Known the earliest gibbon!It turned out to be it ...
Author:Changjiang Daily Time:2022.09.28

Ancient discovery 丨 Discover the earliest known gibbon -based stone! It turned out to be it ...
Paramoberia found in the Yuanmou Basin in Yunnan, a small ape fossil from 7 million to 8 million years ago, named Yuanmou small apes, and proved that this was the earliest known gibbon. The results have been published in the international journal "Human Evolution Magazine" recently.
The gibbon family exists 20 species, mainly living in tropical and subtropical regions in Asia. The gibbon fossils are very scarce, and most of them are found in caves in South China and Southeast Asia in my country.

Yuanmou Little Ape Life scene Formming. (Chen Yu painted)
Ji Xueping, the person in charge of the project and a researcher at the Institute of Animal Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced that more than 30 years ago, paleontologists have repeatedly discovered that they have repeatedly discovered the tooth fossils of the Yuanmou small apes representing multiple individuals. Later, in a field investigation, Ji Xueping accidentally discovered the left lower left side of the Yuanmou Xiaotong's lower left side of the osteotrophic stone. After repeated comparison with the current growth of the osperm, the specimen was initially confirmed that the specimen was a gibbon.
Later, the research team carried out high -precision CT scanning at the Institute of Cardiac and the Ancient Human Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences to determine that this facial keton belongs to a gibbon young individual, with age between 17 and 22 months. Based on the proportion of the teeth, the ape of the Yuanmou small ape is approaching the current auspicious average weight, about 6 kg.
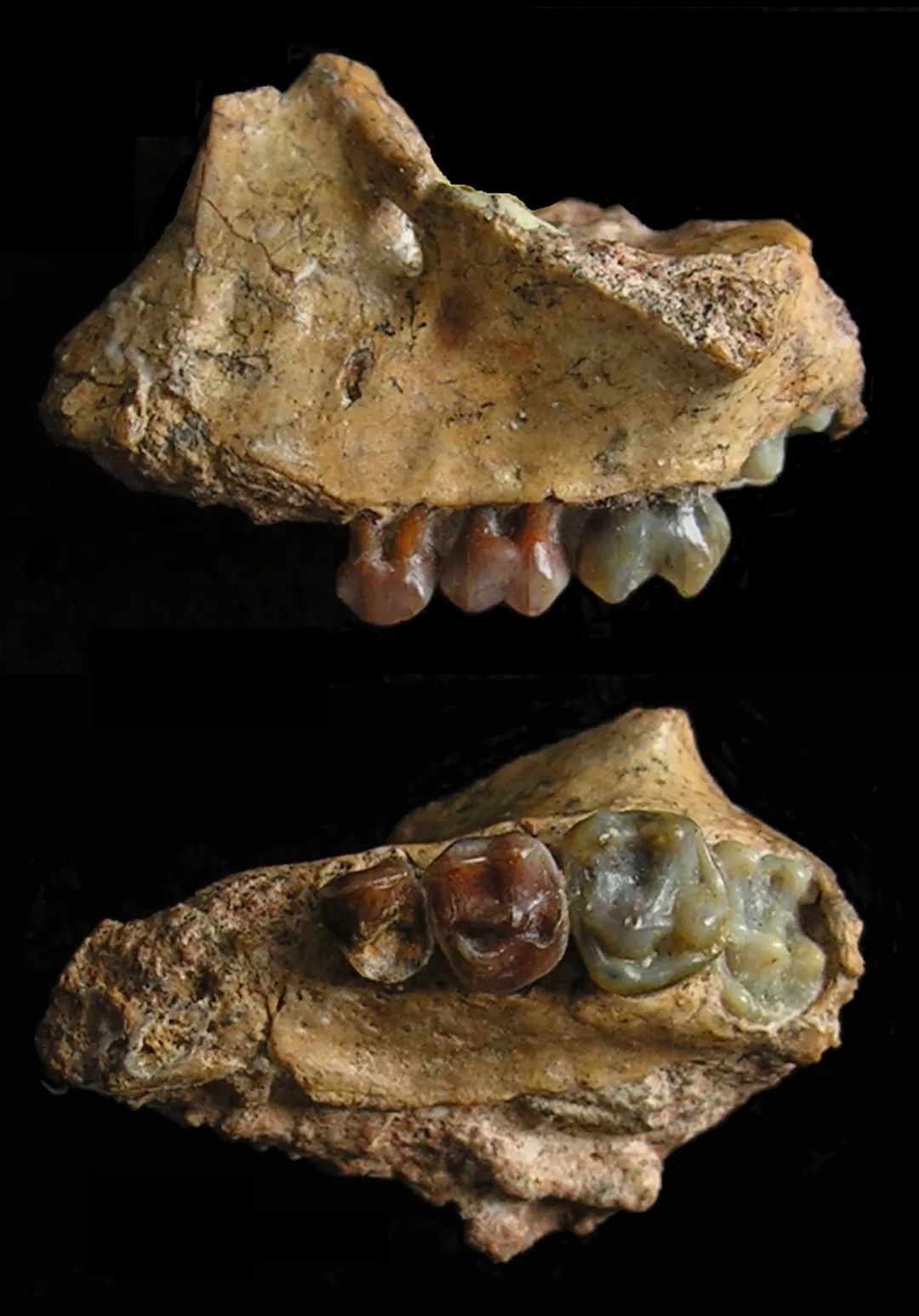
Yuan Mou's young apes are osteotrophic. (Photo by Ji Xueping)
After in -depth research, the morphological characteristics of the teeth and facial bones of the Yuanmou small ape are very similar to the current growth cubs, especially the crown gibbon, but some tooth characteristics appear more primitive. "Although Yuan Mou's small ape specimen is relatively scarce, the discovery of key materials let us finally confirm that Yuanmou's ape is the most likely direct ancestor for the current growth of the aim." Ji Xueping said.
Genetics research shows that the time of the chronicle of the gibbon from the ancestors of the people and apes is 22 million to 17 million years ago, and the time of differentiation of gibbon ancestors is about 8 million years ago. "This shows that the origin time of molecular evidence is basically consistent with the origin time of the gibbon inferred by fossil evidence. The results of paleontology and molecular biology research can be confirmed." Ji Xueping said.

The three -dimensional animation of the small ape's face bone. (Produced by Hou Yemao, the Institute of Ancient Poilis and Ancient Human Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences)
According to reports, the discovery of Yuanmou's small ape filled a section of gap in the history of East Asian small ape evolution. The achievement was completed by the Kunming Animal Museum of the Institute of Animal Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Human Origin Research Center of New York University, and the Institute of Ancient Human Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
(Source: Xinhua News Agency: Yue Ranran Poster Design: Jin Di)
【Edit: Shang Pei】
For more exciting content, please download the "Da Wuhan" client in the major application markets.
- END -
Let the medicine be attributed to the public

Overview of science popularization of medical technical skills in Zhujiang Hospita...
Chinese scientists have obtained the first batch of cosmic viewing field X -rays focusing on imaging sky maps
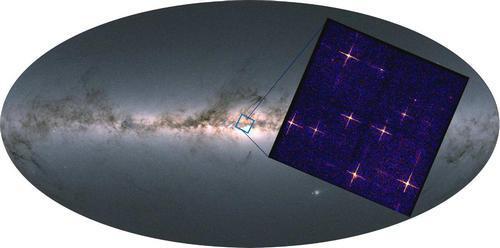
On August 27th, at the Second China Space Science Conference held in Taiyuan, rese...