"Mount Everest" in bacteria appeared!As long as 2cm, visible to the naked eye!
Author:Science popularization China Time:2022.07.09
Produced: Popular Science China
Author: EVEE (School of Life Sciences, Peking University)
Producer: China Science Popularization Expo
If you just glance at a roughly glance, the slightly turbid water in the test tube seems to be no different from the water in the stagnant pond. Among them, there are mixed leaves, sediments, and some thin "silk threads", but if you look closely, these filaments are generally generally shredded. The objects actually floated above the leaves, swinging in the water ...
Is it a parasite? After all, linear parasites are very common in the water, but when scientists get this "thin line" under the microscope, everyone is surprised -these filamentous objects are actually a single bacterial cells visible to the naked eye!

Giant bacterial rendering picture source: scitechDaily.com
Unlike everyone's impression of bacteria on weekdays: the individual is small, most of which can only be seen under the microscope. The cell structure is simple. The bacteria discovered by scientists this time can be called the "giant" of the bacterial industry.
1. The centimeter -grade bacteria visible to the naked eye
In June 2022, the well -known journal "Science" published a research on bacteria. Scientists newly discovered a bacterial species CA.thiomargarita Magnifica, about 0.9 cm long, and the longest one can reach 2 cm. Such a size can be said to be the giant in the bacterial circle. You must know that most bacteria are micron -level, and 1000 microns are equal to 1 mm. This bacteria is 5,000 times larger than most bacteria. You may not have one. Very intuitive impression, for example, this is like a person who meets another person who is as tall as Mount Everest, and instantly judged.
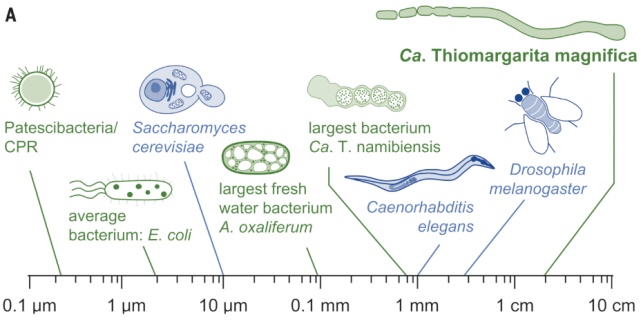
Comparison of giant bacteria and other common creatures: References
From a morphological point of view, this bacteria are white silk, gradually shrinking from the base to the top, forming spores, smooth overall vision, no enchant bacteria. Interestingly, each filament is a separate cell, and there is no split diaphragm in the middle. Except for the top spores at the top of the top, the main body of the filament is separated from the filament.

Giant bacterial morphology picture Source: reference literature
There is no doubt that this is the biggest bacteria found so far, but this is just a distinctive aspect of T.MAGNIFICA. What truly subverts scientists is recognized that the genetic material of this bacteria is packed by the membrane structure.
Second, it is bacterial, but not like bacteria
科学家和这一巨型细菌的邂逅发生在加勒比海的红树林中,他们发现一些白色的细丝附着在叶片沉积物上,但一开始科学家们并未留意这些细丝,只是觉得它们有些奇怪,便No follow -up research, this delay is more than 10 years.
Finally, the scientists of Huiyanzhu found that these white filaments were different and conducted in -depth research. They did not think that this would be a bacteria at first, because these filaments were visible to the naked eye, and they were more like a genuine creature. It was not until scientists who sequenced the 16S 16S ribosome RNA before it was confirmed that this was it. A bacterial.
(Note: 16S ribosome RNA, referred to as 16S RRNA, is part of 30S subunit in the nuclear sugar of prokaryotic creatures. The three types of nuclear categories of nuclear creatures are 5.8S RRNA, 18S RRNA, and 28S RRNA, and there are no 16S RRNA).
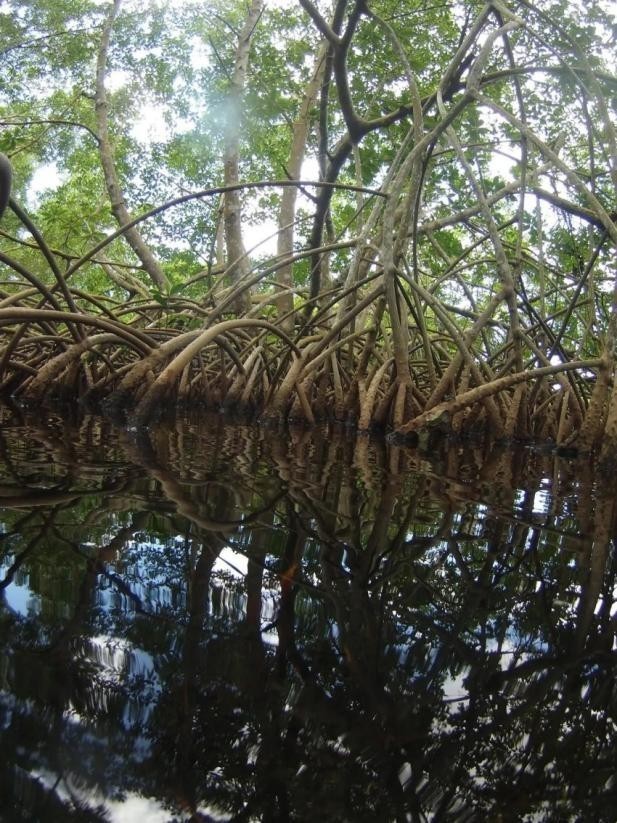

