Detailed explanation of thousands of characters: legal regulations that can be interpreted by artificial intelligence systems
Author:Tencent Research Institute Time:2022.08.07

Cao Jianfeng Tencent Research Institute senior researcher
Abstract: At present, the opaque and irreplaceable problems of the artificial intelligence system caused by the "algorithm black box" are a major distress of artificial intelligence trust and accountability. In this context, the legislation at home and abroad began to regulate the explanations of artificial intelligence from different perspectives such as rights and obligations, and proposed rules such as algorithm interpretation and algorithm explanation obligations. However, the effective implementation of explanatory requirements is still facing many aspects such as technical feasibility, economic costs, legal rules and value conflict, and social demand differences. Facing the future, the realization of artificial intelligence explanatory requirements requires a variety of forces such as law, technology, marketing, and specifications to work together, focusing on improving the transparency of algorithms and promoting user understanding through the "algorithm description" and algorithm -related information disclosure.
Introduction to the problem
At present, the continuous innovation and extensive popularity of artificial intelligence applications is mainly due to the development and progress of machine learning technology represented by deep learning. Machine learning technology enables artificial intelligence systems to perceive, learn, decide, and action, but these so -called "Learning Algorithm" are troubled by "Black Box Privem".
Although people can know the input and output of an algorithm model, it is difficult to understand its operating process in many cases. Artificial intelligence developers have designed the algorithm model, but usually do not determine the weight of a certain parameter and how a certain result is obtained. This means that even developers may be difficult to understand the artificial intelligence system they develop.
The lack of understanding of how the operation of the artificial intelligence system is a major reason for artificial intelligence to bring new laws and ethical issues such as security, discrimination, and responsibility. As a "black box" deep learning model, it is easy to suffer against attacks, and it is easy to produce discrimination with race, gender, and age, which may lead to difficulty in accountability. In the application scenarios of medical care, lending, and criminal justice, the opaqueity of artificial intelligence is particularly problematic.
Therefore, considering the opaqueity and irreplaceability of artificial intelligence, it is particularly important to supervise and govern artificial intelligence appropriately.
In practice, the large -scale application promotion of artificial intelligence depends to a large extent on whether users can fully understand, reasonably trust, and effectively manage the new partner of artificial intelligence. For this reason, ensuring artificial intelligence products, services and systems is transparent and Explainability.
In fact, all sectors have established a basic guiding principle for transparency and interpreting as an artificial intelligence R & D and application.
At the ethical level, the Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI released by the EU "Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI", which is explained as the four ethical principles of credible artificial intelligence. One of the key requirements. The first global artificial intelligence ethics agreement, "Recomration on the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence", proposed the ten principles of all actors of the life cycle of the artificial intelligence system, among which the life cycle of the life cycle of the artificial intelligence system should follow. Including "transparency and explanatoryness". The "New Generation Artificial Intelligence Ethics Specifications" issued by the National New Generation of Artificial Intelligence Governance Professional Committee of China has proposed a number of ethical requirements including transparency and interpreted by artificial intelligence; 9 departments including the National Internet Information Office of China The "Guiding Opinions on Strengthening the Comprehensive Governance of the Internet Information Service Algorithm" uses "transparent release" as the basic principle of algorithm application, and calls on enterprises to promote the open and transparent algorithm and explain the results of the algorithm.
At the technical level, since the 2015 U.S. Defense Senior Research Program (DARPA) proposed to explain artificial intelligence (Explainable AI (XAI) research project, XAI has gradually become an important research direction in the field of artificial intelligence. Researchers and mainstream technology The company has explored technical and management solutions. IEEE, ISO and other international standard formulation organizations actively promote the formulation of technical standards related to XAI.
In terms of legislation, whether in China, the United States, the European Union and other countries and regions, artificial intelligence has entered the vision of legislators and regulators. Personal information, artificial intelligence and other aspects of domestic and foreign legislation attempts to regulate the transparency and explanatory of artificial intelligence from different perspectives such as rights, obligations, and responsibilities.
Although explanatory requirements have become an important dimension of artificial intelligence supervision, the effective implementation of explanatory requirements is still facing many difficulties and challenges. For example, the implementation of explanatory requirements needs to be answered at least five key questions: whose explanation is explained? Why do you explain? When to explain? How to explain? What is the method of explanation? In addition to these issues, the explanatory requirements of artificial intelligence systems are also facing issues that pursue balance with individual privacy, model security, prediction accuracy, intellectual property rights, etc.
