Xu Wenning: "Over the sun" talk about Jade Rabbit
Author:Music club Time:2022.07.30
"Over the sun" words Jade Rabbit
Xu Wenning
What is the medicinal material of rabbits?
Is the rabbit on the moon be male or female?
Why is there no Wangyue Rabbit in the Yuan Dynasty?
Is the toad of the Moon Palace?
Rabbits are often seen in ancient decorative parts and decorations. In traditional Chinese culture, rabbits are regarded as auspicious things, and they are ranked fourth in the twelve zodiac signs. The ancients were called "Jade Rabbit" because of their fur white. The Han Dynasty Wang Chong's "On the Heng · Saying the Japanese": "There are three -legged birds in the middle of the day, and there are rabbits and toads in the moon." Three -legged birds are also known as triple -footed golden birds. bird. The ancients believed that the golden bird was a symbol of the sun, while rabbits and toads symbolized Taiyin. When the sun came out of the sun, and when the moon left, the god of the time was greeted by the sun, and at the same time, the jade rabbit elves in the moon were sent away. So there is a collective name of the rabbit.
In the field of ancient crafts, rabbits are a common animal pattern decoration. The earliest Yutu is currently seeing the rabbit -shaped decoration unearthed from the site of Anhui Hanshan Lingjia Beach. (Figure 1) Jade material is yellow and white, and the decoration is composed of the upper part of the rabbit -shaped and the lower part of the mortise. Arc, tails upward, hind legs squatting in one limb. The tenon is slender, and the top of the four -hole is drilled, which is similar to the shape of the jade combing back of the jade artifact of Liangzhu.

Figure 1 Rabbit -shaped decoration unearthed from Lingjia Beach site in Anhui
The jade comb is a decoration of the ancients with a comb. The pattern on the back of the Liangzhu Culture Jade Comb is the gods and tigers, expressing a sacrifice totem that worships the worship of the spirit. Can the jade rabbits be decorated on the top of their heads during this period. Does it also have a primitive totem worship? In the Han Dynasty Wang Chong's "On the Heng" recorded: "Rabbit sucks and hnds", it is said that the rabbit is very easy to get pregnant, and it seems that licking hair is pregnant with a bunny baby.

Lingjia Beach Turtle
In ancient times, people had observed that rabbits were susceptible to pregnancy, and their pregnancy was 31 days, which was in line with the lunar profit operation cycle. This should be the basic understanding of the ancients to connect the rabbit and the moon together. At this point, the ancients' understanding of the operation of the celestial body could be confirmed from the scinations unearthed from the Lingjiatan site, and the arrangement of celestial stars was confirmed. When the primitive people looked up at the moon in the sky, they looked like a rabbit in the shadow inside, and explained according to the intuitiveness of primitive thinking, and explained according to their common and similar animals.
Rabbit is one of the earliest familiar animals in our ancestors, and has a very vivid rabbit word on Yinxu Oracle. The shadow in the middle of the moon is indeed similar to the rabbit shape, and the myth of rabbits in the middle of the moon naturally occurs. On the other hand, the rabbit totem clan in the primitive clan associates with the shadow of the moon and the shape of the rabbit. Essence
Rabbit -shaped jade carvings are more common in the two generations of Shang and Zhou dynasties, with more realistic shapes. There are many forms of rabbits, mainly with their head -up curled up and low -end bow back. The hint of frightening and uneasiness in the lying on his head is hidden; the low -end bow -back jade rabbit is relatively quiet, docile and tame.
In the late Shang Dynasty, the jade rabbit can also see a relatively lively form. The rabbit opened his mouth, his head stretched forward, and his ears stretched back, but he did not stick to the back, the hind legs curled, and the front leg extended. (Figure 2) The rabbit -shaped jade pendant Shang Dynasty, Anyang City, Liujiazhuang, Henan Province, unearthed in the Archaeological Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Milky white, flat semi -volt, engraved the outline of the ear, nose and foot with a single yin line, and erected the ears towards it. The formation of long ears and short tails is in a clear contrast. A kind of manifestation of the momentum and the sensitive air alarm is portrayed and lively. Except for the contour line, there are no other decorative patterns, smooth lines, simple and rough workmanship, and lifelike. This rabbit -shaped jade pendant has a small round hole in front of the feet. The opening of the jade rabbit in the Shang Dynasty is generally a round hole in the mouth, which can be tied to both or achieved the purpose of expressing the rabbit mouth. But there is also a hole in the tail.
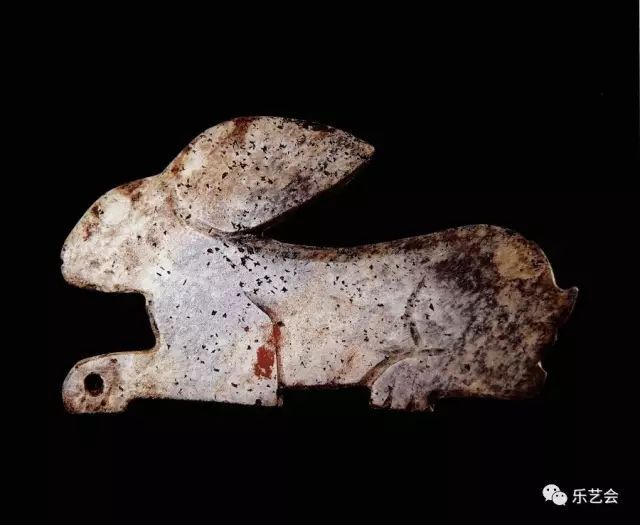

