Can humans "eliminate" gastric cancer?The new version of the consensus pylori infection and gastric cancer are partially interpreted
Author:Digestive liver disease channe Time:2022.08.16
*For medical professionals for reading reference

A glance in the main points of the 8 statements in the consensus!
Recently, the China Gastrointestinal Magazine released the "Sixth National Cycotic Pyriotics Infection Treatment Consensus Report (Non -eraded Treatment Part)" (hereinafter referred to as the "National Six Consensus"). The National Six Consensus is compiled by many domestic scholars, referring to the latest guidelines at home and abroad, and combined with the current status and related research progress of the infection and treatment of Helicobacter pylori (HP) in my country. In order to promote the new version of the consensus better and more standardized, the Chinese Medical Association Gastrointestinal Society of the Helicobacter Pymiology Group also held a new consensus on the National Tour Lecture Council online on June 11 to improve the clinicians in this field. The standardized diagnosis and treatment level of HP infection benefits the majority of patients.
At the launch meeting, "HP and Stomach Cancer" introduced and interpreted by Professor Zuo Xiuli, Qi Lu Hospital of Shandong University. The first time this article summarizes the problems facing HP and gastric cancer, the academic focus of consensus, etc. for your reference and learning.
Expert Introduction

Professor Zuo Xiuli
Member of the Helicobacter Society of the Chinese Medical Association Gastrointestinal Society
Qilu Hospital of Shandong University
HP and gastric cancer: National Six Consensus vs National Five Consensus
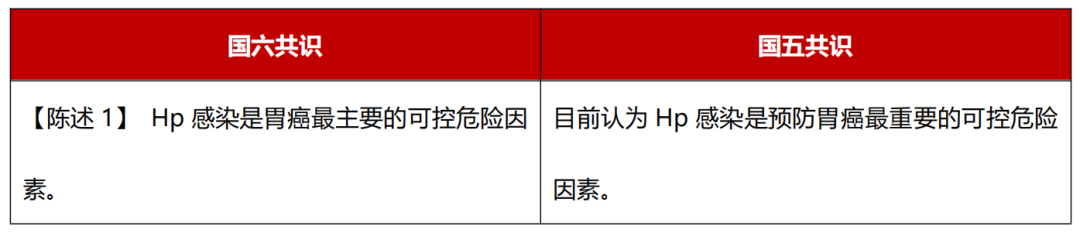
Level of evidence: high; recommendation intensity: strong; consensus level: 100%.
The new version of the consensus is more actively affirming that HP infection is the most important controllable risk factor for gastric cancer in China. In my country, non -cardia gastric cancer and cardia gastric cancer are related to HP infection.
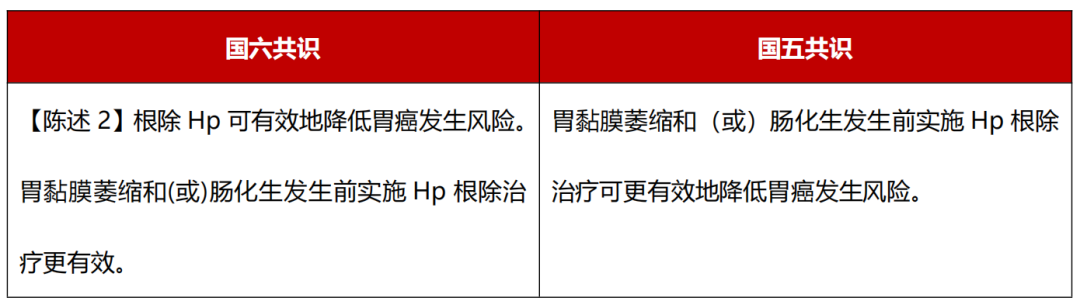
Level of evidence: high; recommendation intensity: strong; consensus level: 100%.
Based on the evidence updated in recent years, the National Six Consensus proposes that eliminating HP can effectively reduce the risk of gastric cancer. In the individual of gastric mucosal atrophy and/or bowelization, HP prevents gastric cancer in the individual. Its effect is better than individuals with gastric mucosa atrophy and/or intestinalized. Elimination of HP can improve the sexual reaction of gastric mucosa, prevent or delay the occurrence and development of gastric mucosa atrophy, bowelization, and partial reverse atrophy and bowelization.
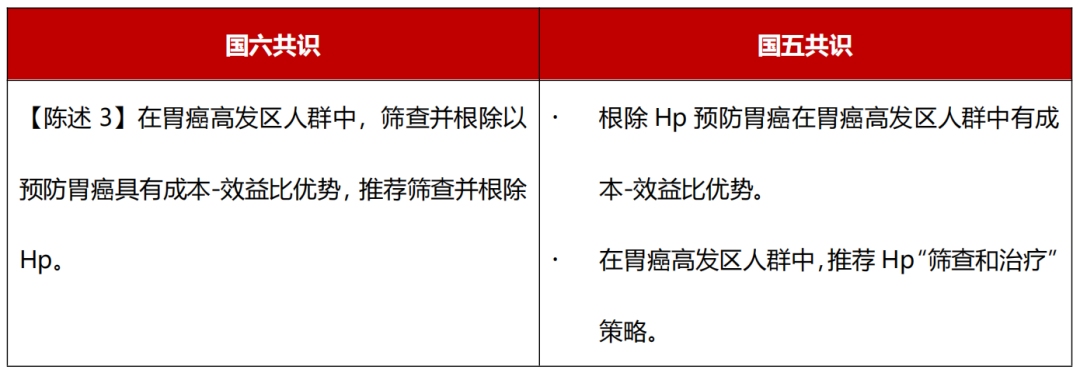
Level of evidence: medium; Recommended intensity: strong; consensus level: 100%.
