India is watching Xiaomi, OPPO, and vivo. How many volumes of domestic mobile phones to go to sea?
Author:China News Weekly Time:2022.09.03

In the past and visible future
India will still be the most "volume" overseas market in Chinese mobile phone manufacturers
Facing the Indian market, Chinese mobile phone companies
At the same time, facing great temptation and great uncertainty
"Xiaomi has successfully thawed more than 700 million US dollars of frozen funds."
On August 19, at the Xiaomi Second quarter financial report analysis meeting, Xiaomi Group partner and president Wang Xiang responded to the latest progress of Xiaomi's tax survey in India. India's business is still in progress.
This is the epitome of China ’s mobile phones to go to sea to collectively encounter twists and turns this year. Since the end of 2021, the news that Chinese -funded mobile phone companies have encountered tax surveys in India have continued. Last year, India had banned a series of Chinese APPs, and this year it was the turn of Chinese mobile phone companies.
The complex status quo of China -India relations and India's ambitions for their own economic development have made India's attitude of more than 70 % of the Chinese mobile phone companies that have occupied their mobile phone markets, but the market size is second only to India in China, but any of the market has made any any any of the Indian India that has made any any any of the India in China. A mobile phone manufacturer is reluctant to leave.
Facing the Indian market, Chinese mobile phone companies are at the same time facing great temptation and great uncertainty. And the outside world's doubts are how far can Chinese mobile phone companies go in India with the increasingly splitting world economy?
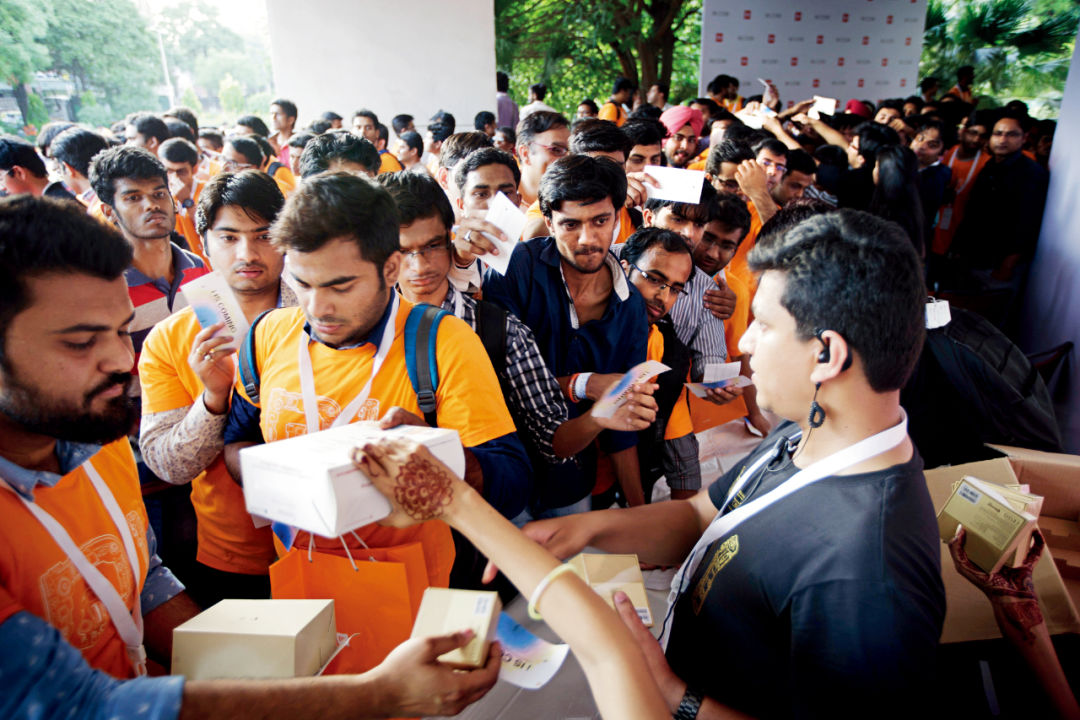
On April 23, 2015, Xiaomi held its first overseas conference in New Delhi, India to launch a multi -language Xiaomi 4i facing India. After the press conference, the participants lined up the Xiaomi bracelet for free. Photo/Visual China
Encountered Indian "census"
On August 3, local time, the Indian Tax Intelligence Administration (DRI) issued an announcement. Through search for the Vivo Indian company factory, it was found that when they imported some products for manufacturing mobile phones, they made false declarations to obtain tax exemptions, totaling 221.7 221.7 In the 100 million rupees, Vivo India has voluntarily paid the 600 million rupee tariff difference.
