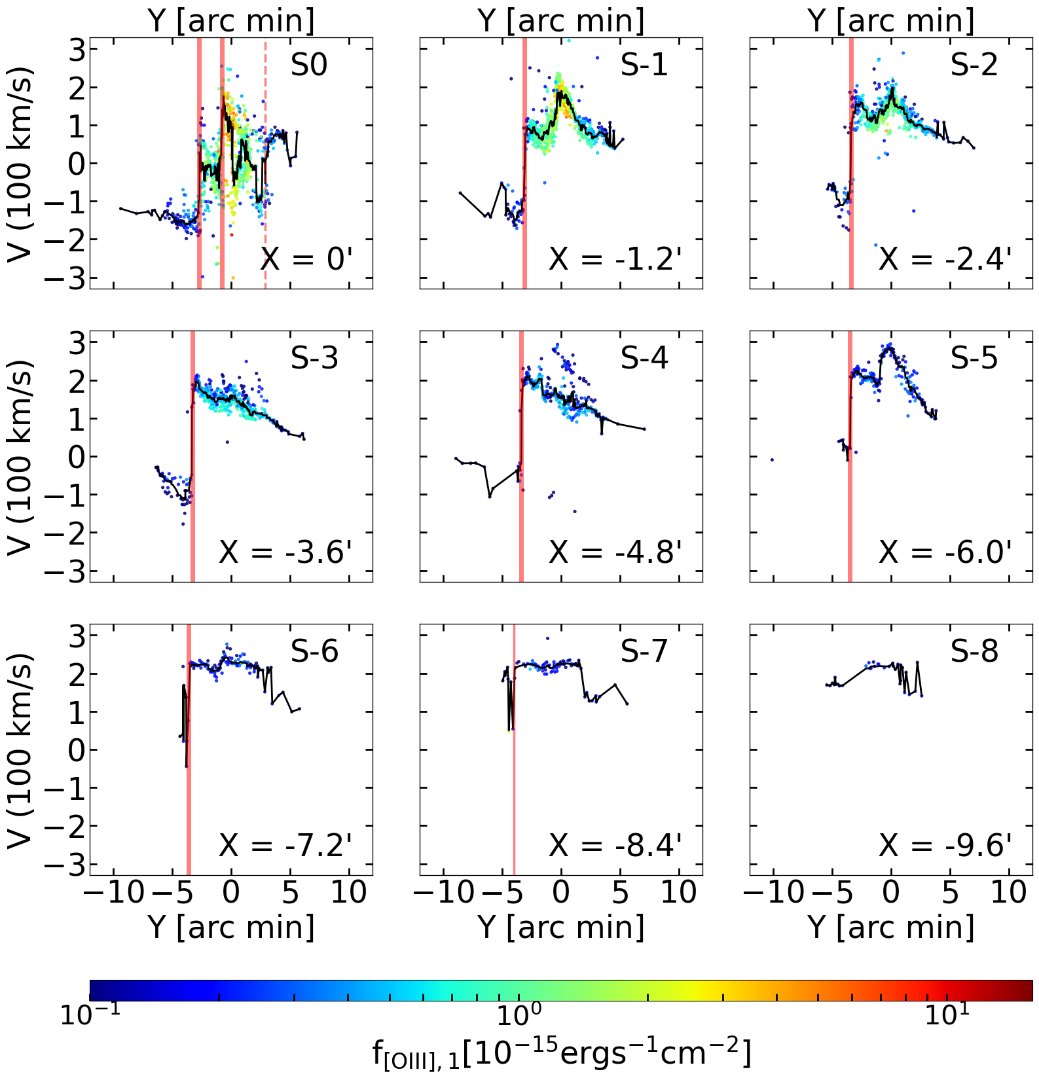
Figure 2. M31 galaxy is far from the wave characteristics of [OIII] from the side of our side. The wavelength of about 500 nanometers [OIII] dual-emitting rays are the section of the visible spectrum, which may only appear in a very low-density cosmic environment. It is the most important launch line in the wavelength range of the Virus-W spectrometer wavelength range one. The data point represents the observation data of [OIII], and the color represents traffic density. Each sub -diagram corresponds to a slice perpendicular to the disc. X represents the position of the slice on the main axis of the disc. The black curve represents the result of the data point is smooth. Red thick lines, fine lines and dotted lines represent the strongest, strong and weaker shocking characteristics. Most trees are distributed in the remote end of the galaxy (under the main axis of the disk).
