86%of Chinese female lung cancer patients do not smoke!Reveal the five major influencing factors
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.08.29
For medical professionals for reading reference

2022 WCLC Voice of China Heavy Study Interpretation
Smoking is a recognized carcinogenic factor. In recent years, the incidence of lung cancer without smoking women has attracted more and more attention. "Among the Chinese population, the proportion of lung cancer without smoking is gradually approaching smoking male lung cancer." Professor Guo Lanwei, Henan Cancer Hospital, at the 2022 World Lung-Cancer Conference (WCLC) conference. SMOKERS revealed this phenomenon and built a risk prediction model of non -smoking female lung cancer.
The "Medical Tumor Channel" specially invited Professor Guo Lanwei to share the current status and predictive models of non -smoke -absorbing female lung cancer.

Scan the two -dimensional code above, get WCLC cutting -edge information and expert views
In China, 86%of female lung cancer is not because of smoking!
In China, the incidence and mortality of lung cancer ranks first in the incidence of malignant tumors and mortality. Data from epidemiological research show that about 53%of female lung cancer worldwide cannot be attributed to smoking, and among Chinese female lung cancer patients, this ratio is 86%.
Exploring the high -risk factors and prediction models of patients with non -smoking female lung cancer will help further screen high -risk population, and provide important reference and intervention basis for early screening, early diagnosis, and early treatment of lung cancer.
Professor Guo Lanwei collected 1,51834 cases of lung cancer from October 2013 to October 2019, and used multi-variable COX regression analysis to determine the relevant risk factors, and established a risk prediction line map. The high -risk factors, prediction results, sensitivity and specificity of this model are as follows:
The study evaluates the age of patients' age, chronic respiratory disease, family history of first -level relatives, menopause, and a history of breast benign disease.
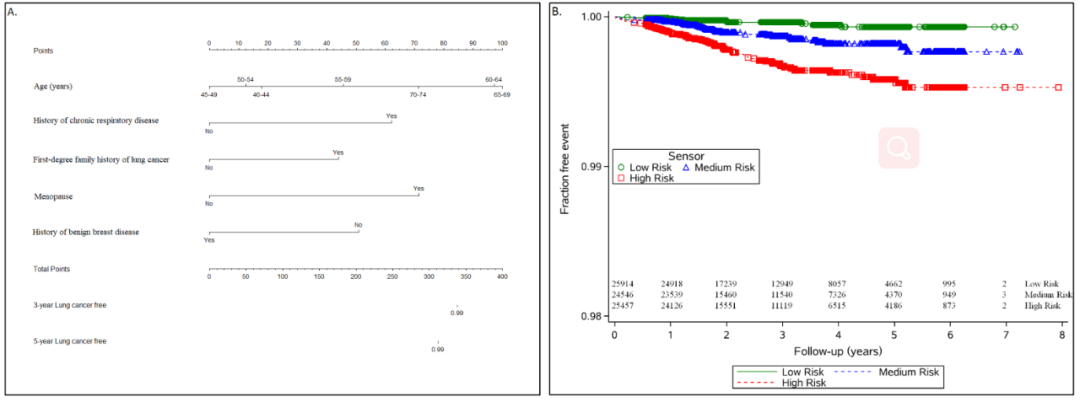
Figure A: Forecast of the risk of lung cancer within 1, 3, and 5 years; Figure B: The incidence of lung cancer in different risks
Professor Guo Lanwei said: "Based on these five prediction factors, we have drawn the risk prediction line diagram of lung cancer risk for 1 year, 3 years, and 5 years. 0.703, all greater than 0.7, this model shows a good distinction. "
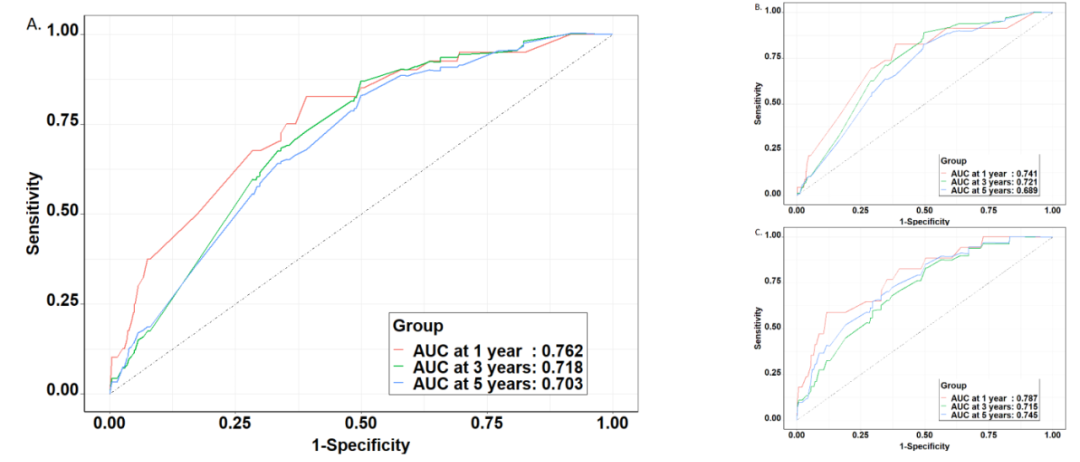
This model is in the overall crowd (A), non -smokers (B), and smokers (C).
Q1: Among the Chinese population, the proportion of non -smoking women's lung cancer is gradually approaching smoking male lung cancer. What are the reasons for this phenomenon?
Professor Guo Lanwei: The burden on the disease of non -smoking women's lung cancer is becoming increasingly serious. Compared with smokers, the determination and intervention of high -risk factors is more important.
Popular disease research has found passive smoking, previous lung diseases such as tuberculosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), etc., indoor radiation (such as soil and rocks, building materials, living water, natural gas and coal The burning of burning), the exposure of oil fume and the family history of the first -level relatives of lung cancer are correlated with non -smoking female lung cancer.
In general, although the above factors show the weakness to the moderate correlation, the main causes of non -smoking women suffer from lung cancer have not been found.
For the means of lung cancer screening, the "Guidelines for China Cancer Screening and Early Diagnosis and Early Treatment" strongly recommends the use of low -dose spiral CT (LDCT) for lung cancer screening. It is not recommended to use chest X -ray examination for lung cancer screening.
This is because domestic and foreign studies have shown that LDCT can significantly increase the detection rate of lung cancer (especially phase -stage Ⅰ lung cancer) while reducing the mortality of lung cancer; although X -ray chest tablets have a certain diagnostic value for lung cancer, but because of its sensitivity, its sensitivity is more compared Low, not suitable for lung cancer screening.
Q2: What major significance do you think this study reports for lung cancer prevention screening and diagnosis and treatment?
Professor Guo Lanwei: Data from epidemiological research shows that about 53%of women's lung cancer cannot be attributed to smoking, and the proportion of Chinese women is 86%. In addition, the exposure of the risk factors of Chinese women's lung cancer and the laws of onset have their own characteristics. The most important thing is that although the smoking rate of women is far lower than that of developed countries in Europe and the United States (China and the United States smoking rates are 2.4%and 23.6%, respectively), the incidence of lung cancer is the incidence rate Closer to (the incidence of lung cancer based on the world's population -based population is 228/100,000, 30.4/100,000, respectively).
This suggests that the current international lung cancer screening based on smoking is not applicable to Chinese women, especially non -smoking women. For non -smoking women, lung cancer screening should be avoided in the early diagnosis, misdiagnosis, and excessive diagnosis and treatment of early diagnosis, so that the screening can be maximized.
However, the development of my country's medical technology level is unbalanced, the early diagnosis of cancer is difficult, the technical requirements are high, and the objective, effective, and easy -to -handed diversion management tools are to help improve the diagnostic ability of grassroots physicians and improve the medical services of grassroots cancer screening. Sexuality and promotion of the foundation of high -quality cancer screening and early diagnosis services.
Therefore, based on China's large -scale lung cancer screening project, this study has developed a simple risk prediction model of lung cancer among non -smoking women and has been verified in internal population. The results show that the model has a good ability to distinguish. After passing external verification, it can be used as a tool to condense high -risk population for non -smoking women in the future, thereby increasing screening income. Q3: Based on the results of the research, what are the aspects of lung cancer screening?
Professor Guo Lanwei: The "Guidelines for China Cancer Screening and Early Premature Treatment" released by the National Cancer Center last year strongly recommended the use of predictive models to determine high -risk groups of lung cancer. And for the judgment of high -risk people in lung cancer, in addition to the current classification standards, it is recommended to establish a risk predictive model based on the data of Chinese population, a risk score of lung cancer, and improve the accuracy of the scope of lung cancer screening.
In the context of accelerating the strategy of "Healthy China Action", the State Council has clearly stated that it is necessary to strengthen early screening of malignant tumors, formulate and promote technical guidelines, expand the scope of screening in an orderly manner, and strive to enable residents to suffer from cancer and cancer, and improve the quality of life.
For ordinary people, the risk of lung cancer is evaluated to understand whether it has risk factors for lung cancer. It is necessary to perform lung cancer screening.
Last year, the National Cancer Center developed the "Chinese Residents Cancer Prevention and Control Action" mini -proceedings, which can realize the evaluation of cancer risk factors including lung cancer, including lung cancer, and provide targeted treatment opinions. After completing the assessment of the risk factors of cancer, according to the results of the evaluation, residents can make an appointment for national free public welfare screening services or make an appointment for self -funded screening by "Green Constitution Screening".
Expert Introduction
Professor Guo Lanwei

Henan Cancer Center
Henan Cancer Hospital
Henan Province Tumor Prevention Research Office
PhD in the Department of Medicine of Tsinghua University/Beijing Union Medical College
Master's tutor of Zhengzhou University
Youth Member of the Statistical Group of the China Clinical Oncology Society (CSCO)
Chinese lung cancer/breast cancer/colorectal cancer screening and early diagnosis and early treatment guideline work group
Member of the Youth Learning Group of the Fortuita Disease Branch of China Medical Care International Exchange Promotion Association
Cancer Innovation Magazine's first Youth Editorial Committee
Outstanding Young Talents of Health and Health Technology Innovation
Member of the Beijing Health Promotion Association Clinical Research Expert Committee
Member of the Professional Committee of Tumor Prevention and Control of Henan Province
Member of the 5th Medical Ethics Committee of Henan Cancer Hospital
Hosted the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Provincial Natural Science Foundation, and the Provincial Science and Technology Reach Project
Published more than 30 SCI and Chinese series papers with the first author/communication author
Participate in the nine parts
Won the first prize and second prize of Henan Province Science and Technology Progress
The first release of this article: the medical world tumor channel
Author: oolong tea
Editor in charge: Sweet
- END -
Huimin County Baojin Organization People's Congress representative inspections

In order to conscientiously implement the supervision of people's livelihood and k...
One state -owned enterprise employee shows up the rich show in the background: drinking 200,000 pounds of tea, he and his father are "Yan Song Yan Shifan" ... official notice

Recently, a set of screenshots of a group of friends involving showing wealth and ...