Figure 2 big ear rabbit -shaped jade pendant business
In the late Shang Dynasty, Jade Rabbit can also see a more lively form. (Figure 3) The rabbit -shaped jade pendant was unearthed from Wang Yutou, Anyang City, Henan Province, and is now hidden in the Institute of Archeology of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Evaluted by Qin Baihua, Suggaining, Eyes, Big Ears, Big Bow, Bottom Back, Droting Monastery, intersecting front and rear feet. Short -tail indicates its prevailing attitude. There are short stripes on both sides of the back of the back. Gouyun patterns are generally used on the jade articles of Shang Dynasty. It presents a high degree of unity on the utensils of other materials of the Shang Dynasty and is a symbolic decoration. On jade, there is still a certain correlation with the body joints of animal jade.
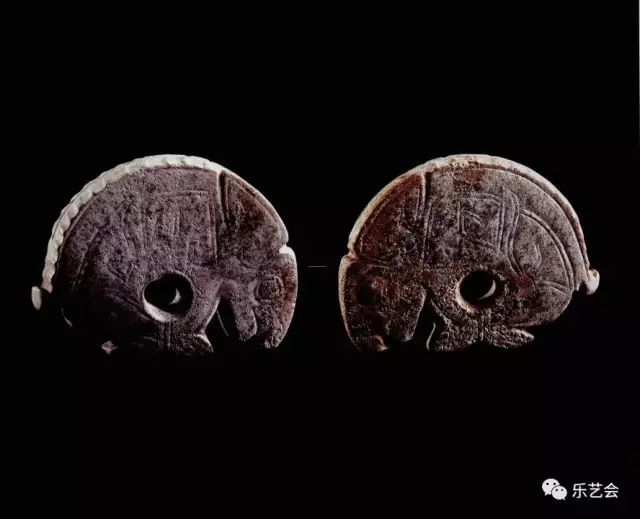
Figure Three Rabbit -shaped jade pendants
In 1974, the utensils unearthed from the tomb 1 of Rujiazhuang, Baoji City, Shaanxi Province were very rich. The burial jade articles were mainly scattered in the head, neck, chest, and abdomen of the deceased in the coffin. Yu Yan and so on have more than 200 pieces. There are other utensils of other textures, such as bronze, pottery, etc.
From the perspective of the parts and quantities of the jade burial, these jade articles are earrings, necklaces on the neck, and the group of pendants on the body. At the same time, the identity of the tomb owner is a noble. Compared to Shang Zhou Yutu, rabbit patterns on bronze wares are extremely rare. What can be seen at present is the early Western Zhou Dynasty rabbit patterns unearthed in Luoyang and the mid -period rabbit -shaped bronze respected in the mid -Western Zhou Dynasty unearthed from Quwo County, Shanxi. The rabbit -shaped jade carvings of the Shang and Zhou dynasties are almost all available for wearing. Picture Rabbit -shaped jade pendant business

In terms of craftsmanship and styling, the rabbit -shaped jade carving workers during the Western Zhou Dynasty were not as fine as the Shang Dynasty. Although it is still mostly chimb, but the decoration no longer is mainly pattern, and there is no lines of the Shang Dynasty jade rabbit. The artistic effects of lines are mainly. The "one -sided slope" knife method is carved with the lines, and the two -sided workers of the sloping knife are outlined to outline the rabbit's mouth, nose, eyes, ears, and limbs and claws of the bone structure and muscle outline.
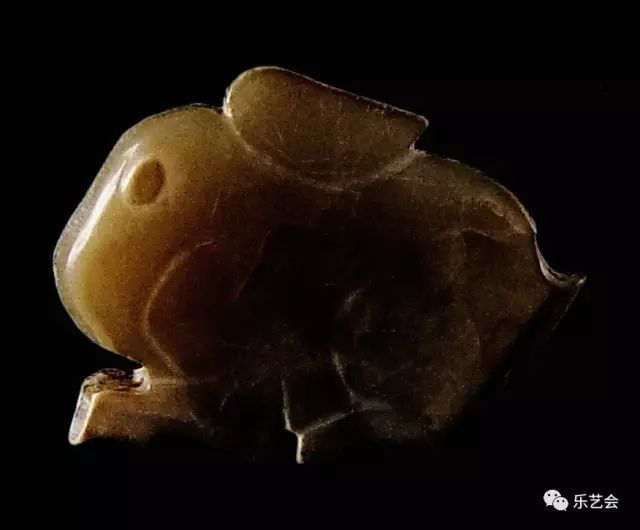
(Figure 4) Unearthed 49 Tomb Tomb, Shangguo Tomb, Wenxi County, Shanxi Province, is now hidden in the Shanxi Museum. White jade, rabbit as squatting, round perforation in the foot, round eyes, square ears, long tails, square feet. The sculptor's ingenuity is unique, grasping the main parts of the rabbit, and exaggerating the method, focusing on the ears and eyes of the rabbit, and the general outline, the details are saved, reaching a state of amazing.
Figure 4 squat rabbit -shaped jade pendant Zhou

