Type I interferon signal to regulate small gel cells in DS and AD
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.07.10

Responsible editor | Xi
#Neuroscience and brain science#
Small gum cells are essential in the cause of brain development and Alzheimer's disease (AD). Small glue participates in maintaining the steady -state and neurons of the brain environment, thereby regulating the synapses, and learning and memory. In addition, small glue cell dysfunction is the central mechanism of AD etiology. Many AD risk genes are highly expressed in small glue cells, and some risks are only expressed in small glue cells. Therefore, the treatment target with small glue cells has great potential in improving the brain development and therapeutic AD in improving the Tang's syndrome (DS). However, the exact effect of small gel cells for DS's brain development and DS patients with AD (hereinafter referred to as DSAD) and the potential molecular mechanism knows very little, which hinders the development of treatment.
DS is caused by the three -twice body (HSA21) of Humans 21. An extra HSA21 leads to abnormal brain development and early occurrence, high -round AD. But how does the extra HSA21 affect the function of small glue cells during the DS brain development? In addition, the association between DS and AD is mainly due to the expression of amyloid -like preparatory protein (APP), and its gene is located on HSA21. The gathering of β-starch-like protein (A) in the DS crowd is very early, and some literature has shown that it has begun during childhood. By the age of 35-40, the pathological changes of TAU were observed in the hippocampus of DS patients. Although the accumulation of β-starch-like protein (A) is recognized by the gathering of TAU, recent studies have found that TAU protein excessive phosphorylation (P-TAU) and the time that gathered in AD human brain appeared much earlier than previously thought that what I thought before was considered as before. Essence For example, the hippocampus brain area shows a small amount and relatively late accumulation of A. At the same time, P-Tau has accumulated from early AD. In addition, the conclusions of AD and DSAD human brain tissue pathology and mouse model analysis are often contrary. For example, the small gel cells reported in the starch-like protein mice model are significantly activated. In the brain tissue of AD patients, especially the sea-horse area that is specially related to the development of AD Positioning with severe malnutrition (DYSTROPHIC) and senescent rather than activated small glue cells. In DSAD, small glue cell tables change with age and AD pathology, and the number of small glue cells in malnutrition and aging state has increased. Therefore, in some important brain areas, the priority accumulation of P-Tau compared to A plaque may induce different small glue cell reactions. These reactions may be more than just activation and inflammation. In addition, what role does the genes on the HSA21 play in this small glue change?
2022年7月7日,罗格斯大学江鹏研究团队在Cell Stem Cell上发表了Type-I-interferon signaling drives microglial dysfunction and senescence in human iPSC models of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease论文,利用人诱导多能Human IPSC's brain organs and chimeric mouse models reveal the HSA21 -encoded I type I interferon receptor (IFNAR) play an important role in the DS brain development process and the response to the pathological TAU. IFnars can improve the abnormal function of DS gel cells and prevent its aging. Research evidence in the body provides a new model for studying the aging of small glue cells, which helps clarify its aging mechanism and provide treatment targets.

