How does the crust do?Scientists have already discovered new discoveries, making us feel novelty
Author:Astronomy online Time:2022.08.21
Where did the crust of the earth go?
The modern sector structure may only begin in the past one billion years.
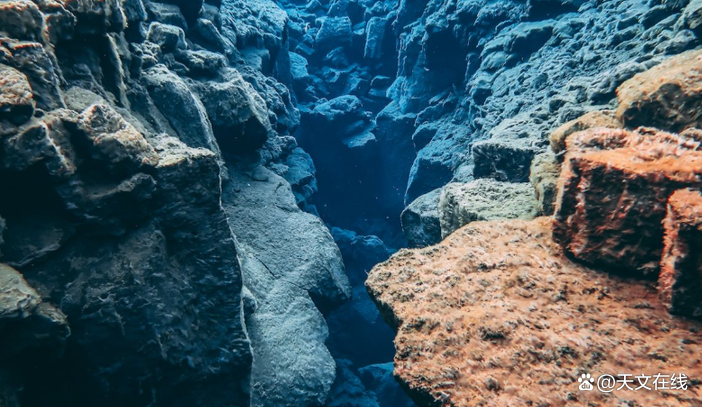

Silfra Hall between the two constructing sectors of Iceland.
Just like a huge pieces of fragmented biscuits floating on the hot milk sea, the shell of the earth is composed of (not so delicious) rock rafts. They are constantly colliding and squeezing each other. This process is called the plate structure.
So what happens when these disappearing crusts sneak into the milky white interior?

The new model shows that they become fragile and bent, like a spring snake toy, but they are not completely decomposed. These models also show that considering the modern sector form, the structure of the plate may only begin in the past one billion years.
The structure of the sector promotes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, creating mountains and islands. At the same time, the continent of the earth that was once a whole block is now separated by the ocean. However, there are still many unknown how to operate the structure of the sector. For example, when one section slips to the other (a area called a dive zone) and disappears in the mantle, what will happen? Squeezing each other is not as smooth as the milk said in the metaphor.
In order to figure out this, the researchers used the dive band's 2D computer model, and used the known material behavior physics to program them, such as how rocks deformed under certain force. Then they observed the model to understand what happened in the surgery band and compared their discovery with the observation results in real life.
Their model shows that when one section dives under the other section, the descending plate will suddenly bend and break down. Bending also causes the grains on the bottom of the board to become thinner and weaker. The pressure makes the plate above basically intact, but there are many fragile places.
This means that the sector will not be split, so they will continue to drive their remaining parts. The main authors and Taras Grya, a professor of Earth Physics at the Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, Switzerland, said that one section can decline for hundreds of millions of years in another section.
GERYA told Live Science that their simulation results match the observation and deep earthquake imaging in the weak area of the Japanese dive band.
KENT CONDIE, a School of Mining and Technology, New Mexico, and a honorary professor of Earth Chemistry, Earth and Environmental Sciences. He did not participate in the study, but said that their models were "stable and meaningful."
When does it begin?
The team also simulated what happened if the temperature inside the earth increased by 270 (150 degrees Celsius), similar to a temperature about 1 billion years ago.

They found that in these simulations, the sector only ruptured in a few miles in the mantle, because of the hot conditions, it could not maintain its own weight in a lower sticky mantle. Therefore, unlike modern dives that can last hundreds of millions of years, the dive at that time ended quickly within millions of years, GERYA said.
He added that the discovery showed that the modern sector structure may not start at some time in the past one billion years.
GERYA said that although the original form of the sector may exist from 3.5 billion to 2 billion years ago, it may be very different from the Earth's experience today in the ancient universe or the ancient Yuan Dynasty. About 1.8 billion to 1 billion years ago, there was a quiet period, and the activities of the sector were much less.
But this is just guessing. He said that there are many controversy when the structure of the sector starts.
Condie agreed with Gerya's view. "Modern sector structure with all geological indicators ... may not start until the last one billion years," Condie told LIVE Science. But "starting at least 2 billion years ago, a form of sector structure has been accompanied by us."
Condie said that despite this, because we do not know the exact temperature of the core of the earth over time, it is impossible to give an accurate timetable to explain when the sector stops splitting and starts to enter the mantle more continuously.
Gerya said that this is indeed the beginning of the modern sector structure. Researchers now want to use more advanced 3D models to explore this phenomenon and their relationship with the earthquake.
related information
The crustal is in geography. It refers to a solid shell on the outermost layer of the planet, which can be different from the mantle with chemical methods. Most of the crusts of the earth, the moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, and other planet are formed by fire. The crusts of the planet have more incompatible compatible compatibility than their mantles.
By: Yasemin Saplakoglu
Fy: Starry
If there is related content infringement, please contact the author to delete after the work is released
Reprinted, please obtain authorization, and pay attention to maintaining integrity and indicating the source
- END -
Qingzhou Yidu Street Party Construction Leading "Five Steps" work method Promote the strong foundation

In order to solidly promote the five Qingqiangji's turn to look back and continue ...
From 7:00 on July 20th, Chenghua District will carry out the third round of full -member nucleic acid testing within the area under its jurisdiction

Announcement of Chengdu Chenghua District on the third round of full -member nucle...