Big Coffee New Rui | Focus on the clinical practice of women's tumors, and talk about the new chapter of the white guide together
Author:Physician reported tumor chann Time:2022.07.18
In recent years, the incidence of gynecological tumors in my country has risen year by year. [1], cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, and endometrial cancer are the most common gynecological malignant tumors. Poor, clinically considering radiotherapy and chemotherapy, in recent years, the application of chemotherapy has gradually been widely used. Neutral granulocyte reduction (FN) is the most common and severe complication of chemotherapy, which not only affects the expected efficacy, but also increases the risk and mortality rate of patients infected after the FN. "China Clinical Oncology Society (CSCO) tumor radiotherapy and chemotherapy -related neutral granulocytes (2021) (2021)" (referred to as "CSCO Lisheng White Guide V2021") provides an important basis for tumor treatment related neutral granulocyte reduction symptoms [ 3]. Here we specially invites Professor Li Yunxia and Professor Wang Xiaojuan of Ningxia Medical University General Hospital to talk about the standardized management of gynecological tumor chemotherapy -related neutral granulocytes and clinical applications of ascending white drugs.

01
Professor Wang Xiaojuan: "CSCO White Guide v2021" instructs the clinical practice of gynecological tumors to effectively improve the clinical survival benefits of patients
01
Rigid assessment of gynecological tumor chemotherapy schemes related to FN risks
Help layered management 层
Common malignant tumors in gynecology include ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, and rare sarcoma. Chemotherapy schemes commonly used in ovarian and cervical cancer include TP and TC schemes, Dorcio+cisplatin+card platinum platinum Wait, the endometrium cancer is more common in paclitaxel+card platinum schemes, while sarcoma uses Dorcisai+Gascotabin and other solutions [4]. Neutrophils of granulocytes are the main adverse events caused by bone marrow inhibitory chemotherapy drugs. FN is the most common and severe complication of chemotherapy.
The most common harm to reduce neutral granulocytes is infection, and not giving antibiotic treatment in time may endanger life. At the same time, the infection of tumor patients is more complicated and difficult to cure, which greatly increases the patient's hospitalization and costs. In addition, neutral granulocytes The reduction of the relative dose intensity and the established cycle of chemotherapy drugs, eventually leading to the difficulty of treatment to achieve the expected efficacy, affecting the survival rate of patients [5]. Therefore, evaluating the risk of patients FN is particularly important for the prevention and treatment of FN. The risk of FN is significantly related to chemotherapy schemes. High school risk drugs that cause FN include paclitaxel+card platinum, Dostcita+card platinum, and Ilidekang and topology of the second -line solution (Table 1).
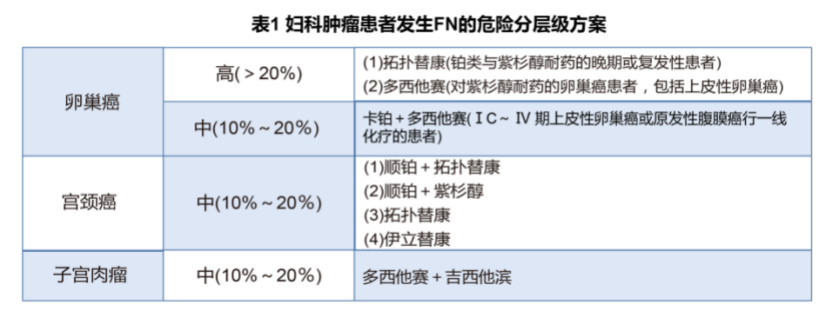
02
"Prevention is more than treatment"
Reasonably choose prevention path
Prevention refers to G-CSF treatment without FN or severe granulocyte deficiency, which can reduce the chance of the occurrence of FN and greatly reduce the occurrence of infection. G-CSF treatment may increase the risk of cancer and the probability of the above-mentioned harm. Treatment is to make up for the dead sheep, and prevention is equivalent to preventing problems before, and in clinical "prevention is more important than treatment." Clinicians need to consider the FN risk of chemotherapy schemes, and combine the patient's own risk factors to correctly select the path of preventing medication.
Clinical doctors can conduct risk assessment and layering based on FN by paying attention to the blood conventional results of 8-14D after chemotherapy, and implementing first-level prevention and second-level prevention paths (Figure 1) according to FN (Figure 1).
