What new progress is worth seeing about NRG1 fusion lung cancer?丨 2022 asco
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.07.01
*For medical professionals for reading reference
List of the latest research progress of NRG1.
From June 3rd to 7th, 2022, the global tumor scholars' long -awaited annual tumor event -the annual conference of the American Clinical Oncology Society (ASCO) arrived as promising. Research result. A few days ago, the conference has ended successfully, but there are still many research results worth further learning and discussion.
Nervous regulatory protein 1 (NRG1) is one of the members of the NRG gene family. NRG1 is closely related to the occurrence and development of a variety of tumors, and during the process of its effect, it has changed a variety of signal pathways related to tumor [1]. NRG1 fusion is very rare, existing in various tumor types, and the incidence of non -small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cases is about 0.3%[2]. NRG1 gene fusion is an emerging carcinogenic driver, which can be used as a target for drug treatment.
This article summarizes some research progress related to NRG1's targeted therapy for lung cancer at the ASCO conference this year [3-6] for readers' reference.
Crestone Research: Serbantumab's preliminary efficacy and safety of NRG1 fusion physical tumors
NRG1 fusion is a rare carcinogenic driver and was found in about 0.2%of physical tumors. NRG1 fusion will cause ERBB3/HER3 excessive activation, thereby promoting tumor growth and cancer cell survival. NRG1 -integrated tumor patients have a poor efficacy of standard treatment. At present, targeted therapeutic drugs for NRG1 fusion positive tumors have been approved to be listed.
Serbantumab is a completely human -source anti -HER3 IgG2 monoclonal antibody. It is confirmed to inhibit tumor growth in pre -clinical studies driven by NRG1 fusion. The 2022ASCO conference announced a preliminary results of clinical research on NRG1 fusion physical tumors.
Crestone is a phase II, global multi -centered, and open label clinical studies developed among adult patients with local advanced or metastatic physical tumors with NRG1 fusion. During the dose range, the dose of phase II clinical trials was determined to 3g, and the venous injection was injected once a week until the standard of treatment was reached. In the expansion stage, queue 1 will be included in at least 55 patients who have received at least one treatment and have not received ERBB targeted therapy. Extensible queue 2 or 3 will be included in patients who have previously received ERBB targeted therapy and/or tumors containing additional molecular changes. This report was the initial data of patients with Serbantumab therapy (3G QW) and researchers evaluated queue 1 patients.
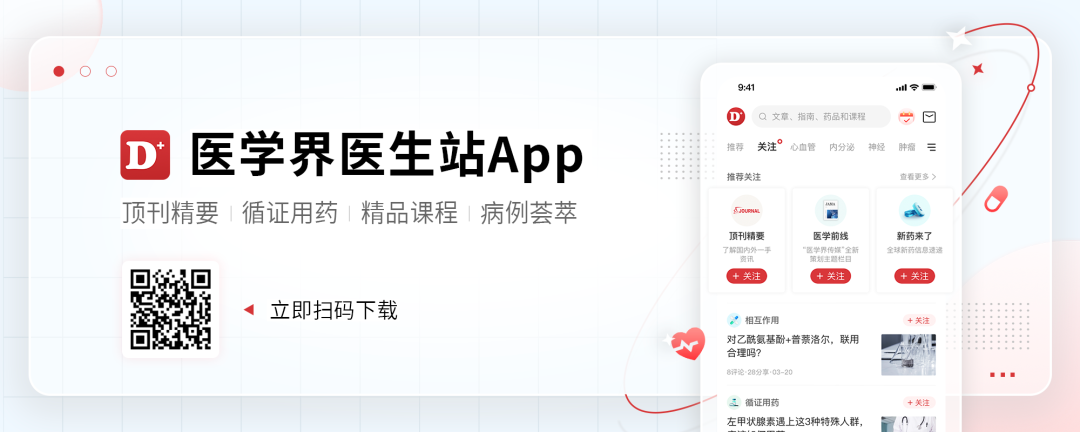
As of January 13, 2022, 12 patients in the queue 1 received Serbantumab treatment (3G QW). 92%of patients were diagnosed with NSCLC, and the second -generation sequencing (NGS) found that 5 different NRG1 fusion mutations (ATP1B1, CD74, ITGB1, SDC4, SLC3A2) were found. Among the patients 1 patient, the objective relief rate (ORR) was 33%and the disease control rate (DCR) was 92%. In the NSCLC patient group of queue 1, ORR was 36%and DCR was 91%.
