Earthquake science 丨 Know the living break layer
Author:Sichuan Earthquake Administrat Time:2022.06.28
The living fault is the main source of danger of destructive earthquake. Its existence means that the risk of potential fault disaster, especially the unpredictable earthquake and related potential hazards. Major security issues.
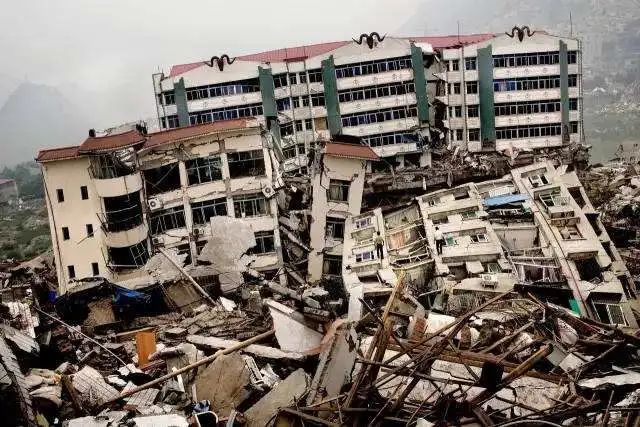

Actual break
# #
The "living fault" term was first proposed by American geologist Lawson on San Andrez, a magnitude 8.3 earthquake in San Francisco in 1906. After that, American geologists Wade and Willis have given more clear definitions: the living fault is new or inheritance and displacement during the modern or historical period, and in the near future, it may continue to move or continue to exercise and generate. The fault of displacement.
Simply put, it refers to continuous activities in the latest geological period, and the event will be broken in the future.
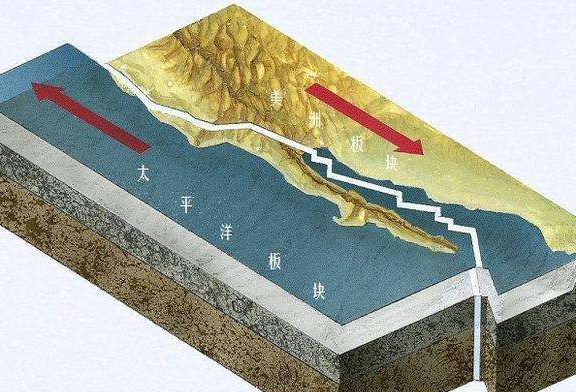
Actual break
#Concept and surgery #
In addition to the "live break -off term" itself, different institutions, departments, and researchers, based on the characteristics of regional structure and their own needs, on the basis of living fault terms, many concepts or terms that are similar or belong to their special types are also proposed. Among them, of which The following are the following main or commonly used.
E Neotectonics and new constructor faults
The "new structure" term was introduced from the former Soviet Union V. Obruchev in 1948 to geological and geomorphology, which refers to "the youngest crust on the earth from the end of the new period to the first half of the earth. sports".
In December 1984, Professor Hancock at the University of Bristol and Professor Williams of Cardiff at the University of Bristol, a "New Structure Conference" convened by Professor Williams at the University of Cardiff. After in -depth discussions, it is recommended to define the new structure as "the constructive movement that has occurred today and the formation of the structure of the constructor."
The "new structure fault" is a significant difference in faulting activities in the background of different global dynamics in recent years, especially from the research on the research of the Stable Continental Regions (SCR). Earthquake recurrence features have been proposed after deeper understanding.
The GEM Fault Earthquake (GFE) Project, which was launched in 2010 (GEM) launched in 2010 (GEM), also regards the "new structure fault" as the main source of earthquake occurrence sources in the world. The definition of its adopted " "Fragmentation of the constructive mechanism today".