The research team found that these trendy characteristics are more regularly distributed in the scale of a thousand -second gap (KPC) magnitude (Figure 3). At present, the latest star dynamic model believes that the main shaft angle of the M31 galaxy is about 17 degrees from the disc [6]. If such assumptions are established, then the wave characteristics are indeed mainly distributed on the front guide side of the stick, which is very consistent with the theoretical expectations of the galaxy.
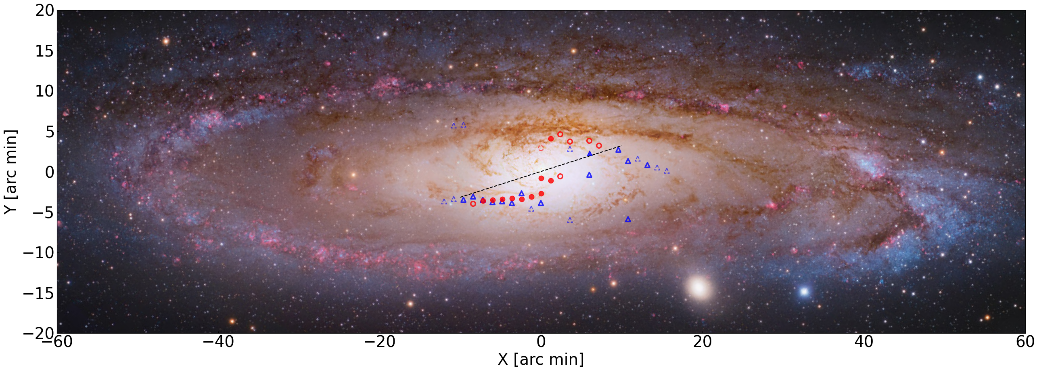
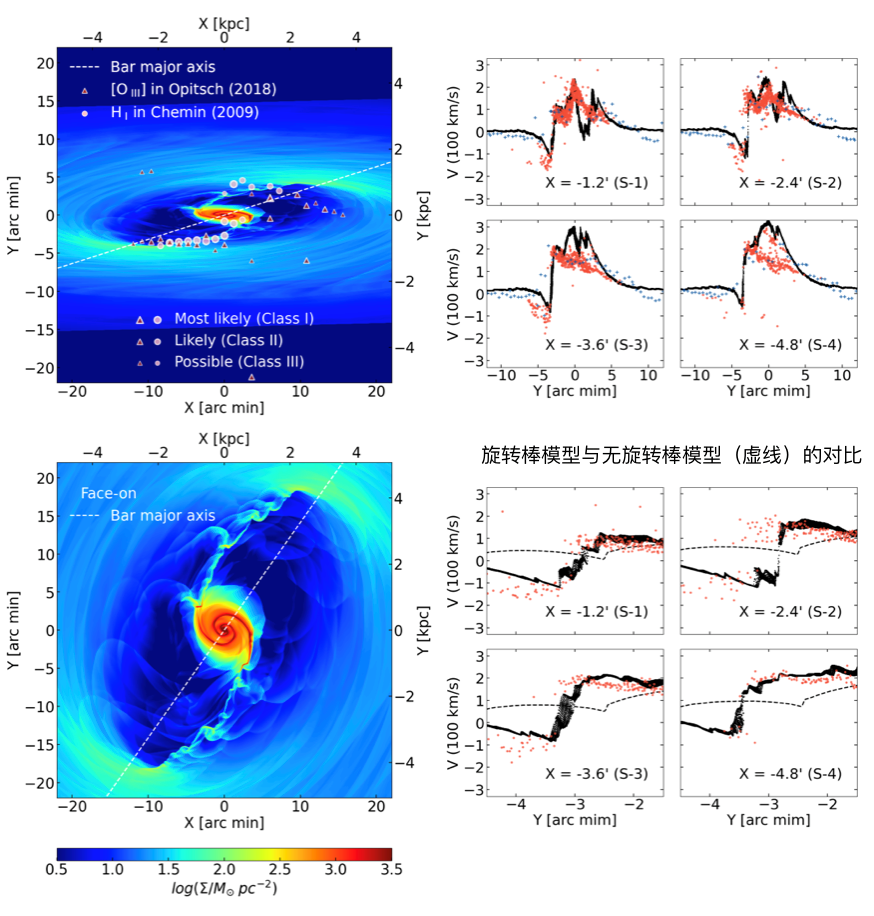
Figure 3. [OIII] and HI's waves are characterized in the space distribution in the M31 galaxy. The background optical image comes from the Hubble Space Telescope, Subaru and Mayall telescope. The red circle and blue triangles represent [OIII] and the wave position in Hi. The signs of solidity, hollow, and virtual frames represent the strongest, strong and weaker shocking characteristics. The dotted line represents the main shaft direction of the rod in the latest dynamic model. "We find that these trendy features are mainly distributed in the nuclear ball area of M31. The strongest jump can exceed 170 km/s, and the speed gradient can reach 1.2 km/second/second gap." :“我们面临的问题是,基于旋转星系棒势场的流体数值模拟能否重现这样急剧的激波特征。”研究团队结合最新的恒星动力学模型,模拟了不同棒转速、气体有效声速和The gas movement under the viewing perspective finally obtained a model that is basically the same as the observation results (Figure 4). The position and speed jump characteristics in the model are basically the same as the observation. The speed of the model is 20 km/second/a thousand seconds, and the effective sound speed of the gas is 30 kilometers/second. The orientation angle of the rod's main shaft and the gas plate inclusion angle of 54.7 degrees and 77 degrees, respectively. The research team also tested the comparison oval nuclear ball structure with rotating rotating sticks, and found that the rotating stick could not produce a ride, and there would be no obvious speed jump characteristics. These discoveries further indicate that the M31 has a rotating center stick instead of a static ellipsoid nuclear ball.