Just a month ago, the Indian Law Enforcement Bureau searched the Vivo India and 23 related companies in suspicion of violating the "Prevention of the Money Laundering" and accused him of nearly half of the sales of Rs 12.5 trillion. It is a huge loss of vivo India to avoid tax payment.
With two taxes within a month, the experience of vivo is the epitome of Chinese mobile phone companies in India this year. At the end of 2021, Xiaomi and OPPO encountered an assault inspection of the Indian Tax Department, which was accused of multiple tax issues. In the next half a year, Xiaomi, Huawei, OPPO, vivo and other Chinese -funded mobile phone companies have encountered different Indian government departments. Tax survey.
Most of the charges are similar. For example, Dri mentioned the problems of vivo in the announcement, and was also used to accuse OPPO tax evasion. DRI said that OPPO deliberately miscalculated when importing mobile phone components, and obtained a tariff reduction of 29.81 billion rupees. Out of encouraging mobile phone companies to migrate the production line of components to local considerations, India has set different tariffs on different mobile phone parts.
"'High -standard legislation, universal illegal law, selective law enforcement' is the universal reality of Indian law. It is difficult for enterprises to achieve sufficient compliance operations. Because India is relatively 'small government', hands and people, Insufficient energy, many times the compliance obligations are simply and rude to enterprises. "Li Qin, a consultant of the Chinese Affairs Department of India Dahengzhu Cheng Law Firm, told China News Weekly that the Indian government focuses on" care "foreign companies. European and American companies have often encountered law enforcement inspections from the government in India, and many foreign companies and Indian governments have long legal disputes.
Nevertheless, the tax survey of Chinese mobile phone companies for half a year is still unusual.

In April 2019, a Xiaomi retail store answered by Kali, India. Photo/Visual China
"For Chinese mobile phone companies in India, this round of tax survey is a 'census', and the tax survey of other foreign companies and industries is more' spot checks." Yang Shucheng, secretary general of the Indian Chinese mobile phone company association, told " China News Weekly.
And Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, etc. are just one corner of Chinese mobile phone companies that have encountered tax surveys. Yang Shucheng recalled that this round of tax survey began at the end of 2021. It was a peak in May and June this year. In August, it became gentle. Only several cases were continuously investigating, and the "census" had ended. According to his estimates, about 60 % of Chinese -funded mobile phone companies have been investigated by taxes. In addition to well -known mobile phone manufacturers, they also include a large number of mobile phone supply chain companies.
Several people interviewed Chinese -funded mobile phone companies who were interviewed believed that this round of tax survey had a lot of impact on the enterprise. Some of the persons in charge of the enterprise were directly taken away for investigation. Difficulty, at the same time, enterprises are also required to pay high fines. However, they all emphasized that this round of tax survey did not touch the root of Indian Chinese mobile phone companies.
At the end of April, the Indian Law Enforcement Bureau seized the 55.51 billion rupee assets of Xiaomi India Company. Xiaomi Indian Company subsequently sued to the court. The court repeatedly extended the thawing period of its bank account and relaxed the use of accounts for foreign remittances. Some Chinese -funded mobile phone companies told China News Weekly that compared with vivo, Xiaomi and OPPO have experienced more than once with tax surveys and accumulated certain experience in responding. Yang Shucheng also told reporters that the Indian appeal process is relatively long, but on the other hand, it is also difficult to truly implement the fine. "There are many gray areas in Indian society, which can solve some problems by negotiating."