Two jade rabbit -shaped websites unearthed from the tomb No. 1 of Baoji City, which are representative works of the mid -Western Zhou Dynasty. (Figure 5) Blue jade, gray -green, slightly transparent, flat body, sheet -shaped, double -sided carving, the same decoration, the first upper, the eyes are bumpy, the mouth is slightly open, the ears are towering back, the short tail is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted, the song is slightly tilted. The limbs are hipped, and the squatting is jumping. There is a round hole in the forefoot.
The jade rabbit -shaped Pei adopts the combination of the ground relief and the carving of the yin line to portray the animal's personality. Judging from the jade rabbit and other varieties of jade, the Jade carving of the Western Zhou Dynasty has developed newly developed on the basis of the Shang Dynasty jade. The Western Zhou Dynasty jade decorated with many flat shapes, good at summarizing the artistic technique of the whole picture with exaggerating the local characteristics, and achieved the image of simplicity.
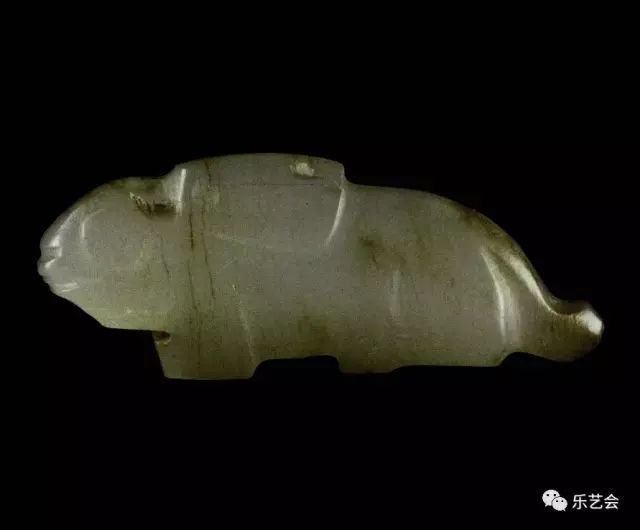
This form of jade rabbit is closer to the jade rabbit during the Shang Dynasty, so as to find the basis for us to find the relationship between Jade Rabbit and Western Zhou Yutu. In 1991, the round sculpture green jade rabbit unearthed from M2009, Shangcun Lingguo Cemetery, Sanmenxia City, Henan Province, broke the form of rabbit -shaped jade carving during the Shang and Week period, giving people a refreshing feeling and more three -dimensional feeling, reflecting the progress of the jade carving crafts in the late Western Zhou Dynasty.
Whether the creation of Jade Rabbit during the Shang and Zhou Dynasties is mixed with emotions related to ideological concepts, and it is necessary to further study, but one thing is certain that people who wear these jade rabbits are unusual, but people with a certain status. It was a common rule used by early jade.
Jade Rabbit

After the Shang and Zhou dynasties, the theme of the rabbit in jade articles is not very common. In 1978, a large -scale wooden tomb unearthed in the middle of the Warring States Period in Suixian County, Hubei Province. Like basically the same, there are two big trees. There are birds representing the sun on the top of one tree. The other tree has a somewhat tiger on the top of the tree, and the body and short tail are like rabbits. , It is considered the historical data of the rabbit to send the Moon Palace.
The legend of the rabbit last month's palace also tells a story in "Myth and Legend and Folk Culture related to rabbits". The narrative plot is more tortuous and intriguing. According to legend, King Wen was dissatisfied with the brutal rule of the King of King, and he recruited the princes in Xiqi, agreed to rebel, and wanted to overthrow the King of King. After the King of Kings learned, he designed to deceive the father and son of Ping Wen into Chaoge and settle under house arrest. In order to confuse the king, King Wen pretended to be stupid all day. The King of Kings tested the authenticity of the Wenwen king, and then killed the son of the king of Wen, which was cooked into the soup to send it to Wen Wang. The king of Wen did not know, and then swallowed his son's broth.
The King of Kings released Wang Wang from prison at ease. After the King Wen escaped from Chaoge, he was distraught, and when he tears, he vomited his son's meat. As soon as the meat fell to the ground, it turned into a white rabbit. After worshiping the king of Wen, the little white rabbit rose to the sky with a fragrant wind. Later, the emperor of the Jade Emperor was moved deeply after the royal view, saying that his father and son were loyal and filial piety. Immediately descended to put the little white rabbit beside him and named it "Jade Rabbit". It also made him accompany the Chang'e fairy in the Guanghan Palace to pound the medicine and cultivate his body to become a immortal. Later, Yutu lived up to the emperor's hope, and the merits were successful. He accompanied Chang'e and made immortal medicine all day long to relocate the pain of the disease.
The theme of rabbits full of Taoism was first seen in the Han Dynasty. It was a reflection of the Han Dynasty's pursuit of longevity and faith in the world of fairy. The image of the rabbit is extremely active on the portrait stone of the Han Dynasty. Among the rabbits on the rabbit on the portrait stone of the Han Dynasty, the rabbit is no longer an ordinary rabbit, but a fairy rabbit. Become an important decorative subject.
Figure Liu Xiang Hongshan Village unearthed from Jiaxiang, Jiaxiang, Shandong