This article aims to clarify these issues and start from the status of technology and industrial development, and put forward specific and feasible ideas for the improvement of legal regulations for artificial intelligence interpreter requirements. Artificial intelligence explanatory requirements and its legislative status quo
(1) Explaimability and value of the artificial intelligence system
Generally speaking, Explanation refers to "explaining the meaning, reason, reason, etc. of something." According to this definition, the explanatoryness of the artificial intelligence system means to promote the interaction between the stakeholders and the AI system by providing information on how to produce decisions and events, but developers, field experts, end users, regulators, regulators, and regulators Different stakeholders have different interpretation needs for the AI model.
The UN's "Proposal of Artificial Intelligence Ethics Issues" defines the explanatory interpretability of artificial intelligence as: "The results of the artificial intelligence system can be understood and explained", which also includes "input, output and performance of each algorithm module. Explanation and how to promote system results. " The National Standard and Technical Research Institute (NIST) put forward the four basic characteristics of explained AI systems in its research report "Four Principles of Explainable Artificial Intelligence":
(1) Explanation, that is, the AI system provides a basis or reason for its decision -making process and results;
(2) MEANINGFUL, that is, the explanation provided by the AI system is clear and easy to understand for the target audience;
(3) Expladianing Accuracy, that is, the explanation can accurately reflect the reasons for the AI system to generate specific output, or accurately reflect the operation process of the AI system;
(4) Knowledge Limits, that is, the AI system can only run when the AI system has sufficient confidence in its output.
Therefore, the interpretability of the AI system not only focuses on the specific output results of the AI system, but also pay attention to the inherent principles and operation processes of the AI system; for example, the AI system responsible for credit approval needs to explain to the user why the loan refuses to issue loans. The recommendation system needs to allow users to allow users Understand the basic principles of personal data such as search history, browsing records, and transaction habits based on users.
In terms of interpretation, the industry generally distinguishes from ANTE-HOC Explanation and Post-HOC Explanation.
Explanation in advance generally refers to the self-interpretable model. It is an algorithm model that can be directly viewed and understood by humans, that is, the model itself is explanation. More common self -explanatory models include decision -making trees, regression models (including logical regression), etc.
Explanation is usually generated by other software tools or manual methods, which aims to describe and illustrate how specific algorithm models work or how to achieve specific output results. For deep learning algorithms with the "black box" attribute, it can usually only resort to explanation afterwards. Afterwards, the explanation is divided into local exploration and global explanation: Local interpretation focuses on the specific output of the algorithm model, and the global interpretation focuses on the overall understanding of the algorithm model.
In addition, the British Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) is different from the guidelines "Explaining Decisions Made with AI). ), And from the perspective of the explanation, the six main types of explanation are proposed:
(1) The explanation of the principle, that is, the reason for the decision -making of the AI system;
(2) Responsibility explanation, that is, participants in the development, management and operation of the AI system, and contact personnel who conduct artificial review of decision -making;
(3) Data interpretation, that is, what data did the decision -making of the AI system and how to use it;
(4) Fair interpretation, which are steps and measures taken to ensure the fairness and non -discriminatoryness of decision -making;
(5) Step and measures to ensure the accuracy, reliability, safety and stability of the decision -making and behavior of the AI system;
(6) The influence explanation is the steps and measures taken to monitor and evaluate the use of the AI system and their decisions on individuals and society. The classification of British ICO has great reference significance for the specific explanation content of understanding explanatory requirements.
The interpretability of artificial intelligence is closely related to the concepts of transparency, responsibility, and accountability. Transparentness means to ensure that users such as users such as AI systems include the facts that will use the AI system in the product or service to inform the user, as well Data sets, etc. Therefore, the explanatoryness of artificial intelligence is closely related to transparency; specifically, increasing transparency is a main goal of artificial intelligence, and interpretability is an effective way to realize the transparency of artificial intelligence. In addition, in many cases, the interpretability requirements of the AI system are mainly to ensure that the AI system can be held accountable and let the relevant actors be responsible. Therefore, it can be said that the interpretability requirements of the AI system are not the ultimate goals, but to achieve other purposes and prerequisites such as responsibility and accountability. Enhance the explanatoryness of the AI system has multiple value:
First, strengthen users' trust in AI systems. User trust is an important condition for the availability of the AI system. In reality, users' distrust of the AI system often stems from users who do not understand the inherent decision -making process of the AI system, and do not know how the AI system makes decisions. Especially in high -risk application scenarios such as finance, medical care, and judicial, if the AI model lacks interpretability, it may not be trusted by users. Darpa's research found that users are more inclined to provide both the AI system that only provides decision -making results.
