[Scientific Research Progress] The complete fossil specimen of the Chengjiang Animal Group reveals the new information of the evolution of the simmered shrimp system
Author:Chinese Academy of Sciences So Time:2022.09.20

The complete fossil specimen of Chengjiang Animal Group reveals
New Information of Qi Shrimp System Evolution
Anomalocarids, as the earliest large predatory animals and top predators that dominate the ocean. They appeared in the early period of Cambrian, marking the existence of the pyramid food chain and the establishment of complex ecosystems during the outbreak of the Cambrian. Qi Shrimp's body shape is weird, and the maximum body length speculates more than 2 meters; their heads consist of a pair of good visual compound eyes, a pair of thorns predatory front limbs, and a radiation -shaped portion. , Expressing the high degree of specialization in predation; its streamlined trunk has a series of pair of paddle -like leaves and gill slices, which are used for swimming and breathing. It also has a slender tail fork, which can play a role in steering and balance in exercise.
Since the first discovery of strange shrimp fossils preserved with discrete front -limbs in the Rocky Mountains in Canada in 1886, in more than 130 years of research history, paleontologists have interpreted different body parts of Qi Shrimp as various various various themselves into various various various various various various various various various various various various various various various various various various various various themrs. Sample animals. With the continuous discovery of fossil specimens around the world, especially the discovery and in -depth study of the complete preservation specimen, Qi Shrimp is now considered a type of primitive limb animal.
Kwai shrimp is named after the earliest Anomalocaris, and is classified as Radiodonta in classification. So far, the earliest fossil records of Qi Shrimp can be traced back to the early Cambrian period of about 520 million years ago, and the latest time to about 4 billion years ago in the early mud pelvis; its evolutionary history is not as short as 120 million years, and Show global geographical distribution characteristics. At present, more than 20 genus and 30 species have been found in the ejaculation teeth of Qi Shrimp, which belongs to four first -class classification units, including ANOMALOCARIDIDAE, AMPLECTOBELUIDAE, sieve shrimp Tamisiocarididae and Hurdiidae. Although the diversity of Qi Shrimp is very high, the complete preserved fossil specimens are very rare, which makes most of the strange shrimp species lack information such as anatomy such as anatomical anatomy outside the front limbs. Because of this, the systematic evolutionary relationship between various subjects and species of Qi Shrimp is confusing, and it has not been well analyzed.
The early Cambrian of the Cambrian in Chengjiang Matthew Tianshan, Yunnan, was the unique fossil treasure trove and world natural heritage. The Chengjiang Animal Group not only has the earliest fossil records with exact accurate shrimp, but also the fossil group with the highest diversity of strange shrimp species so far. In 1994, a research team led by Researcher Chen Junyuan, a researcher at the Nanjing Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, published the Chengjiang Animal Group Fossils, including two complete specimens, in the American "Science" magazine. The public caused a sensation. One of the strange shrimp specimens collected in Mat Tianshan in 1990 (Figure 1) has become one of the iconic symbols of the Chengjiang Animal Group. Since publishing, the fossil specimen and restoration maps often appear in international academic activities, various popular science works and media reports, and as a sign of the Chengjiang Animal Group as one of the 50th anniversary of the 1999 Chinese Academy of Sciences The form of commemorative stamps is publicly issued (Figure 2). However, since the first publication in 1994, this complete strange shrimp fossil specimen has not been studied in depth, becoming a major regret in the field of strange shrimp and early animal evolution research.
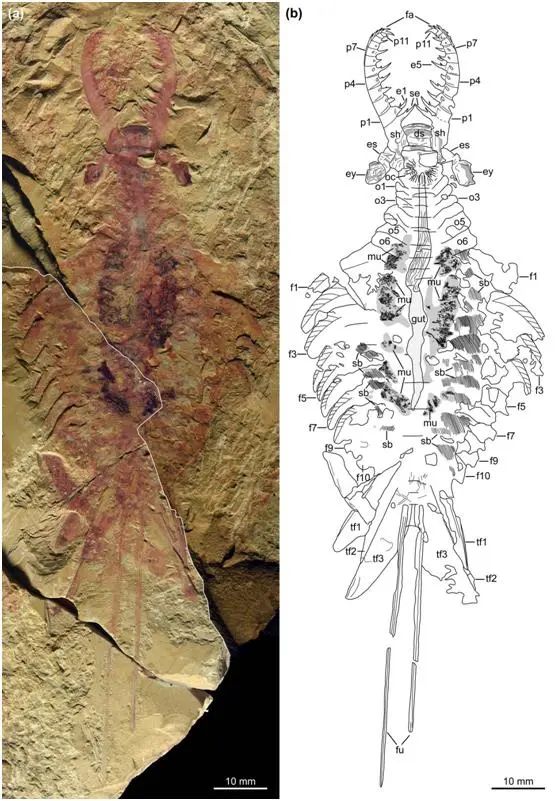
Figure 1 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图 图