The first -level prevention path, that is, evaluating the patient's FN risk layer in the first medication is high risk, medium risk, or low risk. If the patient belongs to high risk, that is, FN risk ≥20%, it is recommended to perform first-level prevention, that is, after the first cyclical chemotherapy, the prevention of G-CSF treatment is given to reduce the incidence of FN; if the patient is a medium-risk level, it is necessary to evaluate the further further. Is there the following situations that cause risk increases: age & 65 -year -old and receiving sufficient dose strength chemotherapy, past chemotherapy or radiotherapy, persistent neutral granulocytes in past chemotherapy, bone marrow accumulation of tumors, recent surgery and/or openness Trauma, liver and kidney dysfunction, FN, malignant blood lymphatic system diseases, and new risk factors of the guide -chronic immunosuppressive such as HIV and nutrition/physical condition. If the patient is a medium -risk level, and then merge any risk factors above, it is treated at high risk to prevent first -level prevention. Patients with low risk are not recommended to use G-CSF prevention.
The second-level prevention path is the second time or follow-up chemotherapy for the patient to evaluate the past cycle. If the patient has FN after the first cycle chemotherapy, or the dose restriction of neutrophil cells decreases, G-CSF patients have been used. Consider reducing chemotherapy doses or changing treatment plans. For patients with G-CSF, G-CSF is recommended. If patients do not have FN or dose restrictions on neutralized granulocytes, G-CSF prevention treatment is not recommended.


Figure 1 The first and second -level prevention paths that prevent FN prevent
03
CSCO Guide to update the main point in the field of women's tumor
Actively guide clinical practice
The guide and treatment content of neutral granulocyte reduction related to radiotherapy -related neutral cells are recommended. It is recommended that in the case of closely monitoring patients with hematology indicators, radiotherapy -related neutral granulocytes can reduce patients with reference to the first level of prevention of neutral granulocytes related to chemotherapy , Two-level prevention principles and treatment principles, use G-CSF to reasonably prevent and treat neutral particle cells caused by synchronous chemotherapy and FN.
The second new content is G-CSF prevention use. If the patient is evaluated as a high risk, it is recommended to continue to use G-CSF prevention per cycle to avoid interruption. The use of interrupt G-CSF will significantly increase the risk of patient FN. The third new content is patients who need to use G-CSF prevention. If (D-1) blood routine test before chemotherapy (D-1) ANC & 30X109/L or leukocyte count & 50x109/L, the amount of G-CSF in this cyclical chemotherapy is halved.
04
During the new crown
PEG-RHG-CSF escort for women tumor patients
During the chemotherapy period, patients should be reviewed 1 or 2 times a week. However, during the epidemic period, patients who were controlled at home could not complete the blood test and injection of related drugs on time. Polyethylene glycol-reorganized human granulocyte stimulation factor (PEG-RHG-CSF) is a long-acting dosage form for reorganized human granulocyte stimulation factor (RHG-CSF). 90%of the patients use PEG-RHG-CSF long-acting lift can stabilize or higher than normal range, which lasts 10 to 14 days to avoid the time of the low valley of neutral granulocytes, thereby reducing the number of blood draws. But the treatment of patients during the convenience epidemic. At the same time, PEG-RHG-CSF long-acting lift can reduce the rate of infection and FN, shorten the hospitalization time and number of times, improve the patient's compliance, ensure that the amount of therapy, the course of treatment, and the performer are performed as scheduled. Quantity and delay therapy [6].
02
Professor Li Yunxia: The treatment methods and technologies in the field of gynecological tumors are constantly updated, and the prevention and control of FN still has challenges
01
Breaking the maternal tumor chemotherapy FN 打
Improving clinical benefits of patients with maternal tumor
Foreign NCCN guidelines are continuously updated every year. In 2017, my country's first "Guidelines for Standardizing Management of Tumor Chemotherapy Related Neutral Graval Cells" was released in 2021. Evaluation, management processes, and standardization of prevention and treatment. Not only is gynecological tumor, other physical tumors and hemalized tumors are processed chemotherapy. More than 90%of patients with ovarian cancer need chemotherapy, 70%-80%of patients with cervical cancer and endometrial cancer need radiotherapy, and even synchronous chemotherapy is needed. As mentioned earlier, the focus of the guidelines is the FN risk stratification and prevention path. Studies have shown that after the application of PEG-RHG-CSF, the an average period of FN per cycle is 5%, the incidence of FN after first-level prevention is 3%, and the incidence rate after secondary prevention is 13%[7]. In contrast, the first -level prevention strategy is better than the secondary prevention.