Second, prevent algorithm discrimination and ensure the fairness of the AI system. Enhance the interpretability of the AI system can help people audit or review the AI system, and then identify, reduce, and eliminate algorithm discrimination.
Third, support internal governance and help create credible and responsible AI systems. Only by fully understanding the AI system can developers be found, analyzed, and corrected the defects in time, and then it is possible to create a more reliable AI system.
Fourth, from the perspective of human -machine collaboration, users can only better interact with it by understanding the AI system. While achieving the expected purpose of the AI system, help the AI system better improve and improve.
Fifth, solve the legal responsibility problem of damage caused by artificial intelligence. Explanation of artificial intelligence can help explore causes and effects, and then help achieve the purpose of legal responsibility, including the purpose of preventing legal responsibility. Because of this, explanatory requirements have become a core consideration of legal regulations for artificial intelligence.
(2) The legislative progress of artificial intelligence explanatory requirements
Globally, the EU's "General Data Protection Regulations" (GDPR) earlier the explanatory regulation of the artificial intelligence algorithm, which is mainly reflected in Article 22 of GDPR. Article 22 of GDPR Focusing on the full automation decision-making (such as the Solely Automated Decision-Making, which is completely automated (such as affecting credit, employment opportunities, health services, education opportunities, etc.), that is, decision-making through technical ways, no Existing human participation).
Specifically, for fully automated decision -making, on the one hand, the right to know and access to the data subject involves at least the following three aspects: (1) inform the fact that there is a process of processing; (2) Provide information about internal logic meaningful information ; (3) Explain the importance of this process and the consequences of expected.
On the other hand, the data main body has the right to request personnel to intervene, express its point of view and ask questions; according to the content of the GDPR preface, the rights of the data subject include "Algorithm interpretation right".
China's legal regulations on artificial intelligence transparency and interpreting can largely learn from the EU GDPR legislative ideas to a large extent.
First of all, in accordance with the principles of fairness and transparency stipulated in Article 7 of the Personal Information Protection Law, and the right to understand the right to personal information given by Article 44, the AI system needs to maintain the necessary transparency when dealing with personal information.
Secondly, Article 24 of the Law made a special provision on the automated decision -making decision -based decision -making of personal information: First, the personnel information processor is required to ensure the transparency and consequences of the transparency and impartiality of the automatic decision -making decision of the algorithm. The second is that for the purpose, for the purpose In the application of algorithm automation decision-making for personalized information, individuals can choose to withdraw (OPT-OUT), which is the right to withdraw; third, for the algorithm automation decision that has a significant impact on personal rights and interests, individuals enjoy the rights and rejection of the required explanation and rejection Personal information processors only make the right to decide through automated decision -making, this is the right to explain the algorithm. These regulations, especially Article 24, are considered to be the right to interpret the algorithm of the Chinese version.
The "Recommended and Management Regulations for the Recommendation of Internet Information Service Algorithms" issued by the National Internet Information Office proposed an obligation to interpret algorithms. The core is the obligation to publicize the information related to the algorithm and the explanation of algorithm decision results. in particular:
First, the providing algorithm recommendation service needs to follow the principles of fairness and justice, openness and transparency.
Second, algorithm recommendation service providers need to formulate and disclose relevant rules for service services.
Third, the regulation encourages the transparency and explanatory of the rules such as retrieval, sorting, selection, push, and display.
Fourth, algorithm recommendation service providers need to inform users of the situation of the provision of algorithm recommendation services, and publicize the basic principles, purpose intentions, and main operating mechanisms of the algorithm recommendation service.
Fifth, algorithm recommendation service providers need to provide users with an option to easily close the algorithm recommendation service.
Sixth, algorithm applications that cause significant impacts on user rights, algorithm recommendation service providers need to provide instructions and bear corresponding responsibilities.