In April 2019, a mobile phone shop on the streets sold many brands such as OPPO. Figure/IC
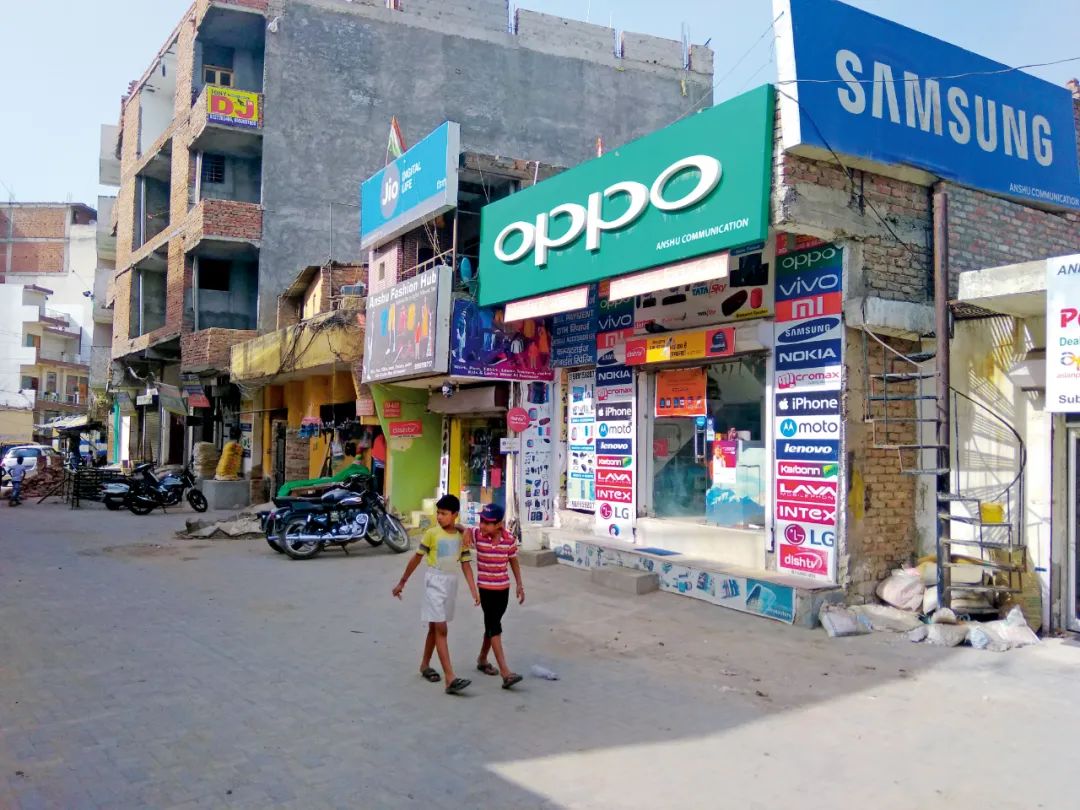

Compared with tax surveys, Yang Shucheng is more worried about the issuance of visas, calling it "the primary difficulty facing India -funded mobile phone companies." "Because of the principle of peering, the current number of visas issued by India is extremely limited, but Chinese -funded mobile phone companies need to manage a large number of management and technical personnel to India. They need to use private relations to open the joints and pay a lot of money and time to get a limited number of visas."
At present, there are thousands of people who need to obtain a visa. During the high peak of 2019, there were about 10,000 management and technical personnel in India's mobile phone industry chain, and only about 1,000 were currently left.
Tax survey and visa restrictions are interpreted as India's no longer friendly to Chinese mobile phone companies. Behind this is India's vigilance of Chinese capital. In April 2020, India issued the FDI New Deal and requested that before investing in India, which bordered its borders, it needs to be reviewed, which is obviously obvious for Chinese capital. In 2021, Chinese companies' direct investment in India's non -financial category fell nearly 70 %, leaving only 63.18 million US dollars.
After the FDI's new policy was released, there was no clear news for more than two years to inform the relevant approval dynamics. It was not until recently that the Indian media had released a small number of FDI applications from China.
"The FDI New Deal is limited to equity behaviors, that is, new enterprises, equity transfer, joint venture with Indian enterprises, and even existing Chinese -funded Indian enterprises increase capital and expand shares. Even some projects may be signed in 2019, but suddenly received when the transaction ended. The restrictions on the FDI New Deal make them only apply for FDI licenses. "Li Qin told reporters that even recently reported that dozens of Chinese projects have received FDI licenses, but it may not be truly set up in India's projects in it. Too much, this can also reflect the impact of India's FDI new policy on China's investment.
The aforementioned Chinese -funded mobile phone companies in India revealed that after the tax investigation, mobile phone companies will slow down their investment in India.
Obviously, Chinese -funded mobile phone companies in India are facing a new round of games.
