How does glue cell affect your emotions
Author:Cool brain Time:2022.06.22

Via: fool mixed plant CDD20
The following is the audio of the full text of Miss Sister
Author | Austin Perlmutter M.D.
Translation | Chunwu Thousand Layers
Reward | Caroline
Grade -Cool Brain Creative
Reading | Pigeon Tsai
Artist | Old carving worm
Edit | Sales increase
1. Small glue cells are responsible for regulating brain immunity, which may help explain the connection between inflammation and depression.
2. Signal transmission between star cell regulating neurons, including emotional neurotransmitters.
3. Small glue cells form an insulation coverage in neurons, but it may also affect multiple aspects of neurons -function -related neurons.
Although we have made progress in the scientific field in the last century, emotional disorders such as depression and anxiety are still very common, and it is difficult to effectively treat it. At present, research is mainly concentrated in the brain and different types of brain cells involved in order to better understand the biological characteristics of these diseases. Most of the attention has received neurons because of the mental health status and treatment. However, more and more evidence shows that the role of non -neuronal brain cells in emotional disorders has provided new opportunities for management and prevention.
Gel cells: onlookers of brain health
Our brain consists of billions of independent cells, and the most famous brain cells are neurons. Considering brain diseases such as dementia, stroke, or emotional disorders, neurons are the most important centers. There are more than 80 billion neurons in adult human brains. However, there are also non -neuron cells, called glue cells, which play a key role in all aspects of our brain health.
Plose cells were originally considered to be connective tissues in the brain-basically just neurons support system. For decades, people have clearly realized that these cells have performed various key tasks in our brain, from promoting the communication between neurons to affecting memory to immune regulation. With all these known functions, it is generally believed that the problem of glue cells will affect everything that recovers from dementia to stroke, and various emotional disorders.
One of the earliest contacts between glue cells and emotions comes from the corpse test of the brain of people with emotional disorders. In a series of small studies, the changes in glue cell density and quantity of the brain areas such as leather layers, forehead cortex and almond nucleus are reported, and these areas are related to emotional regulation. Since then, imaging, laboratory and cell studies have revealed the complex and charming effect of glue cells in emotional disorders.
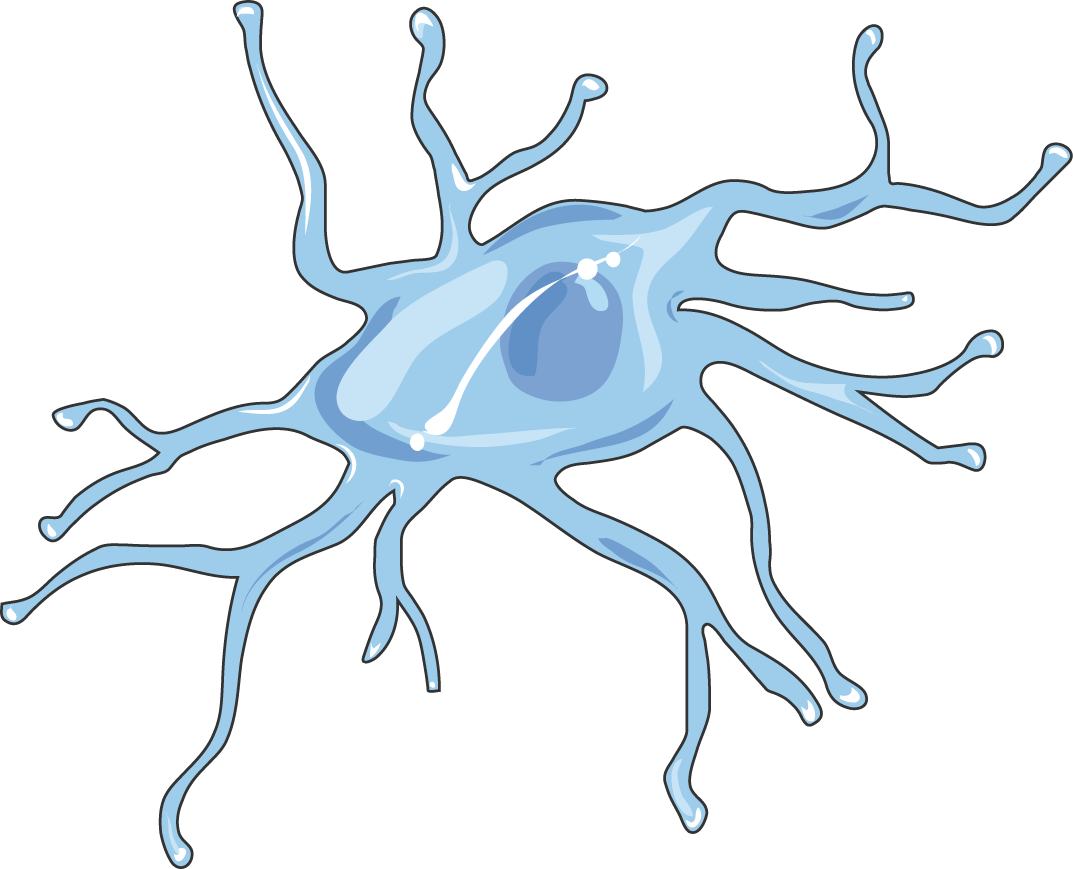
Glial cells
Small glue cells: immune coordinator of the brain
An incredible border called a blood -brain barrier (BBB) separates our brain from other parts of the body to refuse most microorganisms and immune cells. But the existence of BBB does not mean that the brain does not participate in immunity. In fact, the brain has its own special immune cells that patrol the brain and find microorganisms, damage or other problems. These cells are called small glue cells, and they are considered to be important for our brain health and more and more emotions.
As a regulator of the brain immune state, small glue cells are the key to maintaining a balancing of the brain. Studies have proved a clear connection between inflammation and depression. The level of higher brain inflammation is considered to cause depression. The elevation of inflammation in the brain is also related to post -traumatic stress disorder and schizophrenia. Like most systems in our body, small glue cells can be guided to behaviors that are beneficial or harmful to our health. So, how can small glue cells promote too much inflammation?
One of the most important tasks of small glue cells is "surveillance". It is believed that a huge small glue cell network has created a hub similar to the network, constantly analyzing any evidence of any immune threat in the brain. When these cells detect a problem, they will switch to the form of activation and begin to generate various immunochemical substances to help solve this problem. Although activated small gel cells help neutralize threats, long -term activation may cause inflammation that is not controlled by the brain and eventually leads to depression.
It is believed that when the BBB is ruptured and allows immune signals in the blood to enter the brain, small gel cells may be activated and cause depression symptoms. This may occur in the case of physical trauma, infection or stroke, or it may be due to signals from unhealthy intestines or excessive pressure hormones. Finally, it is worth noting that small gel cells also participate in the other two processes involving depression, namely the wiring and growth of the neonatal element (nerve plasticity and nerve generation). Active inflammatory small gel cells are considered to have a negative impact on these two processes, which may lead to depression.
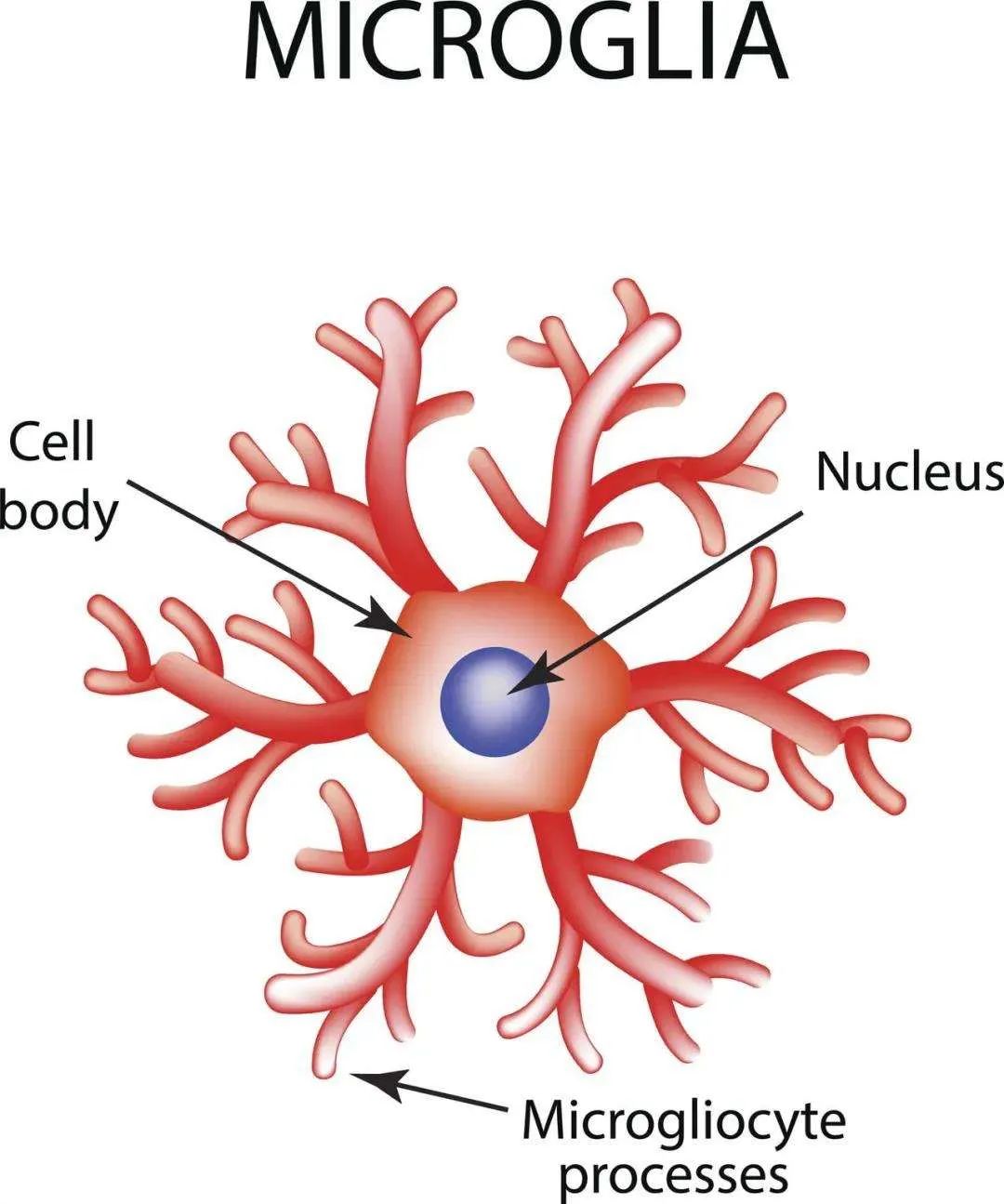
Via: small glue cells
Star cells: the main supervisor of neuron health
Star glue cells are traditionally considered to be neurons support cells, but their role is far more than simple support. Their names come from their shapes (similar to the stars). It is believed that a star cells may interact with millions of synapses. The connection between astrocyte cell regulating neurotransmitters and neurons also constitutes a physical component of BBB.
Since the discovery of star gel cells around 1900, our understanding of its role in brain health has been greatly expanded. In fact, some people have proposed three -way exchanges between neurons (star -shaped glue cell supervision from signals on both sides of the synapse), which implies that star glue cells play an important role in regulating neuron health. It is also believed that astrological glue cells also play a key role in creating new synapses and regulating nerve plasticity. How does star gel cells connect the connection between neurons? One way is to collect and release molecules like GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) and glutamic acid, which plays an important role in brain signals and emotions. Some studies also show that star gel cells can detect and absorb neurotransmitters, such as 5-hydroxyline and norepinephrine, which is considered to be one of the most important molecules participating in anxiety and depression.
Although research is still emerging, some studies have found evidence that the number of star cells in patients with depression and dysfunction is reduced. The reasons for these discoveries are still under research. However, the result may be that if there is no functional astrocyte cells to help regulate the communication between them, neurons will be exposed at the level of toxic excitement (such as glutamic acid), or it may be exposed to might damage the nerve. Yuan Healthy electrolyte (such as potassium) level.
Neurotic stem cell differentiation
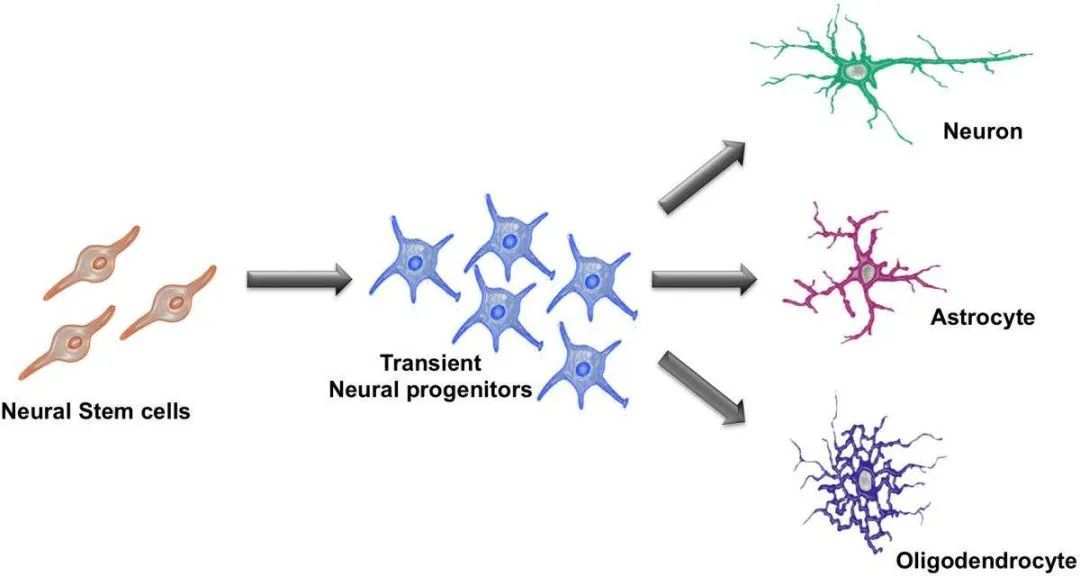
Shao Turbus: Not only the cover of neurons
Shaojo -gel cells are the third group of glue cells found in the brain. The most recognized role in brain health is to produce marrow sheath, that is, wrapped some white coverage of neurons, so that the signal is quickly transmitted in the brain and spinal cord. The neurons with a marrow sheath are called "white quality", and the neurons without the pulp sheath are called "gray quality". Further studies on Shaojie Globe cells have shown that they affect brain energy, learning and memory.
Through imaging research, there are many connections between the health of less glue cells and depression. For example, placing mice in a social isolation state (which is related to human depression) is related to changes in the structure and functions of less glue cells. These changes are related to the damage of the forehead cortex neuronal metal achidity (the forehead cortex is a key brain area involved in depression).
Like other gel cells, less glue cells have neurotransmitters (such as serotonin and dopamine), stress hormones and immune signals. This means that their impact on the environment is very sensitive. Because minimum glue cells can generate signals to promote or anti -inflammatory signals, these cells are likely to actively participate in the health of neurons and our mental health at all times, not just to promote myelinization.
Future outlook
Mental health is still one of the biggest challenges facing today. Traditional treatment methods, even if there are, can not benefit up to one -third of the treatment patients. However, the continuous understanding of depression and neurological biology, and people began to take targeted living intervention measures, all opened the door for more detailed use of existing treatment methods. Although neurons are still the forefront of depression discussions, the existing and being conducting research on glue cells may improve our ability to deal with various mental illness.
Source watermark
Reference (click slide to view)
Perlmutter, a. (june 7, 2022). How glial cells influnce your mood.psyChology today.
https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/the- modern-brain/202206/how-glials-inflonece-dlate-mood
Cool brain long -term collection of brain science and psychological articles, welcome to submit


Please submit a mailbox: [email protected]
Click here, let friends know that you love brain science
- END -
Incident Hebei!Litchi is "full", 8 -year -old girl is admitted to the hospital!Pay attenti

Right now is the season when litchi is listedWith lychee hot salesThe problems rel...
WHO: At this stage, monkey acne epidemic does not constitute "internationally concerned emergencies"
On June 25, local time, WHO announced that the current stage of monkey acne epidemic does not constitute international concerns of emergencies.The WHO held a meeting of the emergency committee on th