(Figure 6) Portrait stones unearthed from Hongshan Village, Jiaxiang, Shandong, and portrait stones or portrait bricks unearthed from various places. The Wonderland images of Queen West are engraved with the jade rabbit. Yutu pounding medicine has become an important element of Han painting mythology. The Han Dynasty respected the Queen Mother of the West as the head of the West Immortal, and was the manufacturer and manager of the long -lasting medicine.
The jade rabbit reflected in the portrait of Han, whether it is around the Queen Mother West or in the middle of the month, is mostly a pestle. In Hanlefu's "Xianghe Song Ci", there is "adopting the magic medicine as the wooden end, and the white rabbit long kneeling into a shrimp pill." And Fu Xian's "Question of Heaven" Yiyun: "What is the middle of the moon? White rabbit pounding medicine." It can be seen that the jade rabbit is made for the Queen Mother West. Yutu pounds the medicine in the Moon Palace, and the material taken is "Shenzhuo Ruomu". If the wood is the huge life tree where the moon god lives, if the wood end is the branches. The jade rabbit is to make the wooden end of the wood, make a pill, and dedicate it to the Queen Mother of the West. As Li Yong said in the article "On the Image of West Queen Mother in the Han Dynasty": "In a image of the Queen Mother of the West, if the combination of the image is reduced to the lowest factor, then the Queen Mother West is matched with the jade rabbit. The image is the visual damage of the Queen Mother of the West. In this sense, it can be considered that pounding rabbits is a sign of the Queen Mother of the West. "
The jade rabbit running in the portrait of Han in the moon wheel corresponds to the golden bird phase flying in the sun wheel, indicating that the celestial body is running. The jade rabbit holding the stick is next to the Queen Mother of the West. It forms a mysterious and desirable Wonderland world with golden birds, toads, nine -tailed foxes, and feathers. Mythical Story Chang'e is widely known. However, I do n’t know that Houyi got the Western Mother's Immortal Medicine because of her success, but in front of the temptation, the husband and wife also had a day of flying. The immortal medicine was stolen by Chang'e. Houyi did not enjoy it. Essence Chang'e had an immortal medicine for his husband and Houyi.
However, it is clear that in the immortal artistic conception of the portrait stone of the Han Dynasty, the lonely Chang'e Shu Guang sleeves could not be found. In Zhang Heng's "Lingxian": "I ask the impermanence of immortal medicine to the Queen Mother of the West. Mang, there is no fear, and then Dachang. E Sui supports himself in the moon, for a toad. "It is said that Chang'e stole the immortal medicine obtained by her husband from the Queen Mother of the West, soaring the moon palace and becoming a toad. It turned out that the toads that pounded the medicine with the jade rabbit in Han paintings turned out that Chang'e changed and had to be sighing.
Figure Seven Sui Bai Yutu
With the mainstream of social consciousness, myths are constantly changing in order to appease people's psychology. However, in Li Shangyin's "Send Far" poem: "Chang'e's pounding medicine is endless, and the jade girls are not willing to take the pot." He Chen Tao's "Watch the Moon on the Sea" poem: "The residence should be lonely, the medicine is sorrowful." The credit of the medicine was given to Chang'e, and it seemed to feel a little comfortable to those who fell in love with Chang'e. This is exactly that with the reform of culture, myths have to keep pace with the times.

In fact, the myth that coexistence of Jade Rabbit and toads in the middle of the month is also the product of the conceptual thinking of the yin and yang in the Han Dynasty. Liu to the "Five Classics" said: "What are the toads and jade rabbits in the middle of the moon? Month, Yinye; toad, yang, and rabbits, Mingyin is in Yangye." "Yuanming Bao" Yun: "In the middle of the month, two toads and rabbits, yin and yang double residence, Mingyang's yin, yin to yin." This is a common interconnection constraint mechanism for things, and it is even more harmonious. Coexistence civilization form.
The Rabbit -shaped jade carving style of the Sui Dynasty inherited the roughness of the previous generation and gradually became neat. According to expert recognition, Li Jingxun's tomb of the Sui Dynasty unearthed a animal object like a white jade rabbit. (Figure 7) Looking at the front of the head, the back of the ears, the facial details are not performed, the forelimb is extended side by side, the hind limbs are curled under the abdomen, the hair is carved with a simple yin thread, and the other parts have no pattern. The perforation of this zoo is very characteristic and cross the abdomen. It is often seen in animal jade carvings like this during the Tang and Song dynasties. As for how to wear silk, it is unknown.
Its jade rabbit Pei is related to filial piety. There is an article of "Rabbit Filial Piety" in "The Biography of the Filial Pilllar of Sui Shi". It is said that there is a person named Huaqiu, who is very filial to serve the mother. At the end of the mother's life, she set up a shed in front of the tomb to keep filial piety for her mother. A hunter chased a rabbit a day, and the rabbit pierced into the Mao shed in a panic, hiding under Huaqiu's knees, and the hunter came in without finding it, so he left. Since then, the rabbit has lived in his house at night, and has been in front of the gate in front of the door. The ancients believed that rabbits could recognize the filial piety home, just like a pigeon was chased, and the pigeons hid under the Buddha's figure, and they were fine. The filial son's home must have Buddha light and auspiciousness, which can bless the light to all beings and relieve the terrorist psychology of the victims.
Figure eight rabbit -shaped jade pendant Tang
A jade rabbit with 2.45 cm long, 1.02 cm wide, and 1.25 to 1.35 cm unearthed from the Tang Dynasty dormitory of Suzhou Pesticide Factory in the Tang Dynasty. Back upward, engraved the eyes with a simple yin line. (Figure 8)