Game India Industrial Policy
"Chinese -funded mobile phone companies have developed in India for more than 7 years, and the other party will also evaluate the three dimensions of taxation, driving GDP growth, and driving employment." Yang Shucheng tried to understand this round of tax surveys against Chinese mobile phone companies from the perspective of India. " Judging from the results of the Evaluation of India, Chinese mobile phone companies do solve some employment problems for India and absorb about 400,000 employment, but it is considered that it does not bring enough taxes, and the role of GDP growth is also very limited. "
Li Qin believes that India has a "two -point method" attitude towards Chinese capital: that is, the division of Chinese automobiles, mechanical manufacturing, electronics, etc., which distinguish between factories in India, requires a lot of investment, can create employment positions, and cannot be said that Investment, and "light -fitting", can attract Internet investment of millions or even tens of millions of users without the need to set up entities in India.
"Later types of investment are directly impacted and affected by the Indian government policies. Although industrial investment is negatively affected by customs clearance and import restrictions made by the Indian government, the Indian government understands that such manufacturing companies can bring employment and advanced. The production and management experience matching the plan of the Indian government 'India's "India", so most of the projects approved by the Indian government's FDI are mostly such production companies, "Li Qin said.
From the perspective of "two points", Chinese mobile phone companies should be welcomed.
In 2014, Xiaomi, OPPO, Vivo and other Chinese -funded mobile phone companies entered the Indian market. At the time, Modi became Indian Prime Minister. The "Indian Manufacturing" initiative planned to increase the proportion of manufacturing in GDP from 15 % to 25 % Essence The following year, the "staged manufacturing plan" (PMP) passed the use of tariffs to force enterprises to transfer production to India.
In 2018, mobile phone billboards such as vivo outside the city of New Delhi, India. Figure/Zhongxin
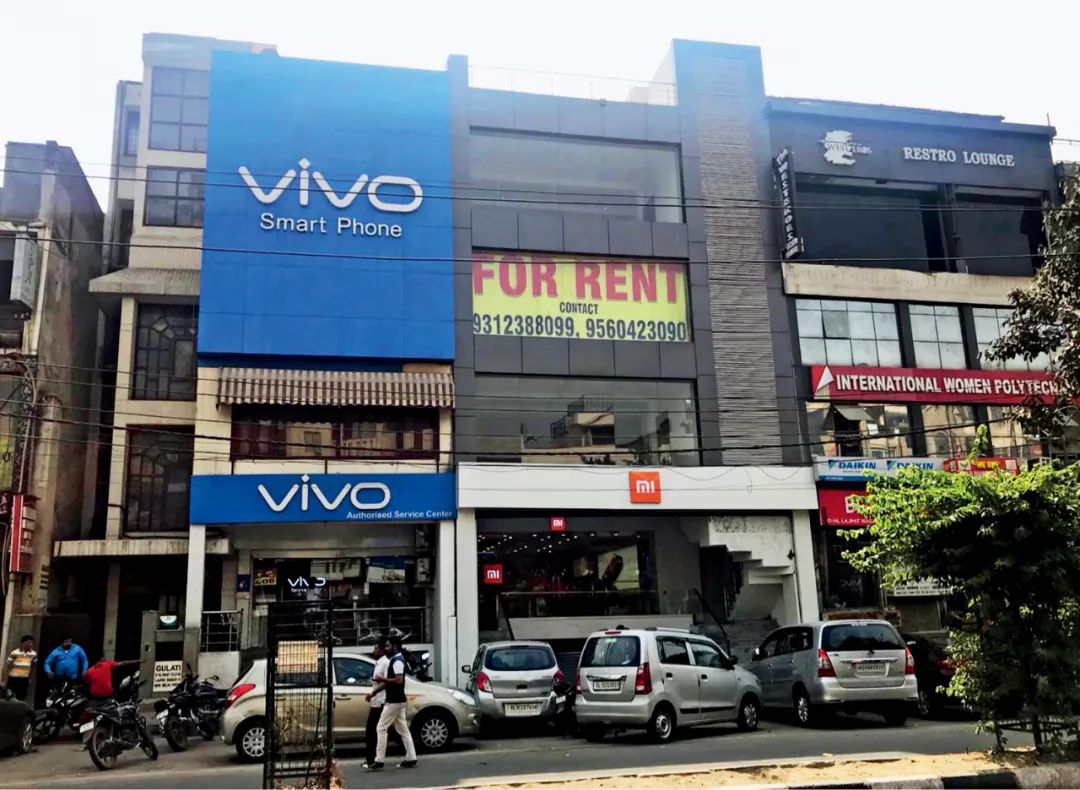

According to the influence report of Vivo 2021, after vivo entered the Indian market in 2014, in response to the construction of "Made in India" in India, and buying a land to expand the factory again in 2018, there are 10,000 employees in the Indian factory. 50 million units gradually increased to 60 million units. In terms of supply chain, 95 % of the current supply chain of the vivo battery comes from India. In 2023, the proportion of local supply chains in the display will reach 60 %. In 2024, the proportion of local supply chain of chargers rose from the current 60 % to 75 %.
