I found a young star, which is very similar to the early sun, and it looks cool
Author:Astronomy online Time:2022.08.25

Astronomers captured the best scene of a young star on the surface of a young star. This discovery may reveal what the sun is young.
The new stars are surrounded by gas and dust, and planets, asteroids, comets and satellites are born from these gas and dust. The main author of the study and the celestial physicist at the University of Boston, Catherine Esparara, said that the star's magnetic field connects the star with the original star plate, and "transmits the material from the disk to the star." Esparate and her colleagues studied the sites deposited on the star through a star magnetic field to the site. She explained: "This mark is called 'hot spots', because the temperature is very high when the material impacts the surface of the star."
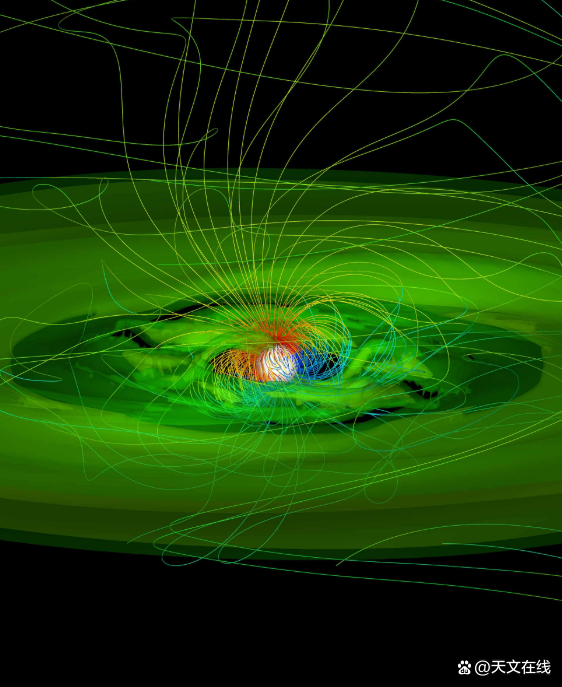
A computer simulation of the accumulation disc, conveying flow (green) and magnetic field (multi -color) on a emerging star. When the magnetic field sends the material from the disc to the north -south pole of the star, the young star will grow. (Picture source: Marina Romanova)
Scientists concentrate their attention on the GM Star of the Royal Pick. The star is similar to the quality of the sun. It is located outside the 420 light years and only about 2 million years of history. In contrast, the sun has about 4.6 billion years. history. In the past, scientific research could not clearly understand the structure and dynamics of these hot spots on the Hengxing. In this new study, researchers used multiple observations to analyze GM stars, including Hubble, SWIFT and TESS Space Telescope, as well as Chile's small pores and medium -pores to study the telescope system, Arizona's Loyer's exploration telescope mirror And Lasanbarez Observatory Global Telescope Network System. This is the first time to conduct such a wide range of time coordinates on a young star, "Esparate said.

Scientists have found that the visible light detected from GM reaches its peak one day after the ultraviolet radiation. They believe that this is because the source of visible light and ultraviolet rays appear and disappear with the rotation of the stars. Researchers said that combined with the computers of the material accumulation to the stars, it was found that the density of the thermal spots on the edge of the star surface from the center to the edges was different. Different density hotspots have different temperatures, so different wavelengths will be emitted. "For the first time, we used the observation results to draw the structure of this hot spots and confirmed the theoretical prediction," Espararat said. "This result allows us to learn more about the sun when the sun is young. Nowadays, the sun has a sunspot in the dark area with a lower surface temperature, and when the sun is young, there will be hot spots." In the future, the research will continue to analyze the GM star. And other stars, discover more details about these hot spots. They introduced their discovery in detail in the "Nature" magazine on September 1.

The star is a celestial body composed of a glowing spherical plasma, and these plasma gathered by gravity. The nearest star to the earth is the sun. Many other stars can only be seen with the naked eye at night, and their ultra -long distances with the earth make them look like a fixed light spot in the sky. The obvious star of brightness is divided into different constellations and star groups, and those brightest stars have specific names. Astronomers have compiled the star directory to identify the known stars and provide a standardized star name. There are about 1022-1024 stars in the universe. But in the earth, most stars are invisible to the naked eye, including all single stars other than our galaxy.

The life of the stars began in the gravitational collapse of a gesture nebula, and it is mainly composed of hydrogen, 氦 and trace heavy elements. The main factors that determine its evolution and final fate are the total quality. A star is glowing most of its life -active period, which is due to its core hydrogen and crickets. The energy released in this process runs through the stars and radiates to the outer space. At the end of the life cycle of a star, its core will become the wreckage of the star: such as a white dwarf, a neutron star, or if the quality is large enough, it becomes a black hole.

The stars in the stars or their residual objects have almost all of the naturally existing chemical elements that are naturally existing. The loss of the star quality or the supernova explosion returns chemical concentrated substances to the interstellar media. They are then used to form a new star. Astronomers can determine the nature of the stars by observing the visual brightness, spectrum, and its space positions of the stars -including quality, age, metal abundance (chemical composition), mutant, distance and space movement.
Stars can form rail systems with other celestial bodies, such as planetary systems, or forms of star systems with two or more stars. When two such stars have similar tracks, their gravitational interaction will significantly affect their evolution. Stars can form a star group or galaxy and become part of this large gravity constraint structure.
By: Charles Q. Choi
Fy: Hhan.
If there is related content infringement, please contact the author to delete after the work is released
Reprinted, please obtain authorization, and pay attention to maintaining integrity and indicating the source
- END -
Refresh the world record!
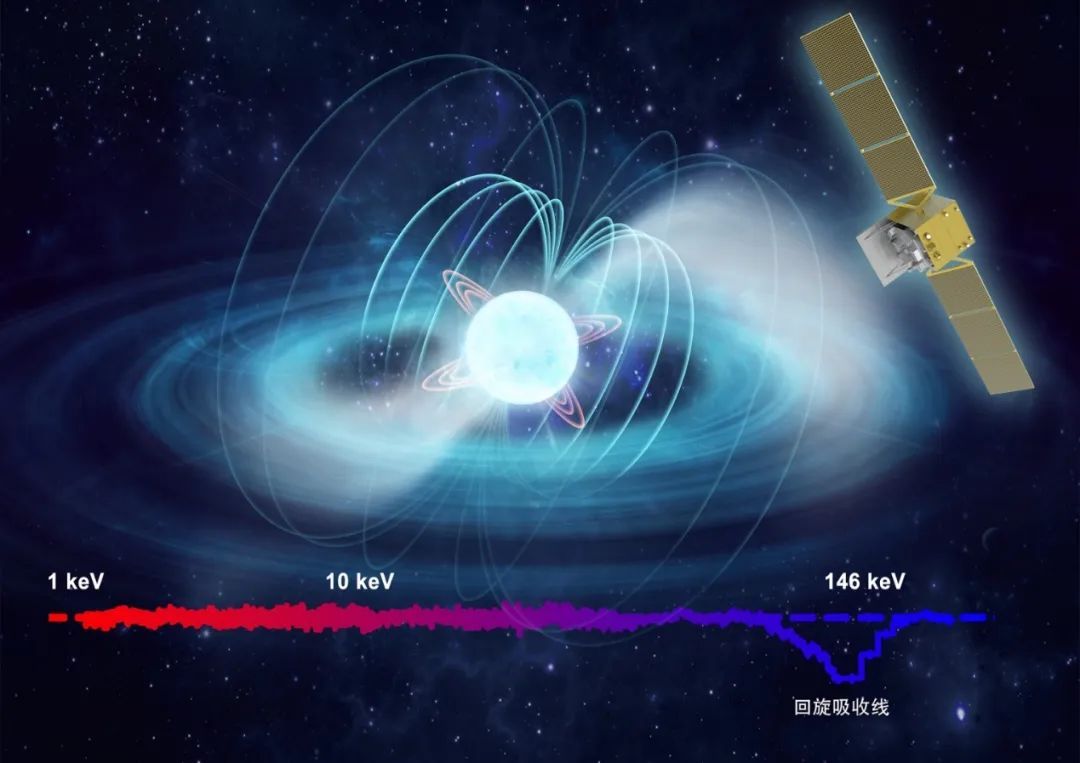
Recently, the my country Eye Satellite Team found that the neutron X -ray two star...
China's ten years · series theme press release 丨 Over the past ten years, my country has formed the largest digital society in the world

Xinhua News Agency, Beijing, August 19 (Reporter Wang Sibei and Bai Yan) The Propa...