maximum!Is 1 cm bacteria called "microorganism"?
Author:Journal of China Science Time:2022.06.27
Text | Xinyu
In the mangroves in the island of Laulipipu in Caribbean, some peculiar silk biology lurks on the rotten leaves sank into the bottom of the sea.
These wire -shaped creatures can reach 1 cm in length, which is the largest single -cell bacteria found so far, and 50 times that of known bacteria.
They live with sulfur oxide.
In 2009, Olivier Gros, a biologist at the University of Leis in France, discovered this bacteria while exploring the mangroves of Guadelopp.
GROS first thought it was a fungus, not a bacteria. After returning to the laboratory, GROS realized under the microscope that this creature is not a genuine creature.
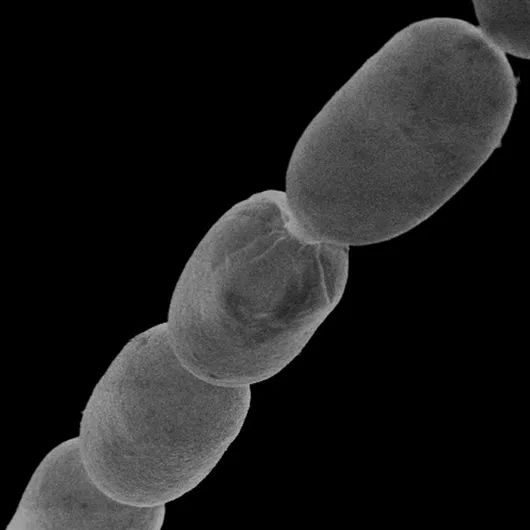
Silk -shaped large sulfur cells have more complex internal tissues than typical bacteria. Image source: Olivier Gros
In 2018, Jean-Marie Volland, a marine biologist in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, used a series of methods to observe these bacteria more carefully and confirmed that it was a single-cell creature.
Related research results were published on June 23 in "Science".
This bacteria is called Thiomargarita Magnifica.
Volland introduced that scientists also found other silk bacteria in mangroves, but they are composed of dozens or hundreds of cells.
The uniqueness of T. Magnifica is that its silk is the longest in mangroves and consists of a cell.
The core of the bacteria is liquid bubbles -an inert film full of liquid membrane, which is surrounded by membrane binding structure.
The researchers named it "PEPINS" and described it as a cell device similar to the intraurate cells.
Among other bacteria, genetic materials float freely in the cells, usually only one ring chromosome.
In T. Magnifica, researchers found that genetic information was stored in thousands of Pepins.
Each of them contains DNA and ribosomes, which have a total of 700,000 genome copies.
There are still many problems about T. Magnifica, including mangrove specific habitats contain a large amount of sulfur molecules and sulfur -consaling microorganisms. Whether it is essential for the existence of this bacteria.
PEPINS itself also needs to observe more carefully to determine whether they all contain the same genetic material, ribosome and protein mixture.
Researchers have sequenced the entire cell, including hundreds of thousands of Pepins.
"But we have not sequenced a single PEPINS." Volland said that they didn't know that each PEPINS contained only one genome copy or multiple.
The discovery of T. Magnifica shows that large and more complex bacteria may be hidden in people's sight. GROS hopes other teams to continue looking for bigger bacteria.
Petra Levin, a biologist at the University of Washington, San Louis, believes that this discovery challenges the volume limit of bacteria smaller than the nantucleic cells.
Bacteria have endless adaptability, it is always surprising that it should never be underestimated.
Related thesis information:
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb3634
"China Science News" (2022-06-27 The original title "Scientist Discovered 1 CM Bacteria")
Edit | Zhao Lu
Capture | Guo Gang

- END -
Chuanxiang Qiuyue: Looking forward to the construction of digital countryside to send more agricultural products to the "cloud"

Cover Journalist Xiong YingyingZhuhai Village, Baijie Town, Naxi District, Luzhou ...
"The entire network promotion" is popular in the circle to open the theme promotion week of "Book Fragrant Gate"

Consumption is a cockpit stone for economic stable operation. The 618 national sho...