According to Yang Shucheng, one of the main reasons for Chinese -funded mobile phone companies in India is that tariffs have increased the cost of purchasing in China. The tariffs imported by mobile phones are 25 % and the tariffs of supply chain products are 15 %. At present, some components and chips are still. It is a zero tariff, but some key auxiliary materials, such as screens, cameras, batteries, chargers, etc. 15 % tariffs, "these raw materials and component production capacity that increased tariffs are the main force to transfer to India." In addition to the tariff factors, the demographic dividend is also a reason for the transfer of production capacity of Chinese mobile phone companies. "At present, a monthly salary of a general worker in India is about 1,000 yuan, but it will reach 3500 yuan to 4,000 yuan in China." Yang Shucheng told reporters.
Talking about the convenience of Chinese -funded mobile phone companies to the Indian Factory, the aforementioned Chinese mobile phone companies told reporters that the popular industrial transfer destinations such as India and Vietnam have been different in recent years. Federal countries, the central government has limited power, and each region has its own policies. Unlike Vietnam, it can achieve "three exemptions and five halves". "Including OPPO, vivo, and several Chinese -funded mobile phone supply chain companies, a total of seven or eight companies purchase land to build a land in India. To coordinate, the process is often complex and long. "
"The part with relatively low technical content in the entire Chinese mobile phone industry chain has already been deployed in India, and local Indian local manufacturers are also using the thousand yuan machine brand that has been migrated to the local industrial chain." Sun Yanzi, chairman of the Worom -Electric Think Tank, told "" China News Weekly.
Obviously, India hopes to give local companies more opportunities. After all, in 2014 when Chinese -funded mobile phone companies intensively entered the Indian market, the market share was closely following Samsung's three major Indian mobile phone brands Micromax, Intex, LAVA, but currently currently They can no longer be found in the top five market share.
"The particularity of the Indian market is that other developing countries will not regard China as competitors, so they will not set up many policy obstacles to Chinese mobile phone manufacturers, but India obviously does not think so." Li Nan, former vice president of Meizu, told "China News weekly".
After 2020, the "Indian Manufacturing" initiative has changed from pursuing import substitution to "self -reliance". The "production association incentive" plan (PLI) was launched in that year. Support India's local manufacturing enterprises.

Previously, Chinese manufacturers were forced to increase through tariffs, import restrictions, and local production subsidies, and the strategy of supporting the real estate chain in this way is only the "sub -superior option" of the Indian government in Li Qin. Enterprises and Indian local enterprises are jointly binding, so that they can bypass the "annoying things" such as government procurement restrictions and resisting Chinese goods, but this will inevitably reduce the autonomy of Chinese investors. It is difficult for Chinese enterprises to accept it and in reality in reality It is also very difficult to find the right and reliable cooperation and joint ventures. "
In the support list of PLI, it is rare for Chinese mobile phone companies. "PLI has not blocked all Chinese mobile phone companies outside the door, and Chinese -funded mobile phone companies are also applying, but it may be more Samsung and Apple supply chain companies." Yang Shucheng believes that the purpose of PLI can not only be understood as support as support. Indian local enterprises, of course, supporting the local industry chain is a future trend, but still requires a long process. "Just like foreign companies came to China after the reform and opening up, Chinese local companies have also experienced the process of learning, but it is relatively short. At present, some Indian companies are learning to learn from Chinese companies in India, but it takes time."