Figure 4. M31 galaxy gas dynamics model. On the left, the M31 model projection to the gas surface density distribution of the gas surface of the M31 model to the sky plane (upper left) and before projection (in the lower left corner). Among them, pink circles and purple triangles represent [OIII] and Hi data. The position corresponding to different slices on the right shows the speed chart. Black data points represent the speed distribution of gas in the model, and red and blue data points represent the observation data of [OIII] and Hi, respectively. In the lower right corner is the enlarged version of the picture in the upper right corner at the swarm, and the dotted line represents a rotating stick model.
The research team believes that this study gives a clear observation evidence of the m31 galaxy with a stick structure, which helps to reveal the history of M31 structure formation and dynamic evolution. The structure evolution of our neighboring galaxy provides great help. The research team will compare the gas characteristics observed in the subsequent research with more gas dynamic simulation to better understand the gas characteristics of the M31 center and the main parameters of the M31 stick.
Feng Zixuan, a doctoral student in Shanghai Astronomical Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Li Zhi, a post -doctoral department of Shanghai Jiaotong University, is the first author of the paper. The main cooperative members of this achievement are the Ortwin Gerhard Group of the Institute of Outside the Institute of Physics of the German Malp Society. The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology, and Shanghai Jiaotong University. The numerical simulation of this work uses the Shanghai Observatory Cluster cluster and the Gravity cluster of the Astronomical Department of Shanghai Jiaotong University.
Note:
[1] Stark, A. A. 1977, APJ, 213, 368
[2] Gerhard, O. E., Vietri, M., Kent, S. M. 1989, APJL, 345, L33
[3] Méndez-Abreu, J., Simonneau, E., Aguerri, J. A. L., Corsini, E. M. 2010, AA, 521, A71, A71, A71
[4] Costantin, L., Méndez-Abreu, J., Corsini, E. M., Et Al. 2018, AA, 609, A132
[5] Athanassoula, E., Beaton, R. L. 2006, Mnras, 370, 1499
[6] BLAía Díaz, M., Gerhard, O., Wegg, C., ET Al. 2018, Mnras, 481, 3210
Thesis link:
Please refer to the original text of the reading
Scientific contact:
Feng Zixuan, Shanghai Academy of Sciences Shanghai Observatory, [email protected]
Shen Juntai, School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiaotong University, [email protected]

- END -
Jinjiang's "core" appeared in the Haichuang Club

Jinjiang News Network June 21 News Recently, the 20th China Strait Innovation Proj...
"Zhu Rong" will welcome the Martian winter solstice

The Zhu Rong Mars northern hemisphere in Mars will usher in the winter solstice on...