The patient's tolerance to the Seribantumab treatment (3G QW) is good. The main adverse reactions are level 1 or level, and no drug dosage is required or reduced.
Table 1. Crane 1 and NSCLC patients' disease relief situation
Preliminary data shows that Serbantumab has a long -lasting treatment response in advanced physical tumors with NRG1 fusion and has good security.
Zenocutuzumab showed a long -lasting reaction in the late NRG1 fusion tumor
The combination of NRG1 and HER3 leads to HER2/HER3 heterogeneity and carcinogenic conversion. Zenocutuzumab is a new type of bilateral antibody drug that can strongly combine HER2 and HER3 receptors, thereby blocking the interaction of HER3 and its ligand NRG1.
A study was included in patients with NRG1 fusion physical tumors who had previously received or did not receive standards. After the group was put into the group, the Zenocutuzumab (750 mg IV Q2W) was injected until the disease progressed or unacceptable toxicity, and tumor imaging examinations were performed every 8 weeks. The main endpoint is the ORR evaluated by researchers.
As of January 12, 2022, 99 patients with NRG1 fusion positive tumor were included. The efficacy of 73 patients who received ≥1 dose Zenocutuzumab were evaluated. These patients joined the group on July 12, 2021 to have the opportunity to follow the standards of ≥6 months and meet the standards of the main efficacy groups. The median age is 59 years old, 58%is female, and the type of tumor includes: NSCLC (41 cases), pancreatic cancer (18 cases), breast cancer (5 cases), bile duct cancer (3 cases), colorectal cancer (2 cases) (2 cases) And 4 other tumors (1 case each), and the number of long -term system treatment lines is 2. The most common fusion partners are CD74 (27%), SLC3A2 (18%) and ATP1B1 (15%).
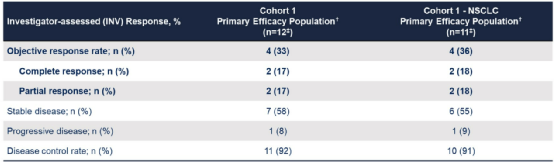
The results showed that among 71 patients who can evaluate the effect, the ORR was diagnosed with 34%, of which 35%of the NSCLC ORR was. 22 patients (13 cases of NSCLC, 6 cases of pancreatic cancer, and 3 other physical tumors) are being treated. The median Dor is 9.1 months, the 6 -month DOR rate is 76%, and the 12 -month DOR rate is 27%. In terms of security, among the 208 patients treated with Zenocutuzumab single medicine, the proportion of level 3 adverse events reported <5%was reported.
Figure 1. The best change of the target lesion from the baseline
The study confirmed that Zenocutuzumab showed strong and lasting effects in patients with advanced NRG1 fusion physical tumors, as well as good tolerance.
Explore the characteristics of Chinese NRG1 fusion physical tumor patients
Among Chinese patients, the research on the incidence of NRG1 fusion in multiple physical tumors based on NGS is limited. A study collection of FFPE samples and matching peripheral blood was used for NGS testing. A total of 47 patients in total were found to have NRG1 fusion, of which 4 of them detected NRG1 fusion at the RNA level.
NSCLC is the most common type of cancer, and the incidence of NRG1 fusion is 0.19%(25/13089). The incidence of NRG1 fusion rates of NRG1 of osteosarcoma, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and colorectal cancer were 0.30%(3/973), 0.16%(3/1850), 0.14%(3/2098) and 0.07%(3/4344) (3/4344). Essence CD74 (10.1%), SLC34A2 (10.1%) and WRN (4.3%) are NRG1's most common fusion partners. Other known partners include CDH1, HMBOX1, Adam5, and UNC5D.
