The Japanese semiconductor industry has risen again like a fighting beast, and the last chance of revival also hopes to be slim.
Author:Electrical technology Time:2022.07.03
The battle for the revival of the semiconductor industry in Japan is an unable to lose, but it is also destined to be a hoped beast.
As the wave of new energy vehicles swept the world, Japan's proud automobile industry had to face the challenge of transformation. Although Japan started the research and development of new energy vehicles very early, it paid the chips to hydrogen energy vehicles. Therefore, when pure electric vehicles are popular in the market, the Japanese cars are also in the passive of the ship's hard -headed.
Every time the market share of pure electric vehicles increases, the living space of Japanese auto companies is reduced by one inch.
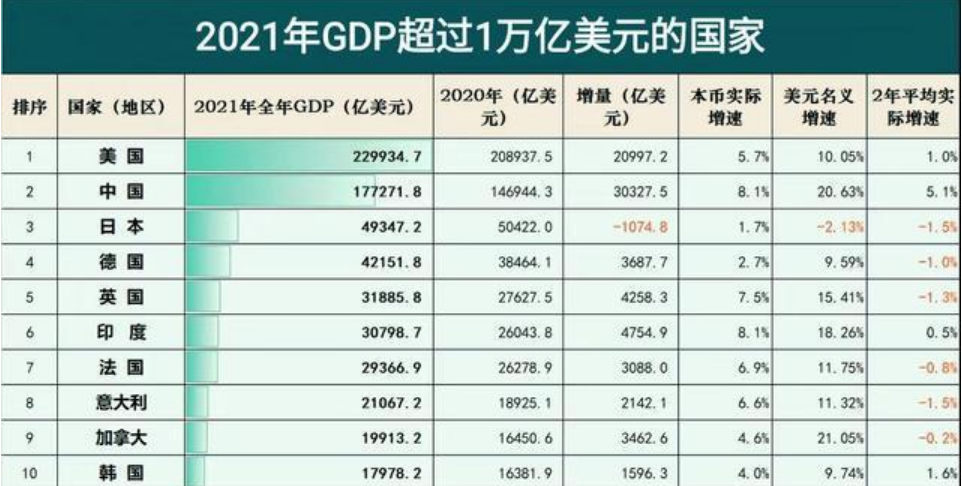
Over time, these changes have gradually appeared in Japan's economic data. Its car exports have fallen from 4.83 million in 2010 to 3.82 million in 2021. At the same time, Japan's GDP also fell from US $ 5.47 trillion in 2010 to $ 4.93 trillion in 2021.
Looking at the market share that is constantly being eaten by new energy vehicles, while promoting the transformation, the Japanese government has also begun to find new support points for the growth of the country's economy.
Last year, Japan released a strategic report of the growth of the semiconductor industry, hoping to raise the semiconductor industry to a more important position and make it another new engine of Japan's economic growth after automobiles.
Judging from the history of the past three decades, Japan's betting semiconductor industry, in addition to looking for a new engine for the country, is also trying to revive the industry that once represented the peak of Japan's manufacturing industry.
In fact, the Japanese semiconductor industry has achieved brilliant achievements in the 20th century. As early as 1986, the semiconductor products it produced accounted for 45%of the global market share. However, with the signing of the "Plaza Agreement" of the United States, Japan's semiconductor industry has also been suppressed by the US government. As a result, the momentum of Japan's prosperity was also severely damaged and fell into a downturn. By 1995, the global share of Japanese semiconductor products fell to 35%, and Japan's economic giant wheel also entered the fog.
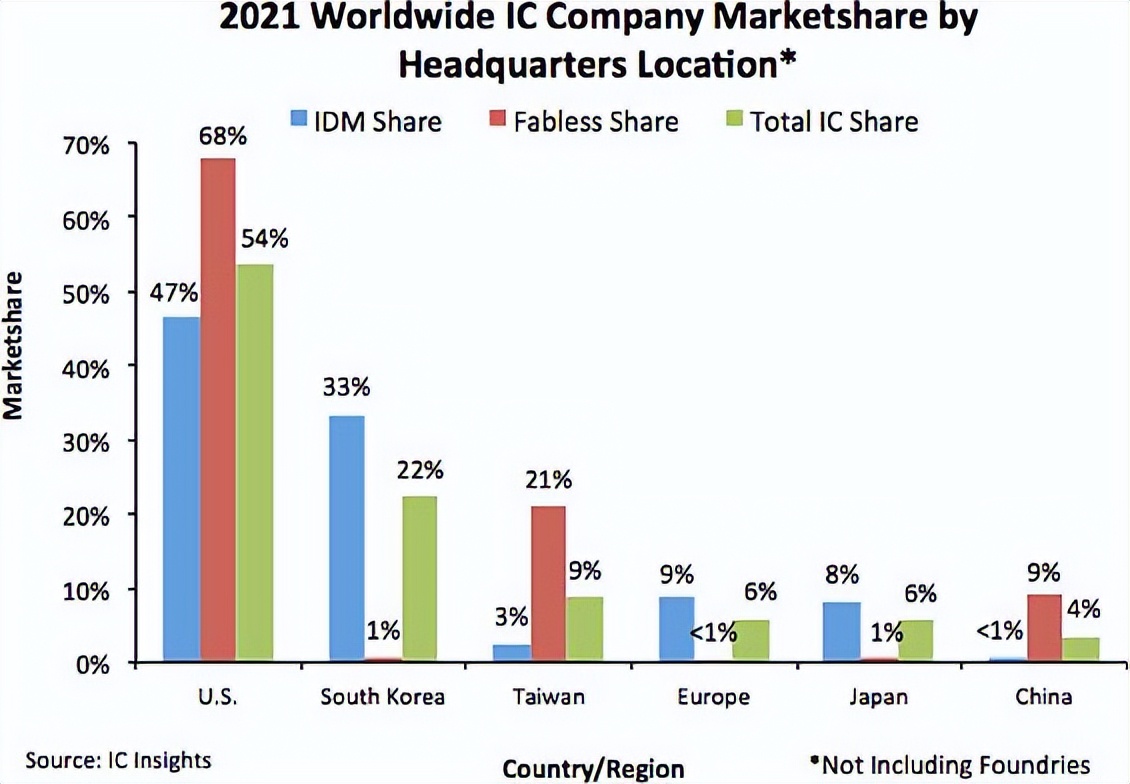
When Japanese semiconductor companies retreated from the global market, companies in the United States, South Korea and Taiwan gradually became the protagonist. By 2021, Japan's share in the global semiconductor market was only 6%, and the market share of the United States and South Korea in the same period was 54%and 22%, respectively.
So, how can Japan, which accounts for only 6%of the market share and builds a new economic engine of a cost country in the semiconductor industry?
In order to promote the development of the semiconductor industry in the country, Japanese Prime Minister Kishida said that the government will provide a huge investment of more than 1.4 trillion yen for the development of the semiconductor industry, attracting TSMC to build factories in Japan. The overall vision was to achieve a three -fold income of semiconductor enterprises in 2030, which increased to the goal of 13 trillion yen.
Through a series of actions of the Japanese government, it is not difficult to find that Japan has made up its determination to revive the semiconductor industry. However, the semiconductor industry is not effective for smashing money, which is the same for Japan.
The Global Semiconductor Industry Research Report in 2021 pointed out that the global semiconductor industry chain is divided into three parts: supporting industries, manufacturing industry chains, and application fields. Among them, the support industry consists of manufacturing materials, packaging materials, manufacturing equipment, and packaging equipment enterprises; the manufacturing industry chain includes three major links: IC design, IC manufacturing, and IC seal testing; field.
As far as Japan is concerned, although its share in the semiconductor market is not high, it remains leading in semiconductor equipment and raw materials. Japanese companies' share in the global semiconductor equipment market is 35%, and its share in the global semiconductor raw material market is 52%. In 2019, its export control of semiconductor raw materials for South Korea is its bright muscle -like operation in the semiconductor industry chain.
However, in addition, other parts of the semiconductor industry chain are still divided into many countries around the world. For example, China provides important raw materials for rare soil, provided by the Dutch Asto Corporation, and manufactured chips by enterprises such as TSMC.
It is true that Japan can use its huge advantages in the field of semiconductor raw materials and equipment to attract companies scattered worldwide to build factories in Japan, but Japan's semiconductor industry must still accept the current status of global division of labor. If Japan is creating the same monopoly market as the last century, it will inevitably be opposed by global semiconductor companies.
At the same time, Japan also needs to consider the labor force of the development of the semiconductor industry. As the country with the worst aging in Asia, Japan's population over 65 years of age in 2021 is as high as 28.9%. At the same time, Japan is also facing the problem of negative population growth. In 2021, the labor population from 15 to 64 in Japan once again decreased by 584,000.
In response to the above problems, Japan has to supplement human resources by replenishing the retirement period. Japan's pension collection regulations stipulate that since the age of 65, retired employees will receive pensions every month, and his pension amount will increase by 0.7%; retired employees will receive pensions from the age of 75, and they will receive pensions from the age of 65. Gold increases 84%per month. Based on such a pension policy, office workers over the age of 7 are everywhere in Japan.

