Global epidemic changes in liver cancer: NASH is the "culprit" with the fastest growing liver cancer
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.07.07

Written article | Enigma
#Liver cancer#
In recent years, with the increase in drinking, the increase in obesity, and the progress of the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV), the epidemic disease of liver cancer is constantly changing. However, the impact of these changes on the burden on global liver cancer is unclear.
Recently, the ROHIT LOOMBA research team of the University of California in the United States published a report entitled Changing Global Epidemiology of Liver Cancer FROM 2010: Nash is the FASTSEST GROWER CAUSER CAUSER CAUSER CAUSER CAUSER CAUSERASER CAUSERASERIVERISM report. It assesss the time trends of the burden on liver cancer and various causes of liver disease in the world. Studies found that from 2010 to 2019, the number of liver cancer deaths increased by 25%. Among them, age standardization mortality (ASDRS) has risen in the Americas, while maintaining stability or decline in all other areas. And during this period, non -alcoholic fatty hepatitis (NASH) and alcoholic hepatitis ASDRS increased the fastest, while HCV and HBV ASDRS declined. Therefore, the global (especially the Americas) takes first -level emergency measures to deal with potential metabolic risk factors and slow down the increasing burden on NASH -related liver cancer.

Liver cancer is the third largest cause of death in the world. The main causes of liver cancer include hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), alcohol and non -alcoholic fatty hepatitis (NASH). In the past ten years, the burden and cause of liver disease have changed a lot. The increase in the coverage of hepatitis B vaccine and the widespread use of antiviral therapy have reduced the burden on hepatitis B virus -related liver cancer globally. Since 2014, safe and effective oral antiviral drugs can be used for HCV, which can also significantly reduce the risk of liver cell carcinoma (HCC), although HCV treatment has no clear impact on global liver cancer burden. The growing economic wealth has promoted the increase in per capita alcohol consumption in the world, which may increase the burden on liver cancer related to alcohol. Finally, in the United States, Europe, and Asia, the prevalence of NASH has also increased simultaneously with obesity and diabetes, resulting in a significant increase in the incidence of liver cancer related to NASH. However, the recent relevant global data analysis is still lacking. In the past, the research on liver cancer epidemiology was mainly concentrated in national, regional or diseased data. Therefore, the data updated from a global perspective is limited.
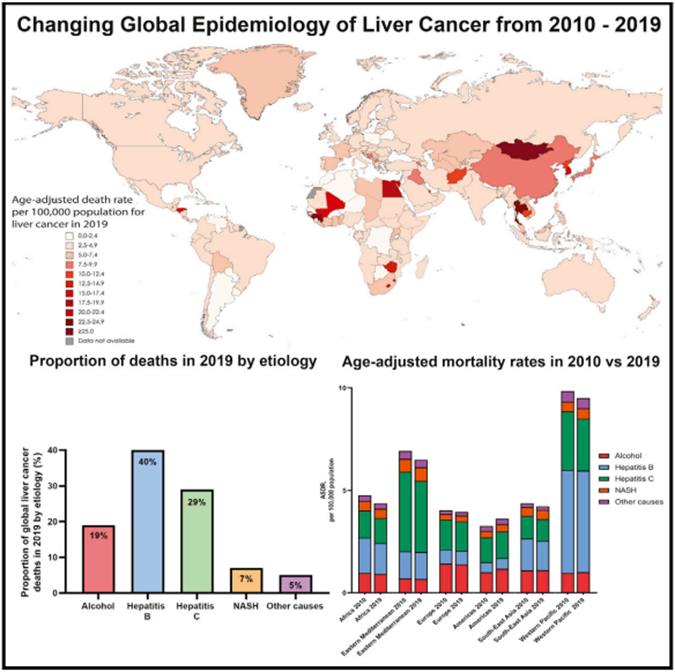
In this study, the author first compared the frequency of liver cancer in the global and different WHO regions through statistical analysis in statistical analysis, and found that it increased significantly in 2019. Next, by analyzing the trend of changes in the frequency of liver cancer death from 2010 to 2019, it has shown an increasing trend. In 2019, the incidence, mortality and DALYS of liver cancer cases in the Western Pacific. From 2010 to 2019, the America's incidence (+41%), the number of deaths (+42%), and DALYS (+36%) increased the largest. In addition, the analysis diagram of the contribution rate of global liver cancer in various regions in 2019 also confirmed this conclusion. Further, the author found that the Americas had increased significantly by analyzing the age standardization accident rate (ASIRS) in 2010-2019. The West Pacific and Europe remained stable, and all areas of WHO declined, of which Africa decreased the largest. Similar age standardization mortality (ASDRS) analysis found that the Americas still increased, the Western Pacific remained stable, while all other areas of Europe and WHO declined, and Africa decreased the largest. The results of age standardized disability adjustment of life (Asdalys) analysis showed that the Americas still increased, and the Western Pacific remained stable, while all other areas of WHO declined, among which the central Mediterranean was the largest.
Subsequently, the author analyzed the burden on liver cancer according to the social population index (SDI), and found that the incidence, mortality, and DALYS in 2019 occurred in countries with a medium SDI. From 2010 to 2019 SDI countries, while mortality, ASDR and ASDALYS occurred in low -to -middle SDI countries. The maximum declines of ASIRS, ASDRS, and Asdalys occurred in low SDI, medium -high SDI and high SDI countries, respectively. The study of the cause of liver cancer disease shows that in 2019, hepatitis B virus accounts for 40%of global liver cancer deaths, followed by hepatitis C virus (29%), alcohol (19%), NASH (7%), and other reasons (5%). From 2010 to 2019, NASH is the world's fastest -growing cause of liver cancer (+39%), while HCV growth is the lowest (+23%). Similarly, NASH is the cause of fasting growth of liver cancer (+38%), while other reasons increase (+21%). ASDRs related to NASH -related liver cancer have increased in the Americas, East Mediterranean, West Pacific and Europe, of which the Americas have increased the most. From 2010 to 2019, the increase in SDI moderate liver cancer ASDR was mainly due to the increase in NASH. Similarly, in the low -level countries in SDI, the increase in ADSR is driven by Nash, alcohol and HCV. In contrast, ASDRS, low, medium, high, and high SDI countries, due to HCV, HBV, and other reasons. In general, this study reported the incidence of liver cancer, mortality, mortality, disability adjustment of life (DALYS) in 204 countries from 2010 to 2019. It shows that NASH is the "culprit" that has led to the fastest growing liver cancer in recent years.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.20222.05.003
Want to know more exciting content, come and pay attention to BIOART biological art


- END -
Xinjiang Kashgar Army Division: Recruits under the "first lesson" red education cast loyalty
Video/Snapshot, T_100, F_JPG, M_fast Controls = Controls data-version/ueditor/video/mp4/20220626/1656179102397.mp4 transcoding = 1 style = width: 400px; After three months of rolling,
Meet the charm lotus to share the fishing feast
Video/Snapshot, T_100, F_JPG, M_fast Controls = Controls data-version/ueditor/video/mp4/20220622/1655861705649347.MP4 transcoding = 1 style = width: 400px; Meet the charm of the lotus