"Prevention of Gastric Cancer: Global Consensus in Taipei, China" defines the incidence of gastric cancer> 20/(100,000 years) as a high incidence area for gastric cancer. The National Six Consensus will merge the two recommendations of cost-effectiveness ratio and gastric cancer high incidence zone to remove the two recommended opinions of HP. It actively affirms the screening of HP to prevent gastric cancer in the high incidence area of gastric cancer. It can also prevent HP -related digestive ulcers and indigestion.
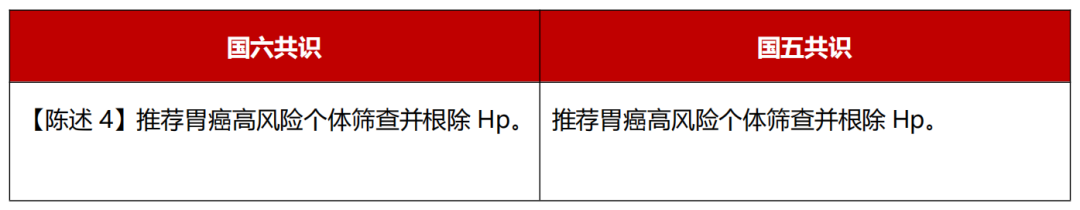
Level of evidence: medium; Recommended intensity: strong; consensus level: 100%.
Patients with gastric cancer, first -level relatives, have confirmed that gastric mucosa atrophy and/or bowelization, gastric cancer high incidence areas or other gastric cancer risk factors (including intake of high -salt/fried/pickled diet, cigarettes, severe drinking), early early) Gastric cancer ESD is defined as high -risk individuals with gastric cancer after treatment.
In addition, age is the independent risk factors of gastric cancer, and the risk of gastric cancer increasing increases with age; in addition, research in Hong Kong in China shows that compared with the general population, people over the age of 60 have a significant reduction in the risk of gastric cancer after treatment. The treatment time is layered, and the risk of gastric cancer for more than 10 years of treatment has been significantly reduced. Studies believe that the effect of the elderly and individuals who develop root treatment as soon as possible, HP root eradication has a significant effect on reducing the risk of gastric cancer [2].
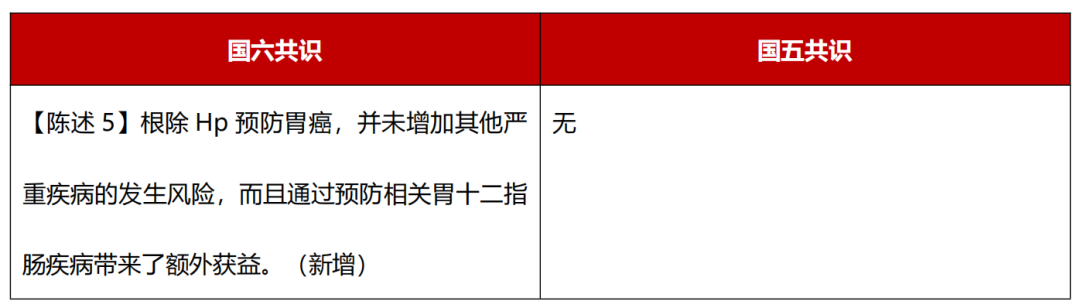
Level of evidence: medium; Recommended intensity: strong; consensus level: 95%.
The long-term follow-up studies of large samples of Lintong in Shandong and Matsuyama, Taiwan have confirmed [3-4] to regulate the risk of eliminating HP to reduce gastric cancer and did not bring serious adverse consequences. For the first time, the new version of the consensus emphasizes that eliminating HP can not only prevent gastric cancer, but also reduce the risk of HP -related digestive ulcers, indigestion and other diseases, and eliminating HP in young adults can also reduce the risk of spreading to Zizai. In addition, the risk of eliminating HP does not increase the risk of gastroesophageal reflux and metabolic syndrome.
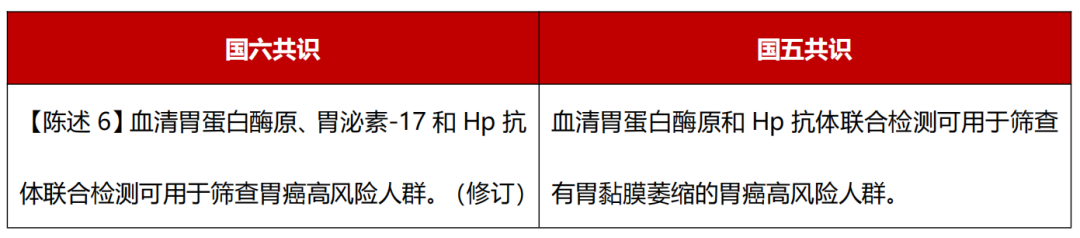
Level of evidence: medium; Recommended intensity: strong; consensus level: 86%.
The Sixth Consensus adds gastrin -17 This serum learning indicator. "Serum biopsy" is a group of serum learning tests including gastric protease (Ⅰ and Ⅱ), gastrin-17, and HP antibodies. Atrophy). Non -invasive serum science screening can be used for screening for high -risk people with gastric cancer.
Chinese scholars have designed and verified the risk of gastric cancer-based gastric cancer-based (HP antibodies, PG, G-17), and dietary habits based on age, gender, serum, and serum indicators (HP antibodies, PG, G-17), and 70.8%of patients with gastric cancer are high-risk groups. [5] The combination of serum science screening and endoscopic examination will help improve the level of prevention of gastric cancer.
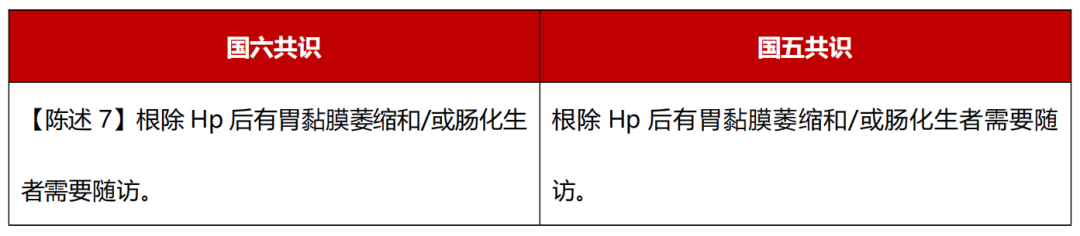
Level of evidence: low; recommendation intensity: strong; consensus level: 98%.
The gastric mucosa atrophy and/or intestinal chemotherapy cannot completely eliminate the risk of gastric cancer after the HP is eliminated. It needs to be followed up with a regular endoscopic. The interval between the follow -up should be determined according to the scope and degree of the pre -cancer lesions and the patient's wishes. The scope of atrophy of endoscopy and/or bowelization and its severity can be judged according to the Kyoto endoscopic gastritis classification system. Pathological tissue evaluation can be scored according to the OLGA or Olgim. Monitoring of lesions. Level of evidence: high; recommendation intensity: strong; consensus level: 97%.
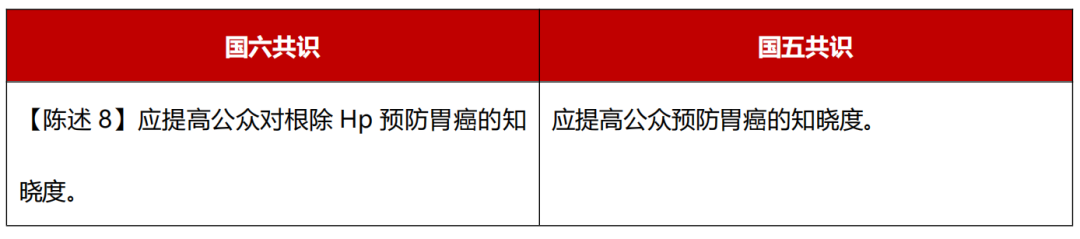
The new version of the consensus more actively affirmed the importance of strengthening the public's awareness of hp to prevent gastric cancer, and put forward the way to improve public education: improving government attention, strengthening public media propaganda and grass -roots health education, correctly guided the public to HP harm and HP harm and Cognition of other gastric cancer risk factors. Valid vaccines may be the best measure to prevent and control HP infection.
In summary, the National Sixth Consensus emphasized that HP infection is the most important controllable risk factor for gastric cancer. It also actively affirmed the screening and eradicating HP's benefits to patients. At the same time, it is recommended to improve public education and strengthen the public to eliminate HP to prevent gastric cancer. know.
references:
[1] The Chinese Medical Society Gastrointestinal Gate screwbacter pylori (HP) academic group. China Gastrointestinal Magazine. 20122 42 (5): 289-303.
[2] Leung WK, Wong IOL, Cheung KS, et al.Gastroenterology, 2018,155 (1): 67-75.
[3] Chiang Th, Chang wj, Chen SL, et al.Gut, 2021,70 (2): 243-250.
[4] PAN KF, ZHANG L, Gerhard M, et al.Gut, 2016,65 (1): 9-18.
[5] Cai Q, zhu C, Yuan y, et al.Gut, 2019,68 (9): 1576-1587.
- END -
Please note that the medical insurance service hall in Jinan is relocated

In order to further improve the service level of medical insurance and provide con...
Announcement on the trajectory of 70 newly added new crown pneumonia -free infection in Dongxiang County

On July 27, 70 newly added new crown pneumonia in Dongxiang County had all transfe...