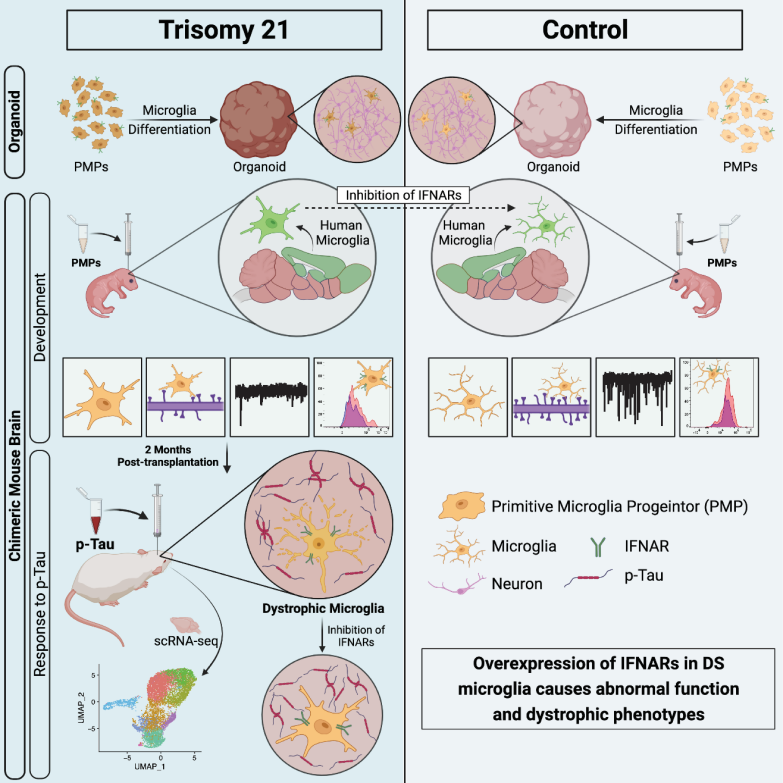
DS small gel cells develop abnormal development in brain organs, human brain tissue and small gel cell chimeric mice
First of all, researchers use the newly developed brain organs of small glue cells in this laboratory to check the functions of DS small gel cells. The use of super -resolution imaging techniques analyzed the synapses of small glue cells. Researchers found that DS small glue cells have enhanced synapses. This result was confirmed in the semi -hippocampus slicing from DS patients. Because in the brain organs, the shape of small glue cells is relatively simple, and it will not show a highly complicated form of branches as in the body. Therefore, researchers have further used the small gel cell chimeric mouse model to further further use it for further further. Research. Similarly, in the DS small gel cell chimeric mouse model, researchers have found that compared with small gel cells in the normal control group, DS small glue cells not only show excessive synapses, but also show simple simplicity Cell morphology. Researchers also used this model to record the excited synapse (MEPSC) and the synapse of the synapgras (LTP) to detect the effects of DS small gel cells on nerve synopsis and plasticity. They found that DS small gum quality Surgery trimming of cells can cause synapses and plasticity damage to neurons.
Inhibit iFnar's expression can improve DS small glue cell dysfunction
Researchers use different detection techniques to conclude that IFNAR's expression in the genetic and protein levels in genes and protein is concluded. Therefore, they assume that the excessive expression of IFNAR in DS small glue cells may be the cause of its development and functional changes. Later, the researchers used the RNAI to reduce the method to inhibit the expression of DS iFnars. They found that this not only improved the form of DS small glue cells, but also reduced their synapses. At the same time, the researchers also confirmed the excessive expression of IFNARS in the DS small glue cells, which can partially improve the neural transmission of the chimeric mouse hippocampus caused by the increase of the synapses of the DS small glue cells. And the synapses are damaged. Pathological TAU can accelerate the aging of small gel cells in the DS chimeric mouse
Next, researchers try to explore whether the aging process of small gel cells can be simulated through the DS gel cell chimeric mouse model. First, the author extracts soluble TAUs from DSAD and CONT. They injected these soluble TAU three -dimensional positioning to about two months of chores. Two months after injection of TAU, they first separated DS small gel cells from the chimeric brain, and then analyzed through single-cell RNA sequencing (SCRNA-seq) analysis found that: DSAD TAU promotes DS small glue compared to The aging of quality cells and disease -related small glue cell genes have also been enhanced. This shows that the DS small gel cell chimeric mouse model can be used to study the aging of small glue cells. Interestingly, they also found that the increase in the aging of the DS small gel cells in the DSAD TAU group to a large extent The upper and elevated type of IFin (IFN) signaling pathway related genes overlap, which indicates that the pathological TAU may induce the aging of DS small gel cells by increasing the IFN signaling pathway.
Inhibit small glue cell iFnars can save the pathogenic TAU induced DS gel cell aging
In order to further confirm that the DSAD TAU found through SCRNA-SEQ can induce DS small gel cell aging, researchers first compared the form of DS gel cells in the Cont TAU and DSAD TAU groups, because the malnutrition form is aggressive small gel quality A prominent feature of cells. They found that the DS small gel cells in the DSAD TAU group showed a malnutrition form, such as the shortened process and the broken beads, but it was rare in the contio group. At the same time, they found that in the same chimeric mouse brain accepted by DSAD TAU, mice gel cells showed a hypertrophy, such as shortening branches and decreased branches, rather than malnutrition forms. This shows that mouse small gel cells may have a different response to human small gel cells. At the same time, they also found that iron protein dyeing closely related to the aging of small gel cells increased significantly in the DSAD TAU group. Through the analysis of SCRNA-SEQ, they speculate that the elevated IFN signal is likely to mediate the aging of the pathological TAU induced DS gel cells. Similarly, using the RNAI reduction method to inhibit the expression of DS iFnars, researchers have found that the shape of DS small glue cells shows less fragmentation process after DSAD TAU injection. In addition, iron protein dyeing in DS small gel cells has also decreased significantly. In short, these results show that after DSAD TAU injection, the expression of IFNARS in DS small gel cells can improve its aging.
In summary, this study confirms that the inhibitory expression of IFNAR's expression can improve the function of DS small glue cells in brain development by using the use of human stem cells and rat cells containing small gel cells. Specify the pathological phenotype of severe adhesive cells caused by pathological TAU protein.
The Peng Jiang research team and the following laboratory collaborated on this study: Ronald Hart, ZHiping Pang, Kelvin Kwan, and Ping XIE team from Ronald Hart, and Ping XIE teams from the Elizabeth Head team from the University of California, and FLORIDA International University's Ying Li team.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.20222.06.007
Want to know more exciting content, come and pay attention to BIOART biological art


- END -
Sweat, soak in his clothes, pay tribute to every adherence!

Since July, the temperature has soared all the wayEntering the Boiling Model in ma...
Over 50 years old, they broke the waves by the wind

When the light people fell into the 35 -year -old anxiety, a group of aunts over 5...