In addition, in the 1978 cities, the collection of Xuchang City was collected in 1978. It is now hidden in a jade rabbit in Henan Provincial Cultural Relics Store, (Figure 9) green jade and round carving. The rabbit is lying on the back, and the long ears are stuck on the back. Eye, eye risk is represented by an arc, and the mouth protrudes forward. The front and rear limbs are illegally, the leg muscles are raised, the hips are thick, and the tail is falling. The lines of the ears, nose, and limbs are decorated with shade. The dense and extensive lines of the yin carved lines are expressed by the animal objects of the Six Dynasties of the Han Dynasty, and the fur engraving line has the characteristics of inheritance. Rabbit's finger claws are also carved with lines, the overall image is simple and solid.
Figure Nine Rabbit -shaped jade pendant Tang
The image of the jade rabbit is similar to a rabbit unearthed from Luoyang as a printed buttons. (Figure 10) uses the rabbit as the button, the back of the rabbit bow, the head on the two front legs, and the hind legs as squatting. In 1974, it was unearthed in the East Suburbs of Xi'an. The rabbit buttons of the Shaanxi History Museum now Tibetan Shaanxi History Museum is the best jade town at present. This town is a white jade cubic shape, with a rabbit on the upper round, and the rabbit is lying in a bow and waist. That is, around the jade rabbit, the vine branches are carved with a variety of grapes; on the side of the surroundings, the same shampoos vine leaves are also decorated with blue dragons and phoenixes, which are commonly used in the Tang Dynasty. Figure ten rabbit -shaped jade printing New Tang

Feng is the longest of the birds, and the king of birds is the most beautiful among the hundred birds. Grapes were native to Europe, West Asia and North Africa, and were introduced into our country after the Emperor Hanwu period. Yuzhen absorbs the artistic characteristics of Central Asia, West Asia and other places, and is both integrated. The carved rabbits, dragons, phoenixes, and grapes are all imply auspicious patterns. Based on the inheritance of traditional jade carving , Left an immortal unique artistic style for future generations.
Tu Tu -shaped Yuzhen Tang

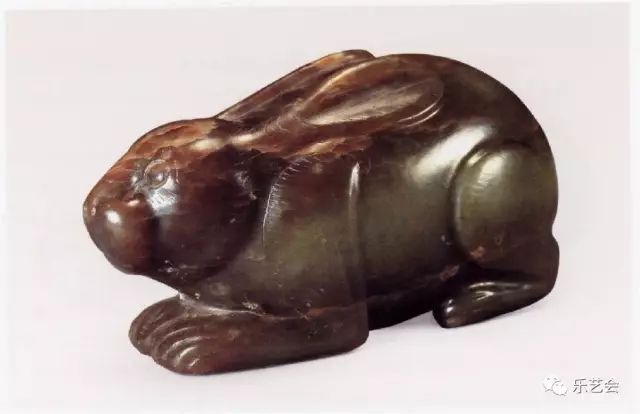
Looking at the jade rabbit from the Sui and Tang dynasties to the Song Dynasty, although the number is not large, they are round carved, generally calm and quiet. The rabbit is lying on the lying, the feet, the ears are attached to the body, or the slightly exposed, the abdomen across a hole, or a hole in the back and abdomen. The details of the jade rabbit from the Sui and Tang dynasties to the Song Dynasty are different. Due to the expression of round carving, the jade rabbit is more realistic than the film carving during the Shang and Zhou dynasties.
Beijing Zhuoyu Pavilion Tu-shaped rabbit-shaped (Tang-Song) (Figure 11) Qingyu Manqin, Qin color is like purple at the end of the moon, and local calcification. The carved rabbit with a photo method is wonderful. Regardless of the muscles and bones, the limbs, the proportions of height, and the weight of the fat, are all clear and true. Thousands of years ago, the ancients could reach this realm, and it was not easy, but it was proud of ancient and modern. Alas, now we are said to be carrying, wearing it in the belt, drooping Duobao, and prevailing in the Tang and Song dynasties.

Figure eleven rabbit -shaped jade pendant Tang and Song dynasties
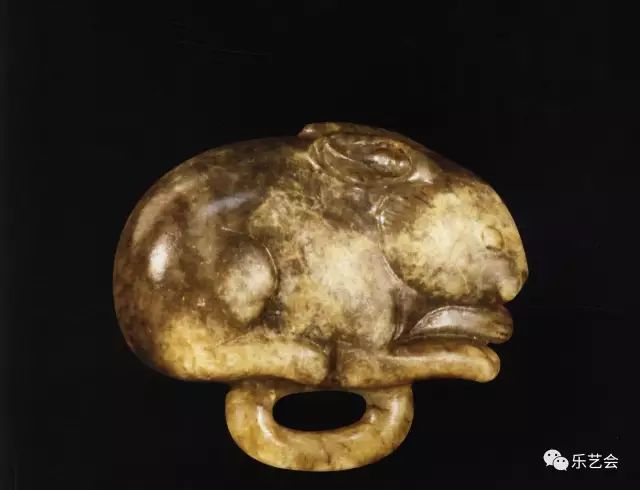
However, after all, the number of jade rabbits in the Song Dynasty was very small, and there were not many in the world. The most famous among the Song Dynasty jade rabbit was unearthed from the Southern Song Dynasty tomb of Guoyuan Village, Wangjiaxiang Village, Wangjiaxiang Village, Kocheng City, Zhejiang Province. (Figure 12) Blue jade, round carved jade rabbit, with concise lines, realistic shapes, and delicate carving. This jade rabbit is the jade town in the earliest educational supplies that can be confirmed. The rabbit is lying in the same way. Double currently views, the eye, ears, legs, tails and other parts are used to make outlines. Rabbit hair is very realistic.
Figure twelve Song Dynasty Jade Rabbit