Although the TC scheme is not a high -risk solution, considering that patients with gynecological tumors are mostly menopausal women, older, some of the peritoneal effusion, severe protein loss, and most patients after radiotherapy. ——The nutrition/physical condition is poor. Therefore, during treatment, clinicians need to combine the patient's tumor type, chemotherapy plan, and their own factors to evaluate the risk of FN. For high -risk patients, first -level prevention is adopted. Preventive path.
During the treatment, the intensity of chemotherapy is positively related to its efficacy, especially platinum drugs, to ensure sufficient amount of chemotherapy, otherwise the efficacy will decline. For patients with synchronous chemotherapy, according to the guideline update, in the case of tight monitoring, the prevention path of neutral particle cells caused by chemotherapy can be treated. Studies have shown that PEG-RHG-CSF is used in preventive treatment during synchronization chemotherapy, which effectively reduces the risk of infection rate and neutral granulocyte reduction, and has obvious advantages in alleviating fever and adverse bone pain (Figure 2) [8].
Fig
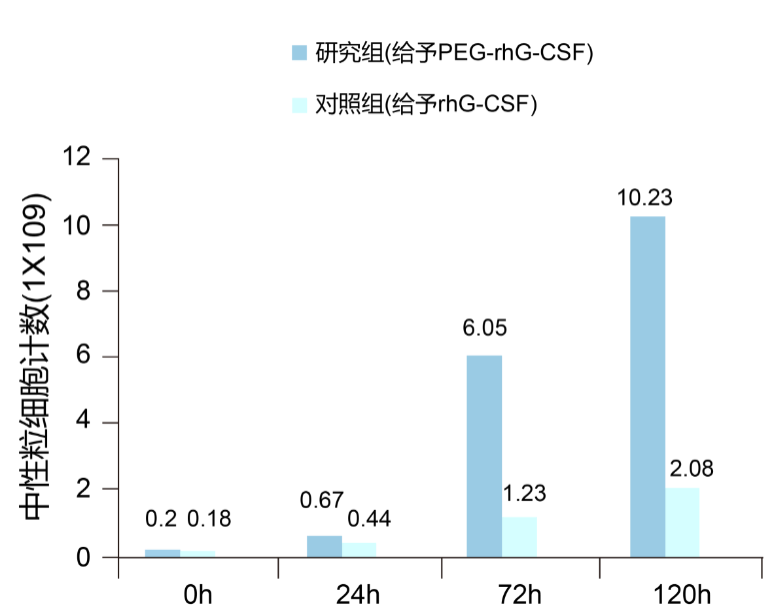
02
Potential challenges of FN prevention
As the new technologies and new drugs of tumor treatment are constantly emerging, the treatment methods are no longer limited to surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and emerging targeted therapy and immunotherapy have been widely used. For example The use of polymerase (PARP) inhibitors and small molecular tyrosine kinase inhibitors. However, the use of new drugs must remain rigorous. For example, the current clinical ovarian cancer adopts full management treatment plan, including standard surgery, sufficient chemotherapy, and subsequent maintenance treatment. In maintenance treatment, PARP inhibitors are widely used in first -line and second -line solutions.
Although PARP inhibitors, although the bone marrow suppression caused by chemotherapy is severe, it will also inhibit the bone marrow and cause granulocyte deficiency. At present, the lack of G-CSF prevention and treatment standards. Similarly, immunotherapy is currently widely used in many tumor treatment. In the "2022NCCN Cervical Cancer Clinical Practice Guide", the first -line combined chemotherapy -immunosuppressor combined with paclitaxel/cisplatin, due to its excellent curative effect, has been included in NCCN's NCCN First -line medication [9]. However, application-oriented death receptor-1 (PD-1) inhibitors can also cause bone marrow suppression, and bone marrow suppression during combined chemotherapy will inevitably increase.