He believes that Chinese -funded mobile phone companies still have a time window in India. "If India wants to reach the level of China's mobile phone industry chain today, it will take 15-20 years. Indian local enterprises in the manufacturing link are in its infancy. Few companies that lag behind Chinese -funded enterprises, currently there are very few companies that have really entered the mobile phone industry chain, or even not. "
Recently, the news that iPhone 14 will produce in India will heat up the industrial chain transfer again, but the current reality is that since 2015, it has been able to use taxes and other means to promote the transfer of the mobile phone industry chain in disguise. They are relatively limited. Yang Shucheng told reporters that the procurement of raw materials and components in India is only about 15 %. It is expected to reach about 20 % this year. Most raw materials and components depend on imported from China. host.
Although the output value of the Indian electronics industry has grown rapidly, it has reached $ 75 billion in fiscal 2019 to 2020, and there is still a small distance from the target of US $ 300 billion to US $ 300 billion to 2026. "Big rear".
"If you want to obtain the Indian market, you need to help India develop the local mobile phone industry." Li Nan believes that the supply chain is inevitable, just like Apple's supply chain in China also needs localization. You can't just want the market of others, but it is a normal commercial exchange.
In February 2015, Huawei's R & D center in Bandol, India. Photo/Visual China
What is the opportunity for Chinese mobile phones to go to sea?

"Chinese -funded mobile phone companies do not do well in the aspects of cognitive India's local laws and regulations, humanistic and religious customs, and the Indian government has not provided much guidelines for foreign -funded enterprises. After the case occurs, the problem is solved, and there is no systemic response. "Yang Shucheng believed. With this round of tax survey and fermentation, Chinese -funded mobile phone companies stayed as the focus. Especially in late July, Honor CEO Zhao Ming once stated that "the Honor team withdrew from India". He said that the team that had been operating in India for a long time a few years ago has been withdrawn, and the relevant business is currently launched through local partners.
"In fact, glory is not suitable for whether to withdraw from the Indian market. When the Huawei system is still among the Huawei system, Huawei and Honor have ended in the Indian market 'three -in and three outs." The aforementioned Chinese mobile phone companies told reporters that After the tax survey, he has communicated with his peers in India. For brands that have successfully achieved in the Indian market, such as Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, Realme, etc., their strategy in the Indian market will not change.
The four manufacturers of Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, and Realme occupy more than 60 % of the Indian market share, while Chinese mobile phone companies have stabilized in the Indian market in the Indian market in the past three years. Yang Shucheng also believes that it will not give up this market easily for Chinese -funded mobile phone companies with a high market share in India, because the space and population dividends in the Indian mobile phone market are easy to see.
The Indian market is indeed attractive enough to make it the first destination for Chinese -funded mobile phone companies in 2014. Nowadays, Chinese mobile phone manufacturers have been difficult to give up India, especially the global smartphone market is in a trough.
According to Canalys, in the second quarter of 2022, global smartphone shipments decreased by 9 % year -on -year to 287 million units. Tell "China News Weekly" that in the future, only the Indian market may maintain growth in the global smartphone market.
India has currently passed a large number of functional phones to the smart phone conversion. In recent years, shipments are about 150 million smartphones and 100 million functional phones. It is in the climbing stage of smartphone shipments. Taiwan's delivery volume has become the second largest smartphone market after China.
"India has a population of 1.4 billion, and the shipments of smartphones will eventually climb to China's existing level." Yang Shucheng believes that the annual shipments of 350 million units through three to five years will be completely expected. A level has approached China's current sales, but the unit price is still unable to compare with China.
Li Nan also believes that the biggest uncertainty in the Indian market lies in the growth of national income.
IDC data shows that in the first quarter of 2022, the average price of Indian smartphones was $ 211, which was lower than the level of $ 402 worldwide. Some people in the industry compare to reporters. At present, the average price of Indian smart phones is 1,000 to 1500 yuan, and China can reach a price segment of 2500 ~ 3,000 yuan. There are still about 1,000 yuan differences between the two. "Therefore, for mobile phone manufacturers, not only the increase in shipments in the Indian market can be expected, but the single -machine price is also in the climbing stage."
Compared with India, some markets with high penetration rates in Chinese mobile phone manufacturers face greater uncertainty. For example, Africa, some insiders told reporters that this uncertainty mainly comes from economic development.
More than 99 % of the business comes from overseas, especially the financial status of the transmission of nearly half of Africa's market share. The growth rate of over 30 %. One of the important reasons is affected by the epidemic. The construction process of Africa's 4G network has slowed down and affected the demand for smartphones. In the second quarter of this year, according to the statistics of Counterpoint, the shipments of smartphones in the Middle East and Africa fell 7.8 % to 38 million units.
Chuanyin also hopes to make breakthroughs in South Asia. Although the market share in Pakistan and Bangladesh reaches 36.8 % and 19.7 %, the market size of the two countries is limited after all. Breakthrough ranked sixth with only 6.9 % of the market share.
In the past and visible futures, India will still be the most "volume" overseas market in Chinese mobile phone manufacturers. Realme has positioned India's second million -level market outside China, but Xu Qi, vice president of Realme, said that at present, the Indian market is still a very large market and an important market for Realme. "But Realme The global layout is very critical, we will not put the eggs completely in a basket. "
"At that time, Meizu avoided the more intense Indian market in Chinese manufacturers, deeply cultivated the Eastern European market, and once achieved sales second only to Samsung in Russia and Ukraine. Avoid the internal rolls with other Chinese brands. "Li Nan told reporters.
"Whether it is a product or sales, the strength of China's mobile phone industry is very strong." Yang Shucheng analyzed the key to the success of Chinese mobile phone companies in India to reporters, and the successful experience of China's success was transformed before copying to India. "For example, OPPO and vivo, in the Indian market, still breakthrough in offline channels that have successfully achieved success in China. At that time, Huawei wanted to copy the strategy of copying the domestic 'high and high beating', and it was obviously inconsistent with the reality at a high -priced product. "On April 5, 2016, at a new OPPO press conference in New Della, India, The models took a photo with OPPO F1 Plus models. Photo/Visual China
"When coming to a developing country like India, Chinese mobile phone manufacturers are basically the story that occurs in China." Li Nan believes that, for example, for example, for the choice of online and offline channels to go to the sea, for mobile phone manufacturers who have the power to go to sea, In the case of, they all have strong online and offline channel development capabilities, and only need to be stationed in different teams to enter different markets. E -commerce penetration rates in different markets are different. For example, with the rise of Lazada, the penetration rate of e -commerce in the Southeast Asian market has continued to increase.
In fact, markets with high penetration rates in Chinese mobile phone brands, including India, are more developing countries in developing countries, but the overall volume of markets in developed countries such as Europe and the United States is still small. Counterpoint has counted in developed countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Japan and other developed countries. The five mobile phones with the highest markets in the market are all cited by Apple and Samsung. For example, in the second quarter of 2022, Apple and Samsung firmly occupied nearly 80 % of the US market.
"Chinese mobile phone manufacturers go to sea, the first choice is to target the marketing of developed countries, or the goal of developing countries, such as Africa, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe. The strength of the accumulated "time difference". "Li Nan admits that the strategy of" time difference "can ensure that Chinese mobile phone manufacturers succeed in developing countries in developing countries.

Nowadays, Chinese mobile phone manufacturers are conducting a new round of choices. When they announced that the team was withdrawn from India, Zhao Ming regarded this year as the first year of the glorious global market. For example, products of $ 99, $ 149, and 199 US dollars, Honor to overseas markets or insisting on building a brand and quality high -end strategy. This year, the products listed in Europe are directly 1099 euros Magic4 Pro. "
Some people in the industry believe that the opportunity of Chinese mobile phone manufacturers in overseas markets will still be "high -end markets" to reporters in the future. "After all, Huawei's high -end machine market in Chinese manufacturers in overseas is almost blank."
Send 2022.9.5 Total Issue 1059 "China News Weekly" magazine
Magazine Title: Behind the advance and retreat of Chinese mobile phones India
Reporter: Chen Weishan ([email protected])
Meng Qian ([email protected])
Edit: Min Jie
Operation editor: Xiao Ran
- END -
"Spider -Man" first show, State Grid Yongjia County Power Supply Company launched a tracked insulating arms car with electricity for the first time

In the past few days, Yongjia County, Wenzhou, Zhejiang has continued to be high -...
Ensuring post -earthquake communication and donations "with work -generation" to help the reconstruction of all sectors of society after the disaster still support Luding 丨 see the cover every day

Cover news reporter Meng Mei Zhang YuexiAt 12:52 on September 5th, a magnitude 6.8...