In summary, there are two main paths for China's legal regulations for artificial intelligence explanatory:
First, the general obligations such as public algorithm -related information and optimization algorithm can be explained to the developers of the AI system, thereby promoting users' overall understanding of the AI system;
Second, in the sense of case, the algorithm decision results that have a significant impact on the rights and interests of individuals, the rights and obligations of the configuration algorithm to explain or explain the user's rights and interests, and solve the problem of information and power between users and developers asymmetry. Essence
But in practice, these two paths still face some problems. For example, what AI systems should be applied to the rights and obligations of algorithms? For the purpose of explaining global, what information of the AI system needs to be provided and what ways should be provided? How to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of explanation? and many more.
Analysis of the problems faced by artificial intelligence explanatory regulations
First of all, although legislation can put forward general requirements for algorithm interpretations, the realization of explanatory requirements is not easy. Not only facing the technical challenges brought by the "algorithm black box", but also many factors need to be considered. The following will be carried out one by one. analyze.
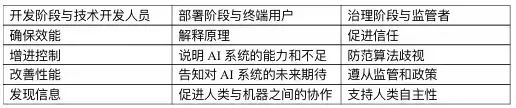
One, object. Different stakeholders such as technical developers, end users, and regulators are different from the needs of algorithms. Moreover, the factors that ordinary users are interested in or understandable and their complexity may be very different from the appropriate information required by professional examiners or legal investigators. For example, ordinary users may want to know why the AI system has made specific decisions in order to have reason to question the decision -making of the AI system. If users think that decision -making is unfair or wrong. Professionals need more comprehensive and more technical details to explain to evaluate whether the AI system meets the general requirements or regulatory requirements of reliability and accuracy. This means that what ordinary users need often understand the explanation of easy -to -understand, non -technical language, rather than a detailed explanation of technical details. It may be contrary to common sense to ordinary users, but it is beneficial in practice. In order to explain the AI system and its output results, it provides ordinary users with a underlying mathematical formula. Even though this may be the most accurate explanation, ordinary users are unlikely to understand. Ordinary users may just want to ensure that the input and output of the AI system is fair and reasonable, not to have a deep understanding of the calculations behind it. Therefore, understanding the real needs of different stakeholders are essential, rather than adopting a one -size -fits -cut path.
Table 1: The purpose of the algorithm interpretation of different subjects at different stages
Second, application scenarios. Different application scenarios may also affect the time and method of providing interpretation. Not all application scenarios need to explain the AI algorithm model and its decision -making results without a lot of details. This depends on whether the AI algorithm decision has a substantial impact on the legitimate rights and interests of the audience. For example, for the algorithm of the distribution location in the restaurant or the algorithm of the mobile phone album, and the algorithm for approval or auxiliary sentences, it is necessary to treat it. If a detailed explanation is required to provide a detailed explanation, it lacks rationality and necessity. Therefore, the draft artificial intelligence law of the European Union divides the AI system into high risk, limited risk and minimum risk according to the different application scenarios, and only puts forward the obligation to interpret the algorithm for the high -risk AI system.
Third, time and place. From the current technology, AI is required to face all application scenarios, and the interpretation of interpretation in real time and large -scale provides is quite challenging and difficult to achieve. The explanatory AI practice in the industry is more focused on the post -after -to -after explanation of different application scenarios.
Fourth, interpretation of correlation or purpose of explanation. Why do you need to explain? The purpose of the AI system is crucial to the application scenario. Compared to the AI system that affects smaller tasks (such as the AI system for recommended movies), the AI system is used to make decisions that affect personal safety or property safety (such as medical diagnosis, judicial trial, financial lending, etc.) More investment and depth explanations.