In order to cope with the shortage of labor with the growth of the population, Japan has also relaxed visa restrictions and foreign labor restrictions. From 2014 to 2018, the total number of foreign workers in Japan has reached 1.084 million.
The semiconductor industry is a highly global industry, but the relationship between enterprises is still affected by the law of the jungle. The United States forced to sign the "Plaza Agreement" with Japan first, and Japan used monopoly to sanction South Korea. Although the incident occurs differently, the cause of the conflict is consistent. Just as the losing market of Japanese automobile companies is occupied by the latecomers, the adjustment of the chip market share per 1%will also cause conflicts.
In other words, if Japan wants to revive the local semiconductor industry, it means that some interests in other countries in the industry chain will be damaged. A question coming to the face -Will the United States agree with the absolute domineering position in the industrial chain?
From the perspective of national development, Japan is determined to revive the semiconductor industry. The golden time of Japan, which has been in the semiconductor market, has been caught up now. In addition to being dragged down by the aging of the population, Japan also has to face the competitors of competitors. Although this semiconductor revival battle could not be lost, it seemed that it could not win the victory. As the last opportunity to leave the Japanese economic rejuvenation, the semiconductor industry seems to be not suitable for Japan.
- END -
Fried, and then "forced demolition"

Geng ZhiAccording to several US media reports, Georgia, a giant stone monument tha...
The Ukrainian photovoltaic power station was attacked by missiles!Does it affect the Chinese photovo

13.06.2022Number of this text: 1445, reading time for about 2 minutesGuide: Recent...