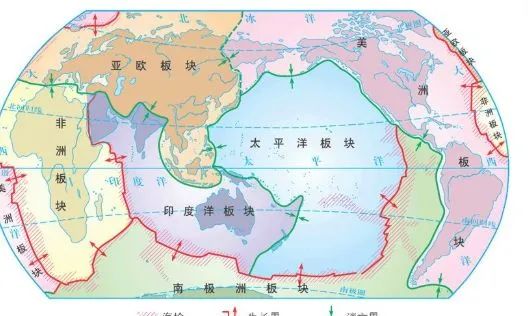
A Capable Fault
The dynamic fault and the dynamic construction sources are commonly commonly required in the risk of dangers in the stability of the site or the location stability of nuclear power stations or nuclear waste disposal. In 1973, the "Nuclear Power Earthquake and Geological Selection Standard" published by the US Atomic Energy Commission (US AEC) first used the concept of "dynamic fault" and was adopted by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). It was originally defined as "there have been many activities since the Chinese renewal (mainly since 500ka) and there are still potential activity breaks or structures in the future."
The International Atomic Energy Commission (IAEA) has always followed the "dynamic fault" term, but the definition and judgment criteria are constantly being updated. The definition of the latest specifications is "a fault that can have obvious potential that can generate displacement on the surface or nearly surface."
The definition of the site selection and related norms of domestic nuclear power plants is: refers to "the fault that may cause the surface or near the ground".

Seismogenic fault:
Earthquake breaks generally refer to the living breaks that "control the occurrence of earthquakes on the space and can produce M≥5.0 destructive earthquakes, or there is a historical earthquake surface rupture, or there is an exact ancient earthquake relic." The global earthquake model (GEM) new fault fault database is defined as "the fault that can produce medium to a large earthquake". The term of the seismic layer is also applied in various standards and specifications in China.
