Why are others more active than you? The original switch is in the brain
Author:Cool brain Time:2022.09.02


Via: freepik
The following is the audio of the full text of Miss Sister
Author | Ingrid Wickelgren
Translation | Caroline
Grade -Cool Brain Creative
Reading | Hu En
Artist | Jenny
Edit | yj
In a recent study published in the magazine of "Nature", Kay Tye and her colleagues discovered some basic things: a molecule in the brain, which can make a kind of The event is marked with positive or negative.
Since her memories, Kay Tye wants to know why she feels like this or that. However, Toy is not just involved in the theory of the soul. She has long wanted to know what happened to her brain for a long time. In the university in the early 21st century, she could not find a course to explain how the electrical pulse was flowing in the trillion connections of the brain, which caused a feeling. Toy said: "There is no neuroscience course I want in the school." Now, Tay leads a laboratory in the Solk Biological Research Institute in Lajia, California.
Via: giphy
She recalled that she was criticized when she discussed her emotions in a doctoral dissertation. Someone told her that the study of emotions had no position in behavioral science. Tayi said disagree at the time, and she was now this attitude. "Otherwise, where do people think that emotions should be expressed? Is it a place except the brain?"
From then on, the research team of Tiyi has taken a step towards the biological foundation of unspeakable experiences such as loneliness and competition. In a recent study published in the magazine of nature, she and her colleagues discovered some basic things: a molecule "switch" in the brain, which can mark an event as positive or negative. Toy is no longer a alien pursuit of these issues, and other researchers are thinking along the same thinking. "Daniela Schiller, a neuroshistarians at the Ikan Medical College of Sinai, said, said," If you have a brain response to anything important, how can it distinguish it or bad? "This will become a core issue in this field in the future.
In Taye's research, this switch was discovered in mice. If it also has a similar effect in humans, it may mean that a person is activated in the brain when he hears the ice cream car instead of the bear's roar. This switching mechanism is important for survival, because animals need to take different actions in different circumstances. "Toy said:" This is the hub that we feel information into motivation. "In evolution, this will directly determine whether you can survive; in modern society, this will determine your mental health and your quality of life.

Via: Tuyuan Internet
If your brain switch is adjusted to a negative experience, it may lead to anxiety or depression. In contrast, excessive desire for rewards may cause the shadow of addiction. Stephen Maren, a neuroscience at the University of Texas AM, said that although he did not participate in the study, he believed that the work might investigate pathology in a way we had never thought about. Although we used to think more about pathology as one or the other system disorders in the past, Mallen said that maybe some mental illness is caused by the imbalance of the brain switch on positive and negative events.
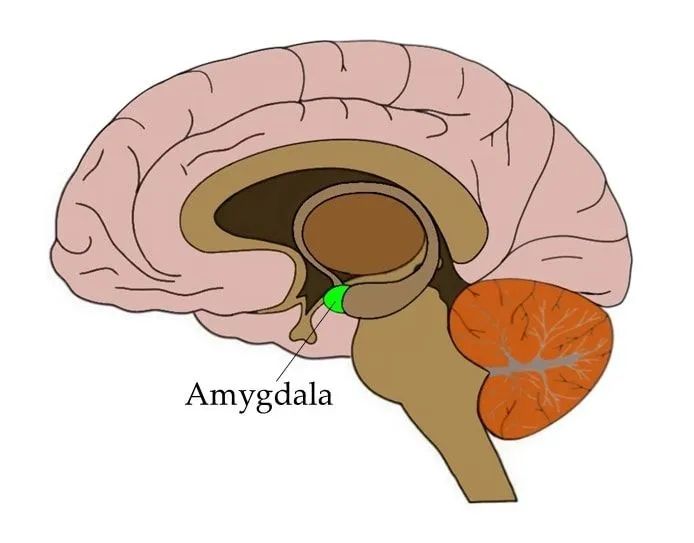
As a graduate student, Tae Yili studied emotions through the almond nucleus. Logically speaking, the almond nucleus is an emotional processing center in the depths of the brain. In 2007, she gave a speech at a meeting, emphasizing that the structure was also important in the study of rewards in addition to the known role in fear. She assumes that different neurons in the almond nucleus are the basis of good memory and bad experience.
In a papers published in 2015, Toy and her colleagues in Massachusetts Institute of Technology discovered these neurons in one part of the almond nucleus, which was called the base almond nucleus. Mouse needs a set of neurons to learn one sound to indicate a sip of sugar water, while another group of neurons require them to connect a noise with a slight electric shock. In order to find these cells, the researchers used a technology developed by Tyie a few years ago. This is a distortion of optical genetics, that is, the genetic element is designed with the genes of light -sensitive protein. Usually, this allows them to be activated by light. Tye designed a method to track the connection of a set of specific nerve fibers with optical genetics.
After determining the orbit of rewards and fear, Toy wanted to know what determines the path of the signal. What exactly is a positive or negative "switch"? When researchers have a catalog of the genes that are opened or expressing in each group of neurons, a difference is very prominent: the neurons in the negative path show more neurotransidine, which is expressed by the genetic gene. Adjust the brain's main excitement neurotransmitters-glutamic acid, which makes a neuron emit signal to other neurons.
According to this clue, Toy and her colleagues drawn all neurons to release neuronin to the outside of the almond base. They found three sets of three different places connected to the brain. In order to figure out which fibers are related, researchers have done something unusual: they use the famous gene editing technology CRISPR to fail the neurotramotidin in each group of neurons. Mallen said that this is the first time that using gene editing technology to selectively delete this type of neurotransmitter from a specific neurons group. As a result, in these neurons group, only one neuron group destroyed the ability of mice to learn to tone sounds with sugar or impact. This group of neurons comes from the hill brain, a feeling center in the brain. Delete these neurons in the mounds to slow down the speed of mice to learn sucrose rewards, while predicting the speed of shock will become faster. This can be proven from some behaviors, such as running slowly to the place where the sugar water provides water. Artificial activation of these neurons leads to the opposite result: the improvement of food reactions and the weakening of fear reactions.
These findings show that the default state of the brain is negative and requires the input of neuroplasia to convert it to more positive things. "We need some things to make our brain enter a state and tell it: 'Oh, this is a valuable environment. I should let my brain system understand the reward," Toy said, "If I didn't do this The brain may be bad by default. "
Via: Tuyuan Internet
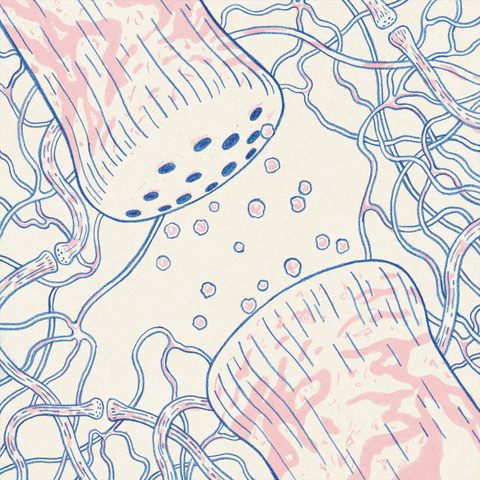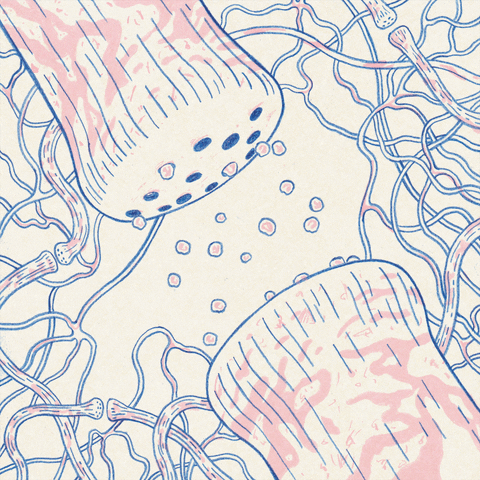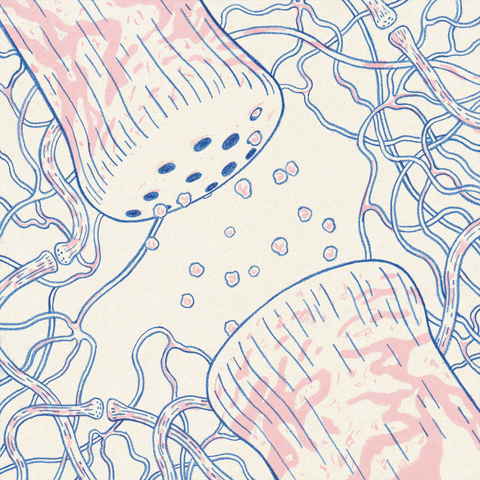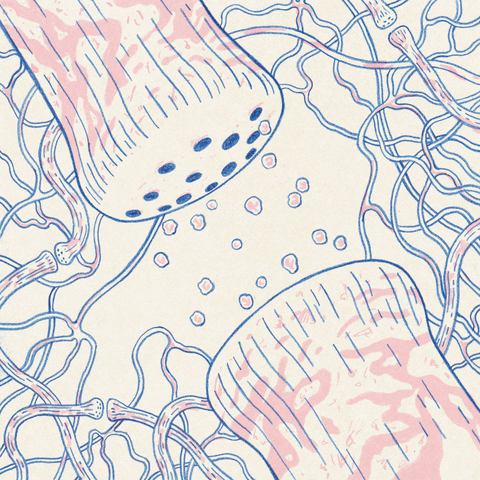
The participation of neuropsy also solves the mystery of time. Animals can learn to connect stimulating stimulus-the sound of guns and injured soldiers or grandparents-associated with gifts-these stimuli are tens of seconds, minutes, or even longer. But the typical neuron reaction, such as the reaction of glutamic acid, occurs within a few milliseconds. Toy said that neuropine can enlarge the glutamic acid signal and make it longer.
Experts say this work may eventually lead to the treatment of some mental health problems. A drug that reduces nervous tension activity may alleviate addiction and follow the reward of rewards by making the brain more biased towards the state of fear. In contrast, enhanced the role of nervous tension may make people who are anxious or depressed looking at the world in a more positive way. Toy said: "This goal is a very attractive goal for a wide range of mental health diseases."
Michael Anderson, a cognitive psychologist at the University of Cambridge, said, however, it is unclear whether this specific discovery will have clinical help to people. Nevertheless, its impact may still be huge. Anderson added: "The more we know the nervous circuits of emotions and regulate, the more likely we will formulate long -term intervention measures on this basis."
In the short term, this work has largely expanded emotional hard sciences, partly, which is a new tool for solving the brain mechanism by invention to solve the brain mechanism. "Malun said:" This job is a technical tour. "In terms of how we manipulate neural circuits, it does push this field in a new direction."
Via: giphy
Reference (click slide to view)
1. Li, H., Namburi, P., Olson, J. M., BORIO, M., Lemieux, M. E. E., A., ... Tye, K. M. (2022). Neurotensin orchestrates Valence Assignment 1-7.
2. Namburi, P., Beyler, A., YOROZU, S., Calhoon, G. G., Halbert, S. A., Wichmann, R., ... Tye, K. M. (2015). A Circuit Mechanismism for Differentiation Positive and Next NEGATIVEASOIVE ASSOIVE ASSOIVEASOIVEA Nature, 520 (7549), 675-678.


Cool brain long -term collection of brain science and psychological articles, welcome to submit
Please submit a mailbox: [email protected]
Click here, let friends know that you love brain science
- END -
The "Fourteenth Five -Year Plan" Development Guidance Opinions of Shandong Provincial Enterprise Culture Construction "released to the outside world

Luwang, June 28th, in order to promote the construction of a strong cultural provi...
Building can be read | Go out of "green tile", do not forget the "soul of sports"

The Shanghai Institute of Physical Education, which was founded in 1952, was the e...