Fifth, technology and economic feasibility. Some advanced and complex AI systems may have technical restrictions when explaining to humans. In terms of economic feasibility, the cost dimension also needs to be considered, and the required cost and investment to explain large -scale also need to be considered to avoid unreasonable details or strict requirements to hinder the deployment of valuable AI systems. Although sufficient time, energy, professional knowledge and correct tools, can usually know how the complex AI system operates, and understands the reasons behind the behavior of the AI system. Application lacks economic feasibility, and it may be suitable to obstruct the application deployment of the AI system with great value (such as saving life). Because the cost of interpretation is very high, the technical resources they have invested are even more huge. If a very high standard is adopted, every result of the AI system is required to be completely traced and provided with detailed explanations, then this may greatly limit the AI system in the most basic technology (such as static decision trees, such as static decision trees To. This will eventually greatly limit the social and economic benefits of artificial intelligence. For example, a medical algorithm, if the result of each diagnosis requires a detailed explanation, maybe this algorithm may never be put into use and generate value. Because each output of a decision may take a few days to provide explanations. Secondly, the interpretability requirements and efficiency, accuracy, security, privacy, cybersecurity, business secrets, intellectual property rights and other important goals are needed. Some forms of transparency and explanatory seemingly attractive, but may bring quite serious risks, and it is almost helpful for improving responsibility and building trust. For example, the data of the source code or a single user does not help understand how the AI system runs and why it makes specific decisions, but it may cause the AI system to be abused or manipulated, bringing significant risks to user privacy and business secrets.
In fact, sharing and open source code is the lowest end and the most invalid algorithm transparency and interpretation method; because the AI system is too complicated, even technical experts cannot measure. So the open source code does not help ordinary users understand the AI system. In addition, the less transparent the algorithm is, for example, the algorithm becomes simple, it can increase the explanatoryness, but at the same time, it may make the algorithm more accurate. This is because there is a natural tension between the predictive accuracy of the AI model and interpretability. In fact, between interpretable and accuracy, if AI applications are not so high in performance, explanation can exceed accuracy; if security is preferred, explanatory can make accuracy, as long as there is existence It can ensure the security measures of accountability.
As the UN "Proposal of Artificial Intelligence Ethics" pointed out, the principles of fairness, security, and interpretability are desirable, but in any case, these principles may cause contradictions and need to be evaluated according to the specific situation In order to control the potential contradictions, we also consider the principle of compatibility and respect for personal rights.
Artificial Intelligence Explanable Future Advancement
It can be seen from the above analysis that explaining the artificial intelligence system is a very complicated thing, and the current legislation in China has not yet formed a unified regulatory path. Regardless of whether the starting point of the explanation is rights, obligations, or responsibilities, they have not established clear and clear rules. Facing the future, regulating the transparency and interpretability of artificial intelligence requires a variety of forces such as law, technology, marketing, and specifications to play together.
(1) Legislative legislation should follow risk -based classification classification division supervision ideas
Common sense tells us that technology applications cannot be perfect and never wrong. The view that technology applications should meet absolute requirements are biased and misleading. In this sense, new technology governance should be risk -oriented, not to completely eliminate risks, but to effectively manage risks. Therefore, legislation should not adopt excessive rigorous regulatory requirements to avoid the requirements of the AI algorithm application in terms of transparency and interpretability. Wuling in technical details; it is necessary to adopt a tolerance and prudent stand, establish a supervision method of classified classification sub -scenarios, support the continuous innovation and development of AI algorithm applications, take into account the overall interests of the government, technology enterprises, and the public. Find a balance between the public interests and safeguarding the public interests of the society.
Specifically, in terms of artificial intelligence interpretability requirements, first of all, disclosing the source code of the AI algorithm model is an invalid way, which not only helps the understanding of the AI algorithm model, but may threaten data privacy, business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets, and business secrets and business secrets. Technical security; second, it is not advisable to explain or explain the results of all algorithm decision -making results without distinguishing the application scenarios and space occasions; again, focus on the disclosure obligations in the application process. Responsibilities need to disclose the fact that the AI system is substantially involved in decision -making or interaction with human beings. Disclosure should provide a key task of AI participation in a clear, easy -to -understand, meaningful way; Data sets, which is not only operable, but also conflict with copyright protection, infringement of users' data privacy or violation of contractual obligations.