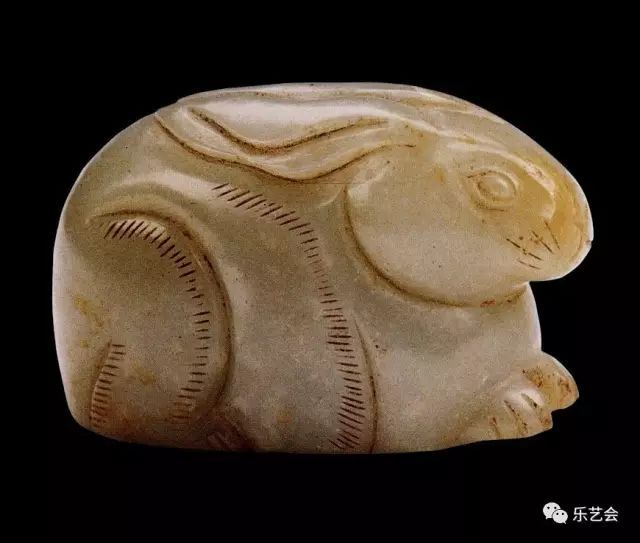
There is a pair of crystal rabbits in the tomb of the Song Dynasty. (Figure 13) was unearthed in the Tengzijing family tomb of Glory Village, Xinhe Town, Xinhe County, Qingyang County, Anhui Province. It is now hidden in the Qingyang County Museum. The crystal is colorless and transparent. The rabbit is lying on the squatting shape. Both eyes look, the ears are erected, the front and back leg are slightly bowed, and the tailless tails are outlined with the thick yin line. The lines are rough and concise. The rabbit's back is drilled up and down, and it is a common characteristic on jade articles in the Tang and Song dynasties.
Figure 13 Crystal Rabbit Pei Song

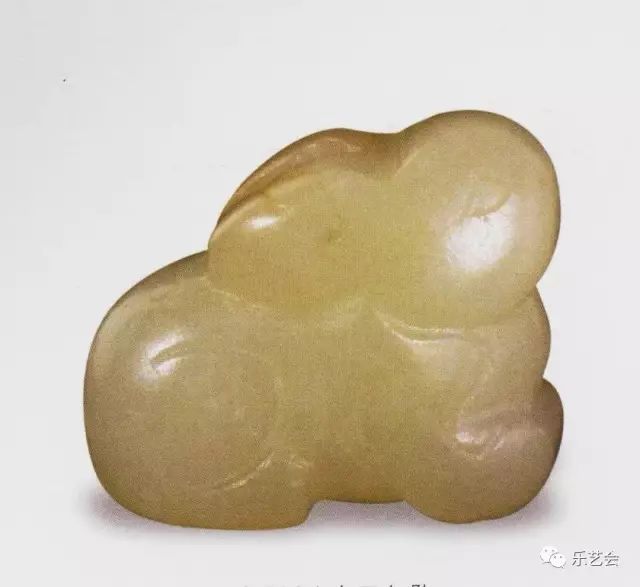
The image of the rabbit on the portrait stone already has a distinctive belief and connotation in the Han Dynasty. It can be clear that the fairy rabbit in people's minds is closely related to longevity and non -aging. And without being replaced by the dynasty, this cultural heritage has been continued. But sometimes it is presented, such as the direct expression of the rabbit pounding theme; sometimes it is hidden, such as the round carved jade rabbit or rabbit pattern of the art room supplies after the Sui and Tang dynasties.
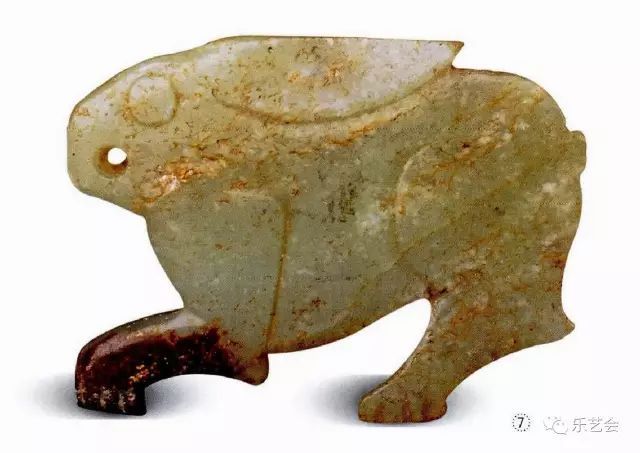
The "Houshan Talking Cong" of the Northern Song Dynasty poet Chen Shidao said: "There is no moon in the Mid -Autumn Festival, then the rabbit is infertility, the mussels are not fetal, Joe Mai is not true, the rabbits look at the moon, the mussels look at the moon, the buckwheat is showing the moon, and the rabbits are all rabbits. Female, but the Moon Rabbit Heroes, I hope to be pregnant. " Here, Chen Shidao played the imagination of the jade rabbit in Wangyue, and pointed out that the female rabbits were all the "Jade Rabbit Wang Moon", and the male rabbit was pesting medicine for the Queen Mother West in Guanghan Palace. Due to the clear induction of the Song Dynasty with a clear "rabbit looking at the moon", at this time, the ancient jade carving rabbits were given to the ancient jade sculptures, and a channel to study the traceability of the ancients of the ancients.
On the occasion of Song and Liao and Jin, the war was repeated. Once the attack was attacked, the people were scattered as rabbits. The craftsmen described differently from the "Gu Rabbit" who were shocked, or some reflections in their own situation. During the Song Dynasty, a large number of decorations and shapes with the theme of looking back at Gu Wang's rabbit appeared on the works of ceramics, puppets, jade carvings, seals, murals, stone carvings and other works. , Carefully take care of it.
The image of the rabbit is roughly divided into the following: 1. Be wary of the shape of looking back and looking around, and secretly coincide with the description of "White Rabbit, walking around the west" in Gu Yan's song. The rabbit looked back at the grass, and his eyes were vigilant. The rabbit did not run away. It was a static expression of the "white rabbit". 2. The rabbit runs like "taking off rabbits". The depicting "take off rabbit" is full of dynamic, flying like an arrow, making people sigh that time has also passed away. "Rabbit" originated from Sun Wu's "Sun Tzu" during the Eastern Zhou Dynasty. Here, the metaphor of the escape rabbit attacks sharply, and the opponent caught off guard, so as to get a way to win. (Figure 14)
Figure 14 rabbit -shaped jade pendant Southern Song Dynasty
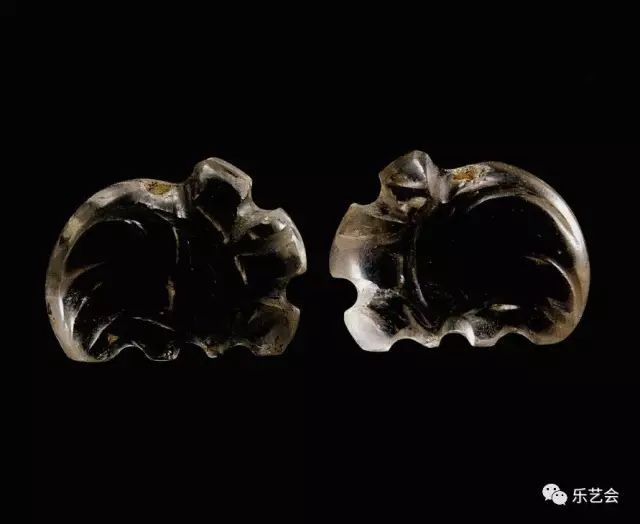
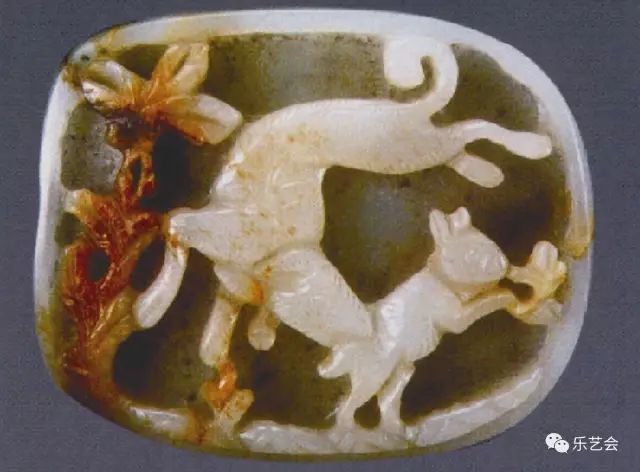
During the Song and Jinliao period, the rabbit's eyes were mostly Gu Yue. However, the sight of the "Gu Rabbit" in the Yuan Dynasty moved down, and it seemed to avoid Gu Yue, especially the theme of the female rabbit Gu Yue, almost gone. The reason may be related to the saying of "rabbits". The Yuan people Tao Zongyi wrote in "Nancun's Portage" and wrote that "the house family members are all rabbits, and the people are always shrinking turtles." Figure 15
Figure 16 Yuan Dai Hunter Hunter Catch Rabbit Jade Witches

Regarding this paragraph, the Qing Dynasty Zhai Yan verified in the "Popular Editor": "Rabbit looks at the moon and pregnant, and the woman is not pregnant and pregnant. Those women who are "rabbits" at home means stealing people. Due to this allusion, the rabbit pattern of the Yuan Dynasty also appeared the pattern of hunting dogs. The rabbit had a little fate of the forest law, which helped the Song and Yuan rabbits. (Figure 15) (Figure 16)
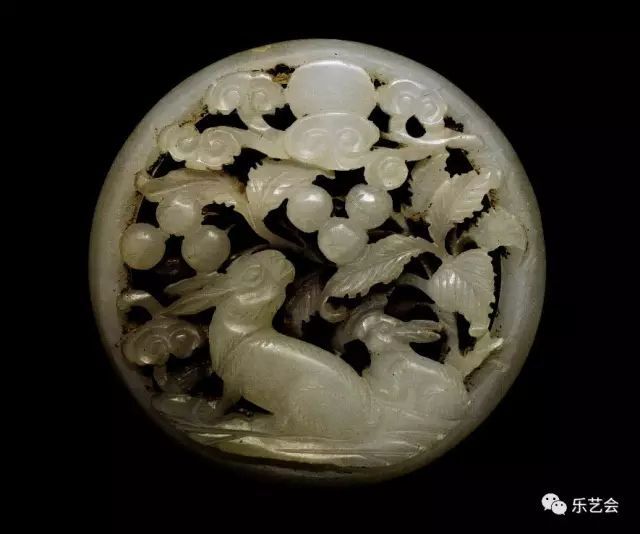
Ming Dynasty Yutu

People in the Ming and Qing dynasties believe that the "anti -insight" of rabbits will lead to "moon out", so it is more popular for the "Gu Rabbit" shape. "Anti -Gu Gu" is the design of the Yuan Dynasty Jade Rabbit as intentional and not looking at the moon; The shadow disappeared during the operation, and it means that Yutu also left the moon.

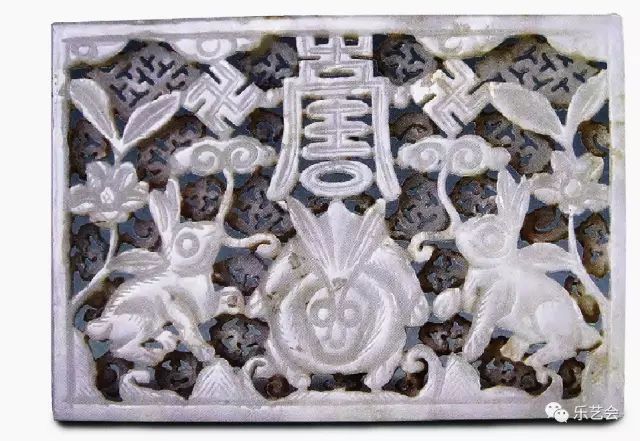
During the Song Liao and Jin period, the "Gu Rabbit" was truly believed to be the moon, and when the moon came out, it was caused by Yutu leave the moon. Therefore, the jade is a jade rabbit in the jade piece, all of which watch the moon under the moon. The Song people Zhang Dongxuan said in the "Heil Aslisa True Scriptures": "Mo Xiangyue's forward -looking jade rabbit", "There is a moon and a rabbit, each other, only the rabbits, the jade rabbit look at the moon, do not sit on the moon to see the rabbits, and the people are born. Lips, covering the opposite. " Zhang Dongxuan explained the position of the moon and the rabbit in detail. When suing the woman's conception, do not go to see the moon, or wear the pattern of the jade rabbit. If the moon is below the rabbit, the "out of the person" (born child) will form a lack of lips [just like it is just like it is like it Rabbit lips]. (Figure 17)
Figure 17 rabbit -shaped jade Pei Ming

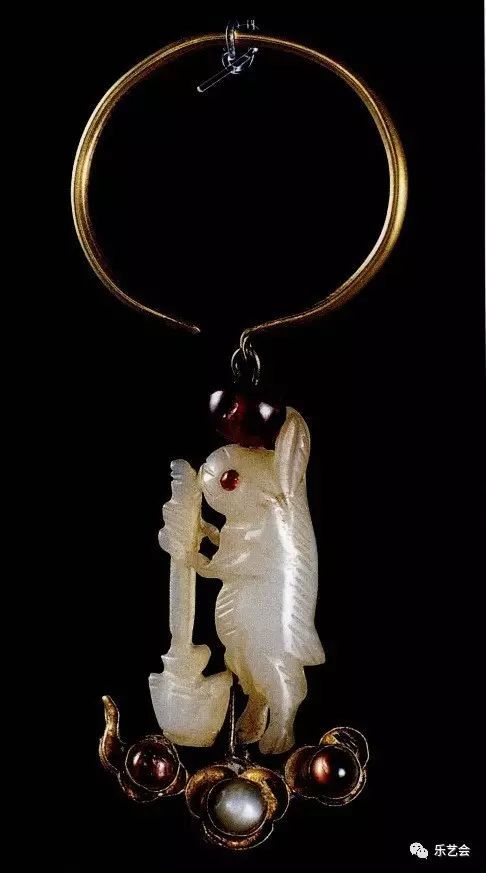
In the late Qing Dynasty, Xu Ke said in the "Circular Bank Banking and Several Class": "Mid -Autumn Festival, the Beijing Master used the clay sculpture rabbit god, the rabbit noodle person, the noodles, and the painting painted. Guijia giant rooms are purchased more, and they are supported by fragrant flowers and fruits.
There are customs in folk customs that "men do not sacrifice the moon, women do not sacrifice stoves", so the Mid -Autumn Festival Moon is generally completed by women. Children often imitate the mother's sacrifice next to them. Therefore, when children participate in the sacrifice of rabbit, they slowly evolve into the child's favorite to buy children's toys.
Rabbit shape in folk paper -cutting
The production and wearing of Jade Rabbit, even in the Qing Dynasty, belong to the played by large households. Of course, as the representative of the moon, the rabbit symbolizes the operation of the moon. The narrative form of the running is left to the feeling of being cherished, leaving human beings such as "time and the sun and the moon are like shuttle".
Figure 18 rabbit -shaped jade pendant
Since the Han Dynasty rabbits have been fairy, in addition to being familiar with the well -known mythical immortality, Yutu has also indicates that people's awakening of life consciousness. Especially the "Twelve Chapters" rabbits are recorded as monthly images in the "Three Cai Drawings" in the Ming Dynasty. It is one of the twelve chapters dedicated to the royal family for ten thousand years. The white rabbit pestle jade earrings (Figure 18) unearthed in the Ming Dingling Mausoleum are the outstanding use of this chapter pattern in the royal jewelry. Therefore, when examining these jade rabbit works, it is necessary to put them in the long river of history and pay attention to their appearance characteristics, and they must also consider their cultural connotation to achieve a more complete understanding of such jade.

Figure 19 rabbit -shaped jade pendant
This article has been authorized by the author.

The picture and text are provided by the author.

- END -
There are 8 reservoirs in Jilin Province to operate over the flood limit of floods

The reporter learned from the Jilin Provincial Department of Water Resources that ...
The scenery here is unique, and you will get in three or five friends to check in ~

In the midsummer season, driving in the Tourism Channel of Prince Mountain and the...