The Karl DeisSeroth group reveals the rules of the brain nucleus encoding information
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.09.25

Written article | Chen Wenqiang
Responsible editor | Xi
Over the past few decades, people's understanding of brain function has been greatly achieved through early electro -physiological records, which requires the dynamic activity of neurons in specific brain areas. However, these research methods have great limitations, because we do not know enough about the cell type of neuron groups. In recent years, with the rapid development of cell biology and molecular biology, neurological biologists have gradually achieved precise control of specific cells in the complex neurons in the brain. The type of nerve cells is identified, and we have greatly expanded our deep understanding of brain function. Nonetheless, we still lack effective tools to integrate data with neurotic cells with specific expression characteristics and brain function.

In order to solve the challenge of the research of the brain neuron group and the molecular manipulation of the cells, on September 15, 2022, the team led by Karl Deisseroth, a pioneer of brain science research from Stanford University in the United States, published on the CELL magazine entitled Cell. -Type-Specific Population-Dynamics of Diverse Reward Computation's research papers, by integrating large-scale electronic physiological records, calcium imaging and behavioral function records, develop a set of computing biological models based on large-scale experimental data, and excavate it for fors Study a new paradigm for computing biology of cell type specific biology.

Researchers choose the nucleus for research. This is because the nuclear group anatomy, transcription group, and ring road connection are special. For example, the nuclear structure is relatively simple, mainly divided into two major sub -regions of the outer and inner side -the outer reins on the outer side. The nuclear (LHB) mainly accepts information from the base brain, frontal lobe, hypothalamus, and base nucleus from the base, and projected into the stamped area and the middle sewing nucleus of the middle brain abdomen. The projection of nuclear groups and other nuclear groups is projected into the nucleus. Over the past few decades, the study of nucleus' cells has mainly concentrated in the neurons group expressed by two types of nucleus -expressed TAC1's nucleus neurons and the component neurons that express CHAT. Based on this, the researchers conducted StarMap in situ sequencing in situ in situ that highly expressed in the 15 inner nucleus, and confirmed the characteristics of TAC1 and CHAT nuclear neuron groups. In addition, the researchers divided the nucleus into 6 types of sub -groups (HB1 to HB6, Figure 1) based on the characteristics of the transcription group correction characteristics.
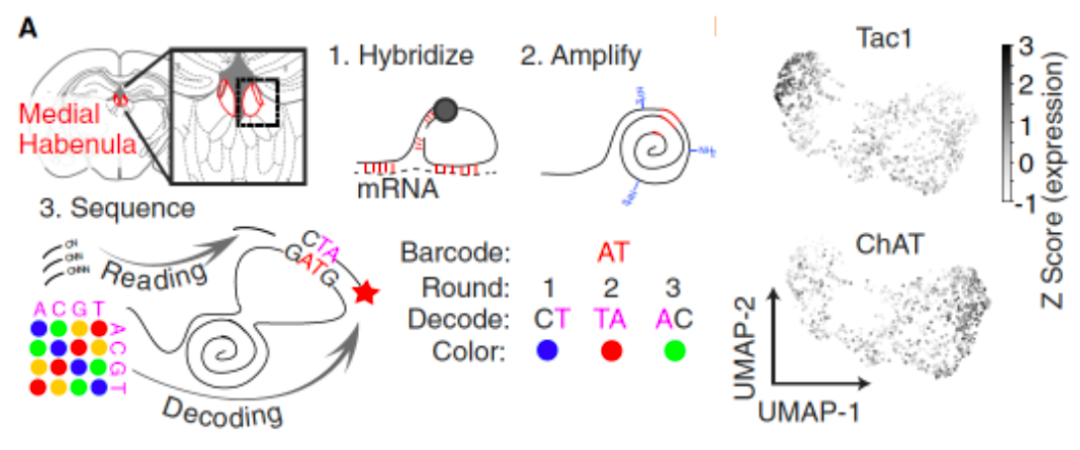
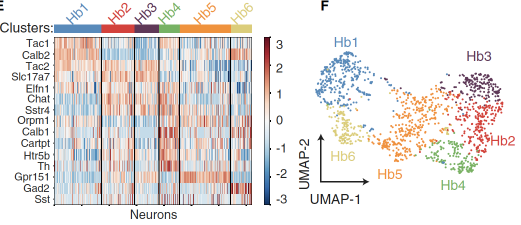
Figure 1. Molecular, anatomy identification of the inner nucleu nucleus type
Subsequently, the researchers used different mice models (TAC1-CRE, CHAT-CRE, Th-CRE, and Calb1-Cre) to verify the functional verification of the calcium imaging of these types of nuclear neuron, and use vision. The spatial task paradigm has studied the characteristics of different cell types of different cell types (Figure 2).这些缰核神经元群体对奖赏信息表现出不同活动性,其中缰核表达Th+神经元和表达Tac1+神经元的活动性最有特点——前者在小鼠接近奖赏区时表现出最大活动性,而The activity of TAC1+neurons reaches its peak in the reward consumption (Figure 2). These studies have shown that the nuclear neuron with a specificity of transcription levels has significant different functional characteristics -TH+Neuron represents the acquisition reward prediction clue, and TAC1+neurons are related to the results of the reward. In addition, researchers have also found that TAC1+Neuron has a long -term activity, which is manifested in the progress of its activity with the progress of the reward response and becomes more stable and lasting, reminding that its activity is affected by the reward experience.

Figure 2. The type of nuclear cell type shows a completely different activity on different reward information
Later, the researchers used the head fixed reward task to train mice, and combined with single -cell levels of twin -optical calcium imaging and single -channel level at the body electrical physiological record (Neuropixels 2.0 [2]), to TAC1+neuron activity The response is further studied (Figure 3). By recording the response of a single -cell level TAC1+neuron to a single reward event, the researchers observed that the TAC1+neurons show clearly increased activity on the reward.
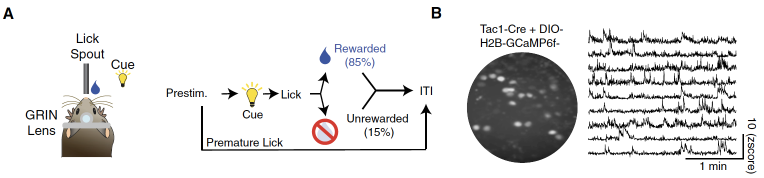
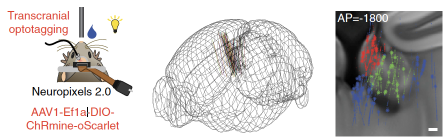
Figure 3. Cell -type specific calcium imaging records and electrical physiological records of single -cell and group levels
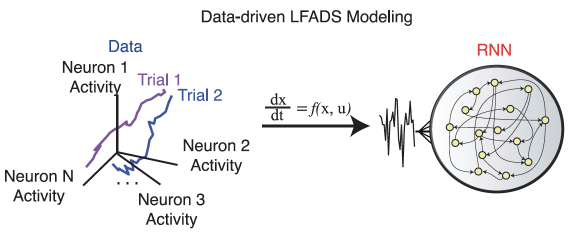
In order to integrate the experimental data of the cell -type specificity, the researchers used computing biological means -potential factors based on the power system (LFADS) to further develop TRLFADS related to cell types, which to cell -type specificity Electricity data and calcium imaging databases are integrated. This TRLFADS system can train a recursive neural network (RNN) (Figure 4). Through the average activity data of TAC1+neurons and TH+neurons in different trials, researchers have obtained the Neural Trajectory of these two types of neurons. Among them, only the trajectory of TAC1+neurons presents a continuous linear attraction (LINE ATTRACTOR), and TH+neuron shows point -like attractives -these geometric arrangements can store information storage in the range of neurons in different times. Logic relationship provides new important ideas. Figure 4. The LFADS model of neuron group activity
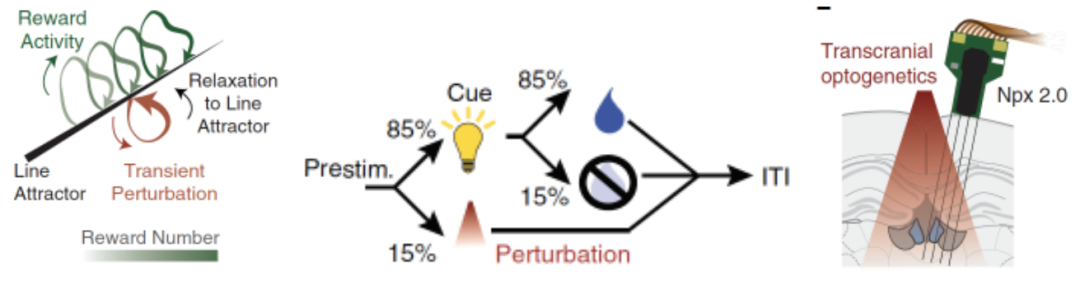
Finally, the researchers used the identified linear attraction to calculate the theoretical prediction of calculating biology on TAC1+neurons, and to verify the new experimental model. The mouse's mutual evidence of the characteristics of the experimental evidence (Figure 5). This computational biology model and experimental biology verification further reminds that the group activity of TAC1+neurons can be used as a linear attraction for integrating reward experience.
Figure 5. Using optical genetic control and reward experience control, the researchers conducted experimental verification of the dynamic model of the linear attraction
One of the two points of this article is to calculate the neurological biology model and a large amount of experimental biological data generated in the calcium imaging records and multi -channel records, and propose a TRLFADS model that can be used for training. This model can generate further test value. Experimental hypothesis. Using this model, the researchers found that the cell type of a specific expression of TAC1 neurons has a new characteristic of response to the reward experience. This research idea helps us to accurately find key biological functions with specific genetic characteristics and specialized brain distribution.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.20222.08.019
references
1. Contestabile, A., and Fonnum, F. (1983). Cholinergic and GABAergic forebrain projections to the habenula and nucleus interpeduncularis: surgical and kainic acid lesions. Brain Res. 275, 287–297. https://doi.org /10.1016/0006-8993 (83)90989-7.
2. Steinmetz, N.A., Aydin, C., Lebedeva, A., Okun, M., Pachitariu, M., Bauza, M., Beau, M., Bhagat, J., Bo¨hm, C., Broux, M., et al. (2021 APR 16). Neuropixels 2.0: a miniaturized high-the.
Want to know more exciting content, come and pay attention to BIOART biological art


- END -
Official announcement hints that the glory X40 color matching detailed configuration exposure: Snapdragon 695+120Hz curved surface OLED screen

After the official confirmation of@从 从 从 will be held on September 15th at 19:3...
"Nature" (Published 20220922) One -week thesis Guide

Compilation | Li YanNature, 22 september 2022, volume 609 Issue 7928Nature Septemb...