In addition, the explanatory requirements of the law on the AI system should focus on meeting the needs of end users. So far, the interpretability of the AI system mainly serves the needs of AI developers and regulators, such as helping developers to investigate vulnerabilities and improve AI systems to help regulators supervise AI applications. Instead of letting end users understand the AI system. A study in 2020 found that corporate deployment can explain artificial intelligence to support internal purposes such as engineering development, rather than enhance the transparency and trust of users or other external stakeholders. Therefore, in order to promote the user's understanding of the AI system, a feasible idea is to learn from the existing information disclosure mechanism of food nutritional composition tables, product descriptions, drugs or medical devices, and risk notifications. The system establishs an "algorithm instructions" mechanism. The EU's artificial intelligence legislation has adopted similar ideas. The Draft EU artificial intelligence law follows the ideas of classified supervision. It provides high transparency and information requirements for high -risk AI systems, that is, developers should ensure that the operation of high -risk AI system operations should be ensured It is transparent enough to provide users with information such as Instructions of USE, and disclose information such as the basic information of system developers, the performance characteristics of high -risk systems, supervision measures, and maintenance measures. (2) Exploring the establishment of a reasonable and moderate and adaptive artificial intelligence explanatory standard for different industries and application scenarios
Although legal governance is important, it can explain the realization of artificial intelligence cannot be separated from the direct participation of technical personnel and technical communities. So far, XAI has become one of the most important development directions in the field of artificial intelligence, but as the US DARPA's review of XAI's review report found, XAI's progress is still very limited, facing many problems and challenges. The most important thing is to establish artificial intelligence explanatory technical standards. In this regard, a key issue that needs to be clear is that the evaluation criteria for artificial intelligence should not be "perfect", but on the basis of comparison with existing processes or human decision -making. Acceptable standards. Therefore, even if the AI system needs to be explained, it must consider explaining the degree. Because the AI system is required to meet the explained "gold standards" (far exceeding the existing non -AI model, which is required by human decision -making), it may not hinder the innovative use of AI technology. Therefore, it is necessary to adopt a folding path to consider the weighing of the interests required by technical restrictions and different explanatory standards in order to balance the practical restrictions brought by the benefits of complex AI systems and different explanatory standards. The author believes that the user -friendly interpretation should be accurate, clear, clear, and effective, and consider the needs of different application scenarios to improve the overall understanding of the AI system: explain whether it accurately transmits recommendations that support the AI systems. Key information? Explain whether it helps to understand the overall function of the AI system? Do you explain whether clear, clearly, related (relatedable), related (relatedable)? Explain whether the sensitivity is appropriately considered? For example, the sensitive information of the user.
Specifies can be promoted from the following aspects to promote the explanatory standards:
First, it is unrealistic to provide explanatory standards for each application scenario of the AI system, but it can provide explanatory standards for exemplary application scenarios. This can provide the industry and enterprises with beneficial references to balance the explanatory requirements of the performance and different standards of different AI models.
Second, for the relevant policies, the best practice cases that have explained the AI explanation and negative practices with negative impacts are all worth trying. Including effective user interfaces to provide interpretation, and record mechanisms for experts and auditors (such as detailed performance characteristics, potential uses, system limitations, etc.).
Third, you can create an interpreted map of different levels. This map can be used to provide minimum acceptable measures for different industries and application scenarios. For example, if the potential adverse effects of a mistake are very small, the explanation is not very important. On the contrary, if a mistake is dangerous to life and property, the explanation becomes vital. Similarly, if users can easily get rid of the constraints of algorithm automation decisions, the demand for in -depth understanding of the AI system is not so strong.
(3) Support industry self -discipline and give full play to the power of the market to promote the development of artificial intelligence can be explained
According to the experience of the US science and technology industry, the work of artificial intelligence can be explained by enterprises and the industry, rather than the government for mandatory supervision, and adopt a voluntary mechanism rather than forced certification. Because market forces will motivate explanatory and reproducible, it will drive the development and progress of artificial intelligence.
On the one hand, from the perspective of market competition, in order to gain competitive advantages, enterprises will actively increase the explanatory degree of its AI systems, products and services, so that more people are willing to adopt or use their artificial intelligence applications, and then maintain their own market Competitiveness;
On the other hand, from the perspective of users, users will vote with their feet, that is, if the user does not understand the operation of the AI system, there may be concerns when using AI systems, products and services The understanding of AI systems, products and services that understands will not be able to obtain the long -lasting trust of users, so users' demand for such AI applications will also be reduced. At present, mainstream technology companies have attached great importance to the explanatory research and application of AI, and they are actively exploring the implementation of artificial intelligence explanatory implementation.
For example, Google's model card mechanism (Model Cards) aims to let people understand and understand the operating process of the algorithm in a popular, concise and understandable way, and conduct describe.