Finding giant bacteria mangrove pictures source: scitechDaily.com
But with the deepening of the research, scientists began to wondering again. The results of 16S RRNA showed that this giant was undoubtedly bacterial, but when they used co -focus laser scanning microscopes and transmitted electron microscope to observe the film structure of these bacteria, there were again, and there were again. Amazing discovery. The genetic material of these bacteria was actually wrapped in the membrane!
Everyone has learned in biological textbooks: bacteria have no nuclear membrane, only parts where genetic material concentration is concentrated. T. Magnifica is not like other bacteria, allowing genetic materials to float freely in cytoplasm, but wraps them in a membrane structure in a membrane structure This is similar to those more complex cells, such as animals or plants. Scientists refer to these cycling cells with genetic materials "PEPINS".
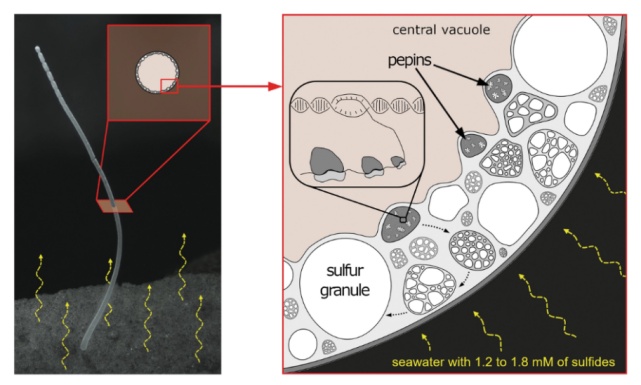
PEPINS picture source in giant bacteria: References
The genetic material in the cycling of the membrane bag in T.Magnifica subverts people's cognition and blur the boundaries between the eukaryotic and prokaryotic creatures!
Third, why can giant bacteria grow so big?
In the academic community, people think that bacteria lack an active intracellular transportation system, which mainly depends on chemical diffusion, which limits the cell shape of cells. In short, the reason why bacteria are so small is that as its size increases, the growth of bacterial cells' physiological or metabolic needs exceeds the range that cells can maintain.
So why can giant bacteria grow so big? This also starts with the complexity of giant bacteria. In addition to the above two different characteristics, the complexity of this giant bacteria is far exceeding other bacteria. The results of the genome sequencing show that T. Magnifica's genome is very large, which is about three times that of our common bacteria. It has 10 million base pairs and contains about 11,788 genes. Giant bacteria have a huge and complex genome picture source: References
Not only that, because PEPINS is widely distributed in giant bacteria, each PEPINS has a set of genome copies, so this giant bacteria is actually a multi -twice (cells contain three or more chromosomes in chromosomes in the cells. For it, for individuals with more than three sets of chromosomes. For, for individuals with more than three sets of chromosomes. This giant bacteria has more than three sets of genome copy) and multiple sets of genetic materials. Scientists detect active protein biological synthesis activity in the PEPINS region. Although the bacteria have a large size, as long as the number of PEPINS is large, they can still meet the needs of metabolic activities.
In addition, T.magnifica bacteria also have a large liquid foam of about 73%of the total volume, and the liquid bubbles are continuously distributed along the entire filament, which makes the cytoplasm restricted in the periphery of the cells. This makes giant bacteria more convenient during material transportation, and even if the body is huge, it can maintain life activities.
Giant Bacterial Central Light Bubble Picture Source: References
I have to say that for more than a century, the cognitive deviation of the size of the bacterial body shape has made people turn a blind eye to giant bacteria. There is no doubt that these giant and complex bacteria are likely to exist in obvious places. Interpret and explore the mystery behind biological complexity.
references:
Volland, J. M., Gonzalez-Rizzo, S., GROS, O., T., T., Ivanova, N., Schulz, F., ... & Date, S. V. (2022). A Centimeter-Long Bacteri DNA CONAINED In metabolicalide active, membrane-break organelles. Science, 376 (6600), 1453-1458.
- END -
Seeing too much "bear children", now there is another "bear parent" and lost the baby on the high -speed rail ...

At the beginning of the summer vacation,Children who appear on the high -speed rai...
Strengthen forestry harmful biological monitoring and maintain ecological environmental safety

On June 17, the Altai Mountain State -owned Forestry Administration Altay Branch a...