(Potential activity fault:
This term is common in the standard specifications of the danger of earthquakes and surface rupture or deformation evaluations formulated by California's Live Broke Aversion Act and the US Nuclear Association (ANS). Since MA), the surface is wrong or deforms, but the faults with lack of exact evidence of the new world activity. "
N New Active Fault:
This is the term used in the domestic geotechnical engineering survey specifications, and is included in the "Engineering Geological Handbook", which refers to "in the modern geological period (10 kA). The next 100 years) may continue to be broken. "This is actually similar to the new world's activity fault, and it is also used in some industry standards such as" Technical Requirements for the Risk Evaluation of Geological Disasters of Construction Land ".
Ar warning factor:
This is the concept proposed by the Japanese earthquake geologist Matsuya Matsuda Matsuda Matsuda Matsuda Matsuda Matsuya, which analyzes the danger of the future fracture risk of Japanese island, and is used to indicate the living fault with a high risk of potential strong earthquakes in the future. H hazardous fault:
This is the term in the danger evaluation guidelines of the dangers of the residual faults formulated by some prefectures in the west of the United States. It is used to guide engineering and buildings to avoid living faults, or to guide localities to formulate relevant laws and regulations.
L Blind Fault:
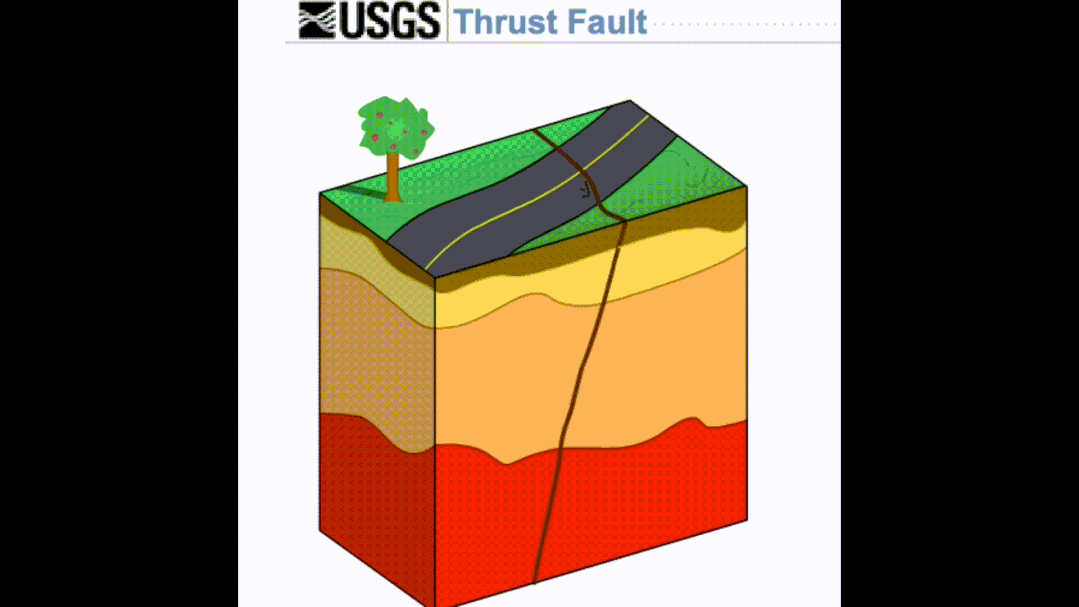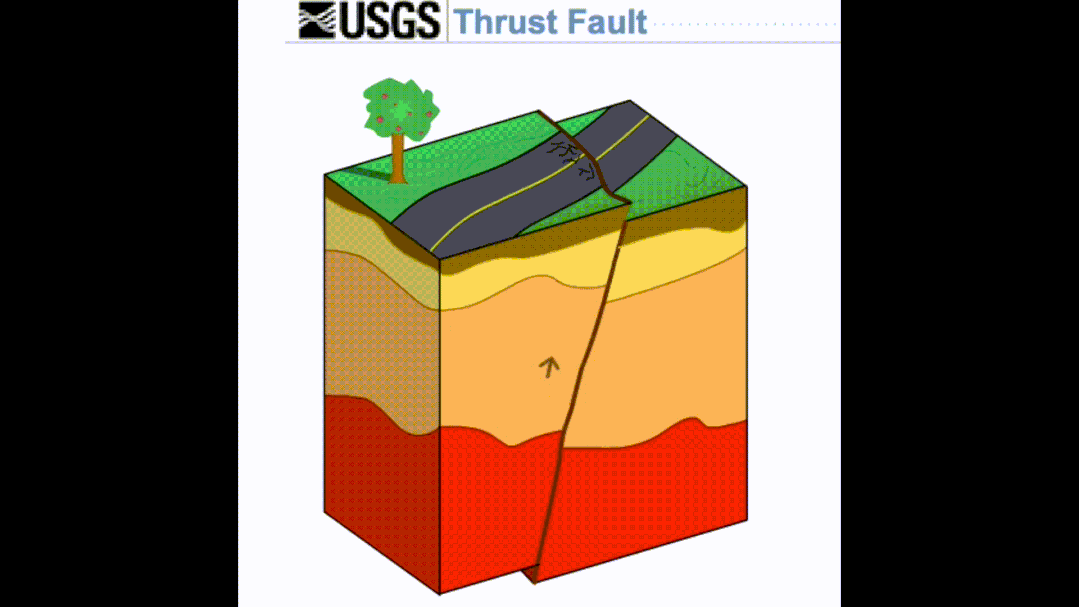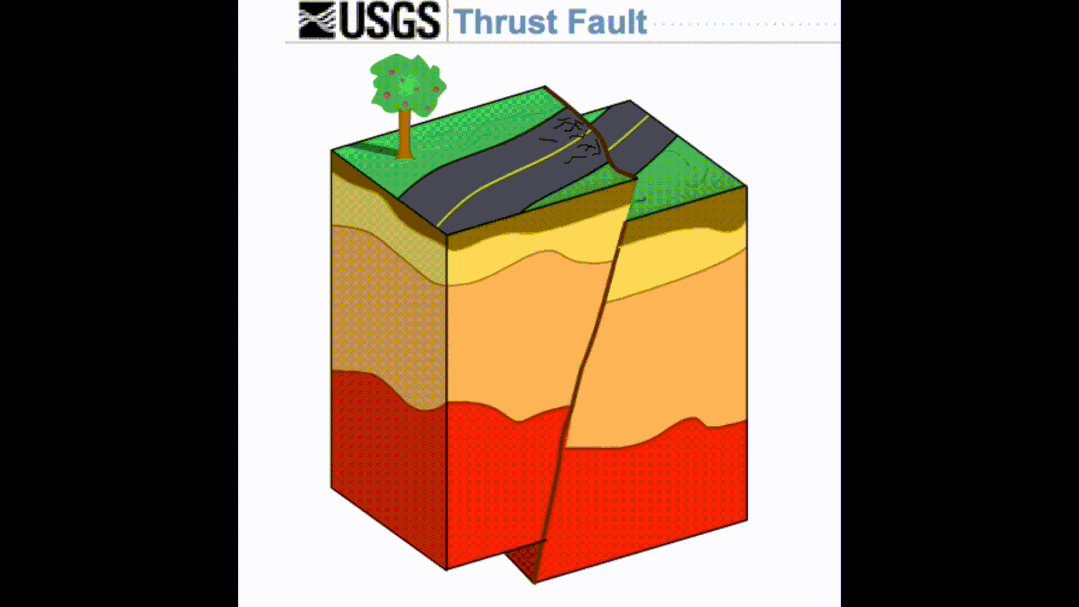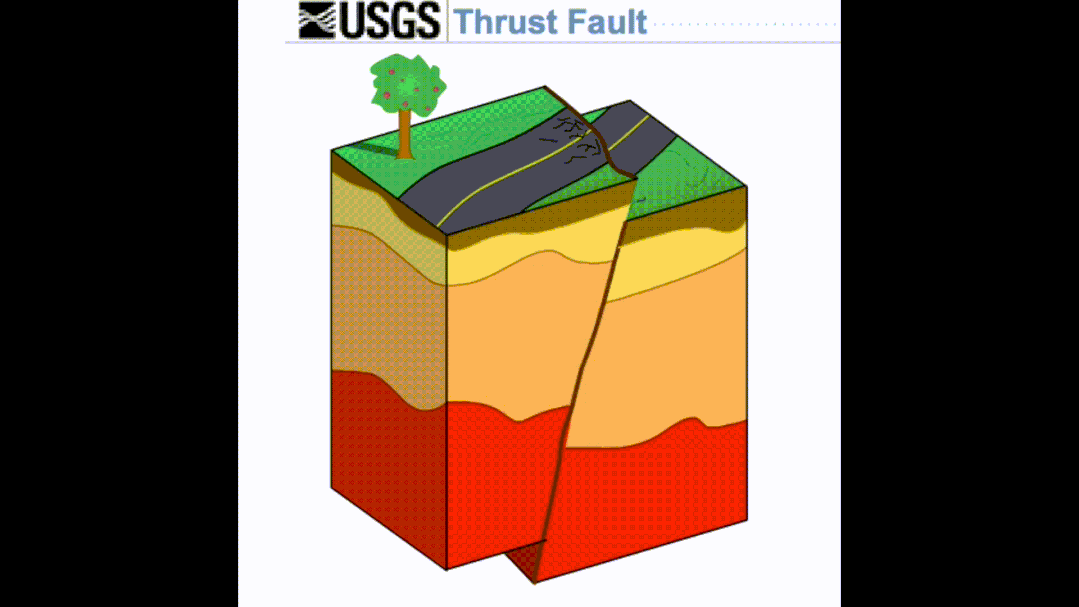
It belongs to a special type in the living fault. It refers to hidden under the surface. Although it does not directly cause the surface rupture, it can cause the surface deformation to break, which usually constitutes a reverse-pleated fold construct system formed by the squeezing and deformation mechanism. The part of the middle, that is, the blind reverse fracture often exists in the lower part of the active folds.
活 Buried or Concept Ac-Tive Fault:
Including two categories, one is covered by the fourth disciplined sedimen, and the activity fault that does not have an eye -catching trace on the surface; the other is the fault that is completely covered by the later sediment after the surface is deformed.
Data reference: "Definition and Classification of Living Fracture -History, Status and Progress" Wu Zhonghai.
Source: Jizhen WeChat
- END -
Constantly strengthen the confidence and determination of technology self -reliance and self -reliance | 2022 National Science and Technology Workers' Day
Author: KexinEditorMay 30, 2022 is the sixth National Science and Technology Worker Day. Respect. During the same period across the country, they carried out their own special activities. The courag
Energy momentum: How should the carbon neutralization of the power industry be achieved?

Recently, abnormal weather such as heavy rain, high temperature, hail, and floods ...