IBM's AI facts (AI FACT Sheets), which aims to provide information related to the creation and deployment of AI models or services, including purpose, expected use, training data, model information, input and output, performance indicators, bias, Lu Lu, Lu Lu, Lu Lu, Lu Lu, Lu Lu, Lu Lu, Lu Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu, Lu Battle, domain transfer, best conditions, adverse conditions, interpretation, contact information, etc. Facing the future, we should focus on self -discipline measures such as the best practical practices, technical guidelines, and self -discipline conventions to support the development of artificial intelligence.
(4) Alternative mechanism and ethical specifications as useful supplements to interpretable requirements
Although explanatoryness is one of the optimal solutions to improve AI technology, not all AI systems and their decisions can be explained, or they need to be explained. When the AI system is too complicated, it is difficult to meet interpreting requirements, or cause the interpretation mechanism to fail and the effect is not optimistic, it is necessary to actively transform the regulation and explore more diversified and practical technical paths.
At present, it is technically advocating to adopt appropriate alternative mechanisms, such as third -party feedback, appeal mechanism and human censorship intervention, conventional monitoring, and auditing. effect.
For example, a third -party marking feedback mechanism allows people to provide feedback on use for the AI system. Common tag feedback technology includes user feedback channels ("click Feedback" button) and vulnerability reward mechanism.
The user's appeal mechanism can form an effective supervision of the AI system and its developers, and it is also an important guarantee for AI responsibility. The standards of China's "Personal Information Security Standards for Information Security Technology" and "Conducting the Practical Guidelines for Network Security Standards" have made specific regulations on user complaints, doubts, feedback, and artificial review.
Conventional monitoring includes strict and continuous testing, confrontation testing, etc., which aims to discover problems in the system and improve timely.
As an important way to ensure the responsibility of AI, the audit mechanism is a record, retrospective and investigation of the application of the AI algorithm. Through algorithm auditing, it can achieve a reverse interpretation effect to reduce the adverse effects of algorithm black boxes.
In addition, considering the lagness of supervision and the continuous iteration of technology, ethical specifications and landing systems such as ethical principles, ethical guidelines, and ethical review committees will be able to exert greater value. It can ensure deployment and use in a credible and responsible way.
Conclusion
The transparency and interpretability of artificial intelligence, along with fair evaluation, security considerations, human AI collaboration, responsibility framework, etc., are all basic problems in the field of artificial intelligence. With the continuous strengthening of artificial intelligence supervision, the transparency and explanatory regulations of the legislation on the artificial intelligence system will also go deeper.
One of the primary problems is that when designing transparency and explanatory requirements for artificial intelligence systems, regulators need to consider what goals they want to achieve, and how to better match these goals in specific situations. Because transparency and interpretability itself is not the purpose, but to enhance responsibility and accountability, empower users, and create ways and means of trust and confidence.
In the future legislation When the interpretability requirements and standards are set, not only the needs of audience needs, application scenarios, technical and economic feasibility, space -time and other factors, but also need to consider operating and pragmaticness. At the same time The balance between accuracy, security, privacy, network security, intellectual property protection and other purposes. It is difficult to obey or follow the high cost explanatory standards that hinder the application of the AI system. If you are required to explain the most detailed explanations in all circumstances without considering actual needs, it may hinder innovation and bring high economic costs to enterprises and society.
Therefore, appropriate explanatory standards should not exceed reasonable and necessary limit. For example, society will not require airlines to explain to passengers why the aircraft has adopted a route determined by the algorithm. Similarly, a similar pragmatic and context -specific path should be applied to the explanatory standard requirements of the AI system. Just like getting a driver's license, I believe that cars can drive safely, and do not need everyone to become professional car engineers. When using the AI system, explanation is not always necessary.
Finally, the value of the "algorithm instructions" in improving the transparency of algorithms and promoting users' understanding of the algorithm is worth further discussion.
The original draft in this article is included in the 76th of the "Moon Dan People's Commercial Law Magazine" (June 2022)
Editor's Choice
Cao Jianfeng, Wang Huanchao, etc.: "Explain the AI Development Report 2022"
Tencent Research Institute: "Why can AI be the next key wave? "
- END -
The highest reduction at the top temperature is 2 ° C official announcement of the preheating IQOO10 series equipped with 3930M㎡ super large VC all hot board

Recently, with the announcement of the# IQOO10# series of new products held on Jul...
The 25th China International Software Expo will be held in Tianjin in November

The reporter was recently informed that the 25th China International Software Expo...