What are the heart toxicity of immunotherapy?How to treat?
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.09.05
*For medical professionals for reading reference
Organize a article!
Immunohistochemicals (ICIS) have been widely used in tumor patients, but its extensive immune -related adverse events (Irae) cannot be ignored. Programming cell death protein-1 (PD-1) and programmatic cell death ligand-1 (PD-1) in human cardiac muscle cells, so the application of PD-1/PDL-1 inhibitor may be the cardiovascular system Cause many adverse reactions.
This article summarizes the clinical manifestations of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors cardiovascular toxicity and potential pathological mechanisms and current diagnosis and treatment methods. This may provide a new perspective for monitoring early toxicity and establishing appropriate treatment for patients with ICI -related heart toxicity.
1
ICI -related clinical manifestations of heart toxicity
At present, the results of ICI clinical trials and the current clinical practice reports suggest a variety of manifestations of ICI-related heart toxicity, such as myocarditis, pericardial diseases, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, and even non-inflammatory left ventricular dysfunction, such as Tako-TSubo myocardial myocardial myocardial myocardium myocardium myocardium myocardium Disease [1] (Figure 1). Some can be expressed as rapid progress, and rapid progress in a few days or weeks after ICI treatment; some can be manifested as chronic diseases, which can lead to a significant increase in the incidence and mortality rate of cardiovascular disease in the long run [2].
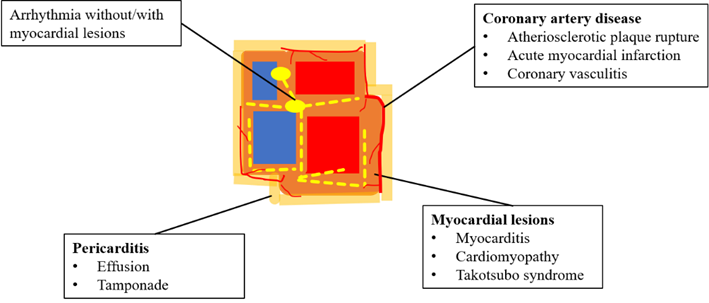
Figure 1 clinical manifestations of ICI related heart toxic damage
1. Myocarditis
ICI -related cardiocarditis, which is acute and outbreak, is the main early ICI -related cardiovascular adverse event (CAES), of which about 30 days after the start of ICI treatment. ICI -related cardiomyphyle -related manifestations are diverse. Light can be manifested as non -specific discomfort, pulmonary edema or acute heart failure, and severe cases can be manifested as cardiac shock, ventricular arrhythmia, multi -organ failure, and even death.
2. Enterprise disease
ICI -related pericardial diseases include pericarditis, pericardial efficiency and pericardial filling. ICI -related carditis can occur alone, and can also be combined with myocardial suffering and myocarditis. The initial symptoms of ICI -related cardiac diseases include chest pain and rapid respiratory. In severe cases, it can quickly develop into respiratory failure. In terms of signs, patients may have signs of pericardial friction, pericardial filling or narrowing, such as cervical vein dilation, Kussmaul ’s signs, strange pulse, pericardial friction sound, pericardial pitch, and foot edema. ECG changes in patients with ICI -related cardiac percaser include PR decrease, extensive saddle ST segmentation, low QRS wave voltage and T wave inverted.
3. Cardiac disorders and conduction diseases
ICI treatment can also lead to cardiac conduction diseases, including atrial fibrillation, ventricular arrhythmia (ventricular heart tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation), and atrioventricular conduction block (Ⅱ degree or complete atrioventricular block). The highest incidence of ICI -related arrhythmia is the premium arrhythmia, including tachycardia of sinus, frequent premature beats, atrial tachycardia, atrial fluttering, and even atrial fibrillation. ICI -related conductive diseases can be manifested as PR intercourse extension and bounted conduction block. In severe cases, it can be manifested as a complete room conduction block or even heart stopping.
4. Myocardial infarction
Patients using ICI may have stable angina pectoris and acute coronary syndrome. The characteristics of myocardial infarction are sudden chest pain, electrocardiogram showing ischemic changes (such as higher ST section, low ST segment pressure or T wave inverted), myocardial calcium protein, ultrasonic cardiac percentage diagram, or heart MRI. abnormal.
5. Non -inflammatory left ventricular function damage
ICI treatment can also lead to non -myocarditis left ventricular functional damage, that is, non -inflammatory manifestations, only manifested as functional damage. ICI-related left ventricular functional damage has a variety of manifestations, such as dilated cardiomyopathy and Tako-TSUBO cardiomyopathy with functional damage to the left ventricular function.
6.ici related valve dysfunction
According to reports, ICI can lead to valve dysfunction, such as medium -weight aortic valve, mitral valve and triral valve reflux. In addition, these lesions are mostly accompanied by myocardial degeneration, such as myocarditis or dilated cardiomyopathy.
2
ICI -related heart toxic diagnosis and treatment
1. Diagnosis and assessment of cardiac toxicity related to heart:
