What is the wind tunnel?How did it be born?
Author:High Energy Institute of the C Time:2022.06.22
The following article comes from WeChat public account: LBM and fluid mechanics, the author rupees and steel eggs
As a topic that every fluid mechanics practitioner cannot be bypassed, wind tunnels almost witnessed the development of modern fluid mechanics. So, what exactly is the wind tunnel? How did it be born?
NASA's official website has a definition of ground gas: wind tunnel is a large pipe with air flow inside. Both Da Vinci and Newton have thought about how to evaluate the force of the flying objects. They realized that they would like to move the model in the air at the required speed or blow the air through the fixed model. The wind tunnel obviously belongs to the latter.
01
Before the wind tunnel
In the era of scientific enlightenment, in order to test the performance of flying objects, scientists have to find a relatively stable natural source of natural wind -people install the model on the top of the mountain or the valley with wind. However, the impermanent natural environment eventually forced the experiments to turn to various mechanical solutions and try to move the model in the static air.
As a result, people naturally thought of casting stone to move the model with a rotary arm high -speed. In 1746, British mathematician Benjamin Robbins passed a rotary arm test that air resistance was a key factor in the projectile flight. His instrument is shown in the figure below, and a heavy object drives the drum, providing a stable rotation speed.

This simple setting is still used until the end of the 19th century. Of course, its defects are also very obvious -the cantilever itself makes the large range of air in a rotating state. What is worse is that the objects at the end of the cantilever have actually flying in their own tail flow. Because the device itself has a large amount of turbulence, the experiments cannot determine the true relative speed between the model and the air. In addition, when the model is rotated at a high speed, it is very difficult to install the instrument and measure the force applied to the model.
Of course, in addition to rotating objects, the movement of objects has moved. In 1904, French officer and aviation engineer Ferdinander Ferber created the device below, using the gravity effect to fix the aircraft model on the rope on the rope. However, the conditions of this device are also very limited, and it is difficult to measure the stress of the model.

At that time, because people were trapped in the uncontrollable air, their ideas were concentrated on how to move objects. In short, if you are an engineer at that time, there is a probability that you will sigh: we need some.
02
The initial wind tunnel
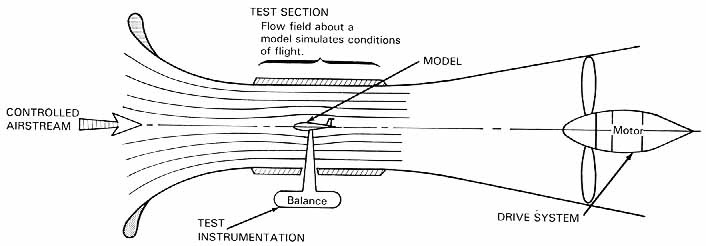
The "Something Better" in the eyes of aerodynamics is a wind tunnel. It consists of a closed channel, and the air is driven by a fan or other ways to pass through this channel. The core of the wind tunnel is the test section. It supports the object through a control agency, and the air dynamics characteristics of the model and its flow field are measured by supporting the balance and other test instruments. The wind tunnel has a strong controlled test ability, making the rotary arm test equipment soon outdated. The model that measures still in the airflow is so simple, thereby opening a new era of aerodynamic research.
Frank H. Wenham, a member of the British Aviation Society, designed and operated a wind tunnel in 1871, which is generally considered to be the first truly wind tunnel in the world. However The model of the wind tunnel has disappeared in the long river of history. The National Aeronautics and Space Museum preserved the copy of the Wright brothers in 1901.
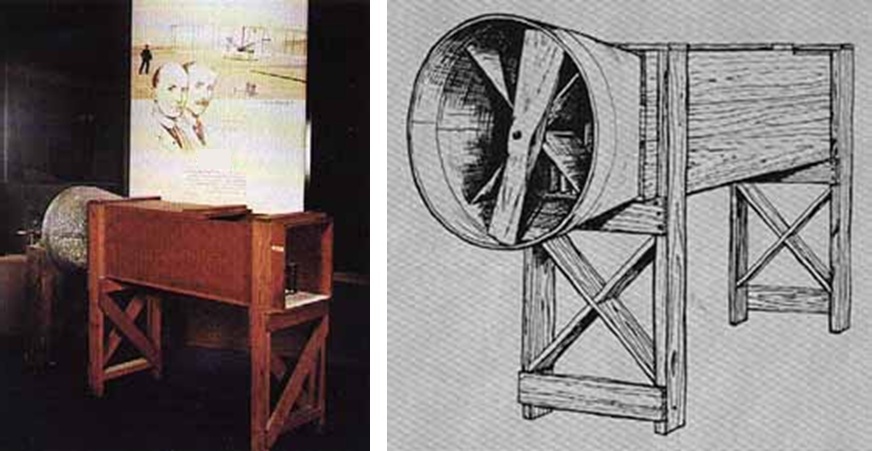
In addition to seeing a little unreliable wind tunnel, there is a very obvious error in addition to it -they have installed the fan on the upper reaches of the wind tunnel, which will bring great interference to the airflow of the test section.
03
Wind tunnel formation
Although the Wright brothers in the United States occupied the reputation of the inventor of the plane, as the World War I came, the focus of the world aviation industry quickly moved to Europe. The aviation laboratory funded by the central government of various countries has emerged in the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, and Russia, which also includes wind tunnels. I have to say that many basic technologies of modern wind caves have been laid in Europe.
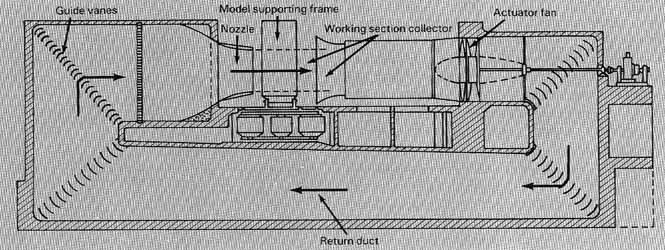
In 1908, in Georite, Germany, the famous air dynamicist Ludwig Pulandte was instructed to build the world's first continuous circuit cave. Puland's wind tunnel uses a pipeline to connect the exit and entrance of the wind tunnel, and install the orientation blades, gauze and honeycomb at the key position to get uniform and quiet flow. With the wind tunnel, Pronte happily tested various wing, streamlined fuselage and aircraft components, and for the first time measured the pressure distribution of the rotating propeller blades. Because the quality of the air flow is more stable and saved by energy, it soon becomes the standard for many researchers.
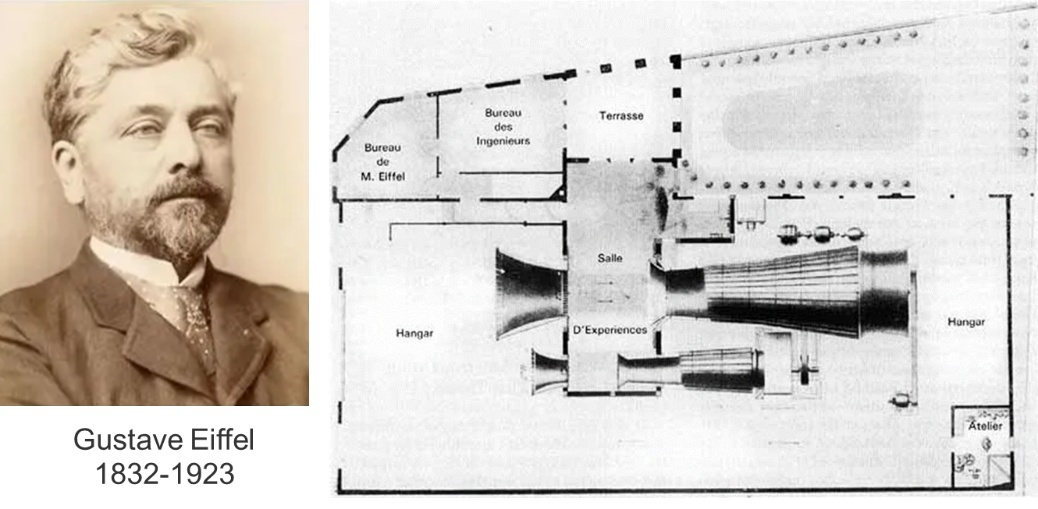
In France, Gustave Eiffel, known for its tower, built a private aerodynamic laboratory with personal funds. Everyone knows that Eiffel is an architectural master and structural expert, but the great gods are so energetic. He is also interested in aerodynamics, and even often parabolizes high -altitude -throwing various shapes of objects from the tower to test air resistance Essence Perhaps he was so careful to build the Eiffel Tower.
In 1909, Eiffel built the first open wind tunnel on the God of War at the foot of the tower. The diameter of the wind tunnel is 1.5 meters, providing power from a 50 -kilowatt electric motor, and a diffuser was installed to reduce power consumption. The airflow turns into the test section at a speed of up to 20 meters per second, and returns the nozzle through the open space inside the building. Eiffel has tested more than 4,000 in this facility, but a few years later, the French government suspected that he had taken too much place and recovered the God of War. So Eiffel, who was unwilling, built a larger and higher wind speed. Although it is not as popular in the world as Geitin's root wind tunnel, Eiffel's wind tunnel also has its unique advantages. Its structure is simple and stable, and it is also adopted by many researchers. Therefore Wind tunnel type.
Of course, the other two European powers were not outdone, and Britain and Russia also established their own wind caves in the early 20th century. In 1903, Thomas Stanton began to build a wind tunnel in the UK, and made its debut in 1912, claiming that its wind tunnel had "the world's most stable air power flow". The first important wind tunnel in Russia was built in 1904 by an outstanding scientist D. RiabouchInsky. He built a complete air dynamic laboratory in Kurchino, not far from Moscow. The diameter of its wind tunnel test is 1.2 meters and is equipped with a cylindrical cover to calibrate and eliminate turbulence in the airflow.
04
Development and chase
After the end of World War I, the predecessor of NASA, the National Aviation Advisory Commission (NACA), clearly described the future technological development trend in the first annual report submitted to Congress: The progress of the war will have a large number of different types of aircraft and well -trained personnel after the war, which will quickly enable the aviation industry to enter the business field.
They built NACA No. 1 wind caves in 1920. This is a low -speed wind tunnel. Compared with European wind caves, it looks much simpler and there is no return circuit. Because the data obtained from the wind tunnel is not realistic and cannot be used for aircraft design, the No. 1 wind tunnel can only be called a tool for learning.
But this is just the beginning, the construction of NACA's wind tunnels is non -stop. In 1921, more than 20 wind caves have been built around the world, but all large wind caves run under normal atmosphere. This means that the experimental results obtained by the proportional model in the wind tunnel are questionable, because the number of countless outlines such as the number of Renault and the parameters of the actual flight of the full -size aircraft cannot be matched.

In June 1921, NACA boldly decided to build a wind tunnel that can change the air pressure. This is the variable density tunnel (VDT) of Lamili Lab. In March 1923, VDT began to run, and soon became the main source of air dynamics data under Gaoren. It tested a variety of aircraft models from the bulky Zeppelin airship to military aircraft.
Aviation professional friends may be more familiar with another important contribution to VDT. In 1933, NACA released an important technical report that provided air dynamics data of 78 related wing -type section. Like many research on NACA, this very boring but high technical report provides complete wing-type information, the gospel of scientific researchers, and eventually brings a successful aircraft design-DC-3 transport aircraft, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B, B -17 transport aircraft and the famous P-38 fighter, the latter became the main opponent of Japanese zero fighters during World War II.

05
Ultrasonic speed cava
Until 1932, NACA's wind tunnels were asian speed. After Joseph S. AMES became the chairman of NACA in 1927, he decided to give priority to the development of high -speed wind tunnels, especially the development capabilities of cross -sound speed and supersonic research capabilities.
In 1939, based on its latest 24 -inch high -speed tunnel, NACA provided a series of new high -speed winged air dynamics data for the US aviation industry. These winged types quickly evolved the propellers of high -speed aircraft. These propellers provided power for US fighters at a speed of 500 miles per hour, and these fighters played a huge role in World War II.
The war has greatly stimulated the development of the aviation industry. During World War II, Germany had increased its aviation research facilities ten times and had five research centers. However, it is not easy to build a large -scale high -speed wind tunnel -the power required to drive the wind tunnel is proportional to the three times of the wind speed. German engineers thought of another way, and they built large gas storage rooms in the cave to replace the driver fan. By the end of the war, Germany had at least three different supersonic caves, one of which could produce 4.4 Mach of the ultrasound speed.
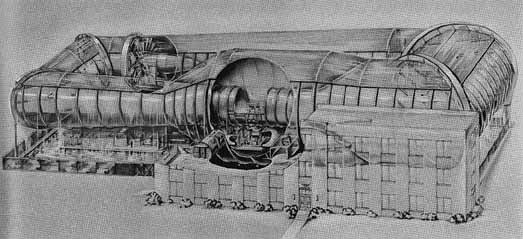
NACA's research is not far behind. By the end of World War II, the United States had built eight new wind caves. Among them, the world's largest wind tunnel located in Moffett Field near Sanville, California. It can test full -size aircraft at a speed of 250 MPH. The vertical wind tunnel located near Wright Airport in Ohio is used to test the performance of helicopters and its rotor.
06

Technical change
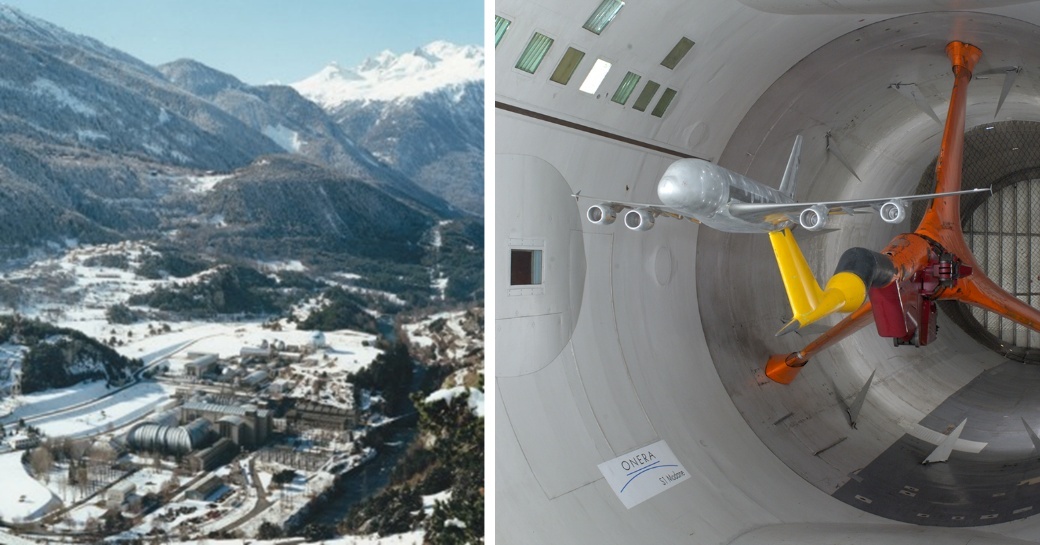
After World War II, the technical transfer and commercialization entered a peak period, the most representative of which was the S1MA wind tunnel. The wind tunnel began construction by German engineers in the Austrian Alps during World War II, and was later identified as compensation for war to France. The wind tunnel was used in 1952. It is driven by a pair of rotor, with a power of 88 MW, which is higher than the Da Gogho aircraft carrier. The diameter of its test section is 8 meters, and the maximum wind speed can reach Mach. The wind tunnel undertakes a large number of commercial aircraft development and verification work, and is still one of the most important wind caves in the world. Like the S1MA, there are still many wind caves in service after World War II, and even old antiques like Eiffel Wind Tong have also exerted surplus heat in the construction field.
However, more wind caves have gradually withdrawn from the historical stage within 20 years of the end of World War II. Instead, they are replaced by wind tunnels with lower energy consumption and more suitable for commercial use in vertical fields, such as S4MA spacecraft wind caves, CAPUA icing wind wind Caves, S2A car wind tunnels and so on.

07
Car wind tunnel
From about the 1960s, with the pursuit of low energy consumption and control stability of cars, the position of air dynamics in automobile development has become increasingly important, and wind tunnel testing technology has gradually shifted from aviation to cars.
And there is a huge difference in geometric shape and operating conditions in cars and airplanes. For example, cars will produce more obvious blockage and even tailing, ground effects, more complicated turbulence flow, etc., making people more and more consider construction construction. Special car wind tunnel.
Like the aviation technology wind tunnel in the war years, the car wind tunnel of the peaceful age has sprung up. Today, a large number of full -size car wind caves are running day by day. Wind tunnels and so on.
Conclusion

As the most important assistant and witness of the development of aerodynamics, wind tunnel testing technology has spawned a large number of technological iteration and innovation, and serves product research and development in many industries. With the rise of fluid mechanics, numerical wind caves have also become an important means of aerodynamic research. In the new era, what kind of sparks can numerical methods and physical wind caves collide? Please look forward to "digital twins from physical wind caves to numerical wind caves."
-End-
This article is reprinted from WeChat public account: LBM and fluid mechanics Author: rupees and steel eggs
Reprinted content only represents the author's point of view
It does not represent the high energy office of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Edit: Azheng
- END -
The 20 -year report of the forest reform ④ | Create smart forestry!Silla is like this →

The 20 -year report of the forest reform ④ | Create smart forestry! Silla is like...
Summer vacation with Grandpa | Submitted works

*由 This article is uploaded by the Letsfilm author MSG, and the copyright belongs...