The difference and connection between the combination probability and condition probability
Author:Data School Thu Time:2022.06.29

Source: Deephub IMBA
This article is about 2300 words, it is recommended to read for 9 minutes
This article explains the differences and connections between the combination probability and conditional probability.
Joint probability P (A率B)
The probability of two incidents (or in order) together.
For example: the probability of throwing coins is ¹⁄₂ = 50%, the probability of turning 2 fair coins is ¹⁄₂ × ¹⁄₂ = ¹⁄₄ = 25%(this can also be understood as 50%50%)
P (a) b) = p (a) ⋅ p (b)
For two coins, the sample space will be 4 hh, ht, th, and tt. If the first coin is H, the remaining result is 2 ht, HH. This means that the first incident may affect the second event.
For example: The probability of selecting 1 green ball from 10 different colors is ¹⁄₁₀, and the probability of 2 green balls in 10 balls (2 green, 2 blue, 2 red, 4 yellow)排 × ¹⁄₉ (This arrangement combination will be clearer)
in short. When the first incident affects the occurrence of the second incident, they are related events.
P (a) b) = p (a) ⋅ p (b | A)
Here, P (B | A) is read as the probability of B after A. This is the probability of the B event when the A event has occurred. This is called conditional probability.
Joint probability and condition probability
Example: A triangular area in the city is polluted by chemical industry. 2%of children live in this triangle. 14% of the tests are positive for excessive detection of toxic metals, and the positive detection rate of urban children who live in the triangle are only 1%.
Considering: T means a person living in a triangular area, and P represents a positive person.
When it says that 14% of children in the area are positive, it means that if a child is randomly extracted from the triangle, it will have 14% of the chance to test as positive. This is P (p∣t)
The explanation of P (p∩t) is the probability of positive in the triangle after random selection in the entire population.
Understand
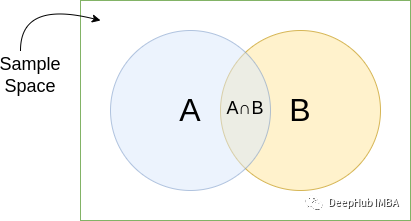
P (A∩B) is the probability of both A and B (there is no additional information.)
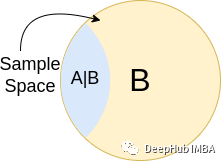
P (a | b) is the probability of A. A.
Let's understand it through an example. There are 60 students in a class. 33 people like blue, 23 like red, 20 students like these two colors, and 4 students like orange.
1. What is the probability of choosing a student who likes red and blue?
This is very simple: p (b) r) = ²⁰⁄₆₀
2. What is the probability of choosing a blue student from the students who like red?
We will check the probability of students with a specific selection from specific students.
There are 23 students who like red. There are 20 of these two colors.
P (b | r) = r
Through Ventu and the above examples, we can say that in these two cases, the results of the incident have not changed, but the sample space is decreasing. therefore:
- END -
From black and white to color, Harbin Institute of Technology takes you to appreciate the beauty of the micro -world!

Beauty, everywhereAs long as you have the eyes that are good at discoveringHave yo...
2022 Scientist Spirit Education Base 丨 Institute of Animal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences

A few days ago, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Science and Technology,...