Figure 2 Qi Shrimp Memorial Stamp
Recently, Zeng Yan and Researcher Zhao Fangchen of the Researchers of the Nanjing Poto Institute of Poto Poor creatures carried out fine morphological anatomy on related fossils including this complete strange shrimp specimen. It was found that this classic strange shrimp fossil specimen is different from other species that have been named in the shape of the forelop attachment, the number of paddle -like leaves, and the composition of the tail fan, which should belong to a new species. Researchers use this fossil specimen as a positive specimen and name them as the Innovatiocaris Maotianshannsis to commemorate Mr. Chen Junyuan's scientific spirit and contribution to the research on the outbreak of the Chengjiang Animal Group and the Cambrian. Research results were published online online on the Journal of the Geological Society.
This hat Tianshan pioneering shrimp orthopedic specimen shows the exquisite soft body biological characteristics including the intestine and muscles, and also reveals the spatial relationship between the front limbs, eyes, and shell of the head of the shrimp. And the dissection details of the neck, paddle -like leaf. According to these new anatomical information, the researchers cooperated with Yang Dinghua, a fossil recovery master of Nanjing Potoosaus, to develop three -dimensional art recovery of Hat Tianshan (Figure 3).

Figure 3 Innovatiocaris Maotianshannsis 3D art recovery (produced by Yang Dinghua, guided by Zeng Han and Zhao Fangchen)
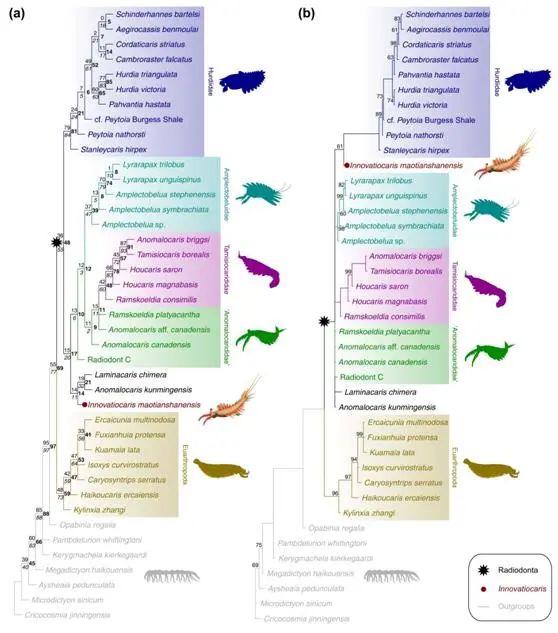
Based on the new anatomy clues, the researchers also found the relevant structure that had not been reported before the Anomalocaris Canadensis specimen in the Bolgis shale biological group in Canada. In addition, the researchers also described the new species of strange shrimp that may belong to the pioneering shrimp based on the discrete front -limb specimen, which described the Ninovatiocaris? SP. SP. SP. Innovatiocaris? Multispiniformis. These anatomical information provides valuable new data for the study of Qi Shrimp. On the basis of morphological anatomy data, the researchers used systematically to re -analyze the systematic and evolution of Kwai Shrimp. Earlier studies have shown that the front limbs of Qi Shrimp have obvious morphological differentiation in different areas from the base to remote. Although the characteristics of these morphology have implied valuable evolutionary information, this information has not received the attention of the previous system research. Based on this, the researchers systematically sorted out the characteristics of the strange shrimp, detailed codes of the morphological differentiation of different parts of the front limbs. And Bayesfa evolved tree reconstruction. Relative to previous research, the resolution of the relationship between the strange shrimp system has been significantly improved. At the same time, according to the evolutionary relationship between the four families of the strange shrimp and the evolution position of some strange shrimp species, it put forward new views (Figure 4). The analysis of the system shows that the Hat Tianshan pioneering shrimp does not belong to any of the four subjects known as the known Qi Shrim. The difference between Hed shrimp is close to the root of the tree that the shrimp evolved trees. Therefore, Mat Tianshan pioneering shrimp provides an important reference point for the origin and evolution of strange shrimp.
Figure 4 Trees of the strange shrimp system obtained by the study are the results of the simplicity method (a) and Bayes inference (b), showing the evolution of the puppet Tianshan pioneering shrimp
This study has been supported by the National Key R & D Plan, the Strategic Pioneer Science and Technology Special (B) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Laboratory of Modern Paramissions and Stylology.
◎ Thesis related information:
Han Zeng, Fangchen Zhao*, Maoyan Zhu, 2022. Innovatiocaris, a complete radiodont from the early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte and its implications for the phylogeny of Radiodonta. Journal of the Geological Society.
https://doi.org/10.1144/jgs2021-164.
Copywriting | Zeng Han (Nanjing Institute of Geological Paradosure of Chinese Academy of Sciences)

Capture Edit | Liu Yun
Copywriting review | Chen Xiaogen
- END -
The Wuzhen Summit of the World Internet Conference this year will hold the six key activities of the "Reuters" in late September
On August 23, the World Internet Conference Wuzhen Summit Zhejiang's hosting work leadership group informatization work department organized a blower of related work news such as the 2022 Internet Li...
WAIC2022 丨 More than 20 key industrial projects signed a plan to invest over 5 billion yuan in Pudong
21st Century Business Herald reporter Zheng Zhiwen Shanghai reportIn 2019, Pudong New District was officially unveiled as the first artificial intelligence innovation application pilot zone in the cou