In the face of the occurrence of FN behind immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy and synchronous distribution chemotherapy schemes, how to apply G-CSF, it is necessary to adopt preventive and therapeutic drugs, etc., and put forward new challenges to clinicians. After patient radiotherapy, the use of short -acting, long -term and white white use methods, duration and other issues need to be further clinical practice and research to support guidelines update, more detailed explanation of related issues, and guiding clinical clinical. 03
Professor Li Yunxia summarizes
Neutral granulocytopenia is the most common hematological toxicity of bone marrow inhibitory chemotherapy. The degree of reduction and duration are directly related to the risk of infection or even death in patients, which has adverse effects on the relative dose intensity of chemotherapy drugs and patient prognosis. Patients with reduced neutral particle cells caused by radical chemotherapy should conduct stratified management. Before the first treatment and after each chemotherapy cycle, the risk of FN occurs in accordance with the type of disease type, chemotherapy scheme, and patient risk factors of patients with tumor patients. G-CSF for individualized prevention and treatment is very important in clinical treatment.
With the continuous renewal of treatment methods and technology in the field of gynecological tumors, there are still new challenges in prevention and treatment of neutral granulocytes, which need to be further clinical practice and research.
Expert Introduction
Professor Li Yunxia
A Department of Tumor in Ningxia Medical University General Hospital

Chief Physician and Professor of Ningxia Medical University General Hospital
The first deputy chairman of the Ningxia Anti -Cancer Association Women's Tumor Special Committee
The first member of the Ningxia Anti -Cancer Association Chemotherapy Commission
Member of the Ningxia Anti -Cancer Association Tumor Nutrition and Supporting Treatment Professional Committee
Members of Gynecological Oncology MDT Team of the General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University
Member of the Gynecology and Oncology Group of Ningxia Medical Association
Members of the China Anti -Cancer Association Clinical Oncology Professional Cooperation Group
In terms of chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, targeted therapy, biological immunotherapy and advanced cancer pain treatment, and palliative treatment of various physical tumors, have accumulated rich experience. Especially in the diagnosis of gynecological malignant tumors and drug treatment
Expert Introduction
Professor Wang Xiaojuan
A Department of Tumor in Ningxia Medical University General Hospital

Deputy Chief Physician of the Department of Internal Medicine of Ningxia Medical University General Hospital
Member of the Ningxia Cancer Association Tumor Rehabilitation and Passing Treatment Committee
Ganqingning malignant paste effusion treatment expert alliance member
References: (slide and view)
1. Guo Ying, Li Yuhong. Gynecological tumor during pregnancy: Guide based on the third international consensus meeting. China Practical Gynecological and Obstetrics Journal. 2019.35 (11): 1282-1285.
2.Ba Y,Shi Y,Jiang W,et al.Current management of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia in adults:key points and new challenges:Committee of Neoplastic Supportive-Care(CONS),China Anti-Cancer Association Committee of Clinical Chemotherapy, China Anti-Cancer Association.Cancer Biol Med.2020.17 (4): 896-909.
3. Uncle Qin, Ma Jun. The China Clinical Oncology Society (CSCO) tumor chemotherapy-related neutral granulocyte reduction symptoms (2021).
4. The Chinese Medical Association Gynecological Oncology Branch. Gynecological Oncology Platinum Platinum Drug Clinical Application Guide. Union Medical Magazine .2021.12 (06): 881-901.
5.Weycker D,Li X,Tzivelekis S, et al.Burden of Chemotherapy-Induced Febrile Neutropenia Hospitalizations in US Clinical Practice, by Use and Patterns of Prophylaxis with Colony-Stimulating Factor.Support Care Cancer,2017,25(2): 439-447.
6.Zou D,Guo M,Zhou Q.A clinical study ofpegylatedrecombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor(PEG-rhG-CSF)in preventing neutropenia during concurrent chemoradiotherapy of cervical cancer.BMC Cancer.2021.21(1):661.
): 238-47.8. Ma Yiming, Zhang Mingchuan, Zhang Xinhui, etc. The clinical value of cervical cancer synchronous distribution of PEG-RHG-CSF.
9.ABU-Rustum NR, Yashar CM, Bean S, ET Al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Cervical Cancer, Version 1.2022 [EB/OL]. [2022-05-01] .https://www.nccn.org/guidelits/guidelines-detail? Category = 1id = 1426.
Capture: Hu Haiyan
Edit: Wang Lina
- END -
Huazhong University of Science and Technology has just announced: officially launched!

Just announced!Huazhong University of Science and TechnologyInternational Educatio...
Exploring a folk song of Xishangdian

At the Symposium in the Red Culture and Rural Revitalization of Shunhe Town, Mache...