Of the 47 patients with NRG1 fusion, women (49%) and men (51%) were distributed evenly, with 44.7%in the later period (III), the median age was 57, and the median TMB was 3.3 MUTS/MB. TP53 (48.9%), CDKN2A (14.9%) and ERBB2/FGFR1/MUC16/SMAD4 (12.8%) are the most common mutation genes that occur at the same time. 50%of ERBB2 mutations are amplified and 2 cases are breast cancer. Only one patient showed ALK fusion and 1 case showed FGFR1 fusion. Among all patients, KRAS P.G12X mutations accounted for 8.5%, EGFR mutations accounted for 10.6%, including 2 cases of L858R mutations and two 19DEL mutations.
The study found that the incidence of NRG1 was 0.19%in the incidence of NSCLC in China, and its incidence was the same as that of common tumors. NGS sequencing and Origifus algorithms have advantages in detecting NRG1 fusion and providing partners' structural information, and may provide guidance for more accurate treatment solutions.
A study in research: Evaluate the efficacy of Afutini for patients with advanced/metastatic physical tumor patients in NRG1 fusion
Afutinib is an irreversible pan -Erbb tyrosine kinase inhibitor, which is a potential treatment for NRG1 fusion -positive tumors. A study aims to explore the safety and effectiveness of Afutini in patients with NRG1 fusion -positive physical tumors. This forward -looking and real world research will be included in NRG1 -fusion -positive patients who can be evaluated with evaluated effects. Faritinib was treated until the disease progressed or the patient was no longer tolerated.
Incident standards include: late -stage NRG1 fusion, non -resection/metastasis, and non -blood system malignant tumors in the diagnosis of histological or cytological diagnosis. The exclusion standards include: the driving gene mutations that have been accepted by ERBB targeted therapy, and have used NRG1 fusion in the past. FDA approves targeted therapy. The main endpoint of the study is the ORR determined by the independent center. The secondary end points include DOR, DCR, and security.
Figure 2. Study design

references:
[1] Liu Jing, Cao Shuhua, Zhao Xi, Yang Yunlin, Ning Fangling. NRG1's expression and mechanism in non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Jilin Medicine, 2020,41 (4): 777-779.
[2] Jonna S, Feldman Ra, Swenson J, et al. Detection of nrg1 Gene Fusions in solid tumors. Clin Cancer res. 2019; 25: 4966-4972.
[3] Daniel R. Carrizosa, Mark E. Burkard, YASIR Y ELAMIN, ET Al.crestone: Initial Effical and Safety of Seribantumab in Solid Tumors Harboring NRG1 Fusions.2022 ASCOACOACOACO3 322 ASCO8STRACOCOACOACOACOACOAT 322 ASCO8STRACOACO3 3
Shaohua Yuan, Hui Chen, Liwei Wang, et al. LandScape of NRG1 Fusions Based on NGS in Chinese Solid Tumor Patients. 2022 ASCO ABSTRACT #E15073.
Protocol data. 2022 asco Abstract #TPS3180.
*This article is only used to provide scientific information to medical people, and does not represent the viewpoint of this platform


- END -
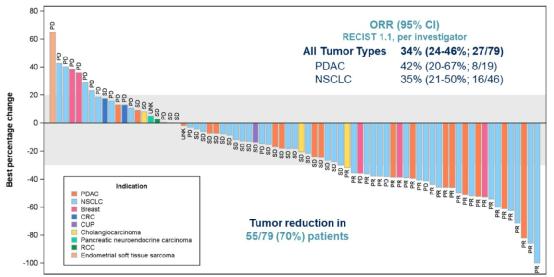
The latest release of "Top 100 Chinese Medicine Hospital"!Hubei hospitals are on the list
Wuhan Evening News July 10th (Intern reporter Jiang Mengqing) On July 9, Ailie's T...
Is HPV vaccination single dose feasible?What is the effectiveness of the nine -valent vaccine?

notBehind vaccine supplyAmendments to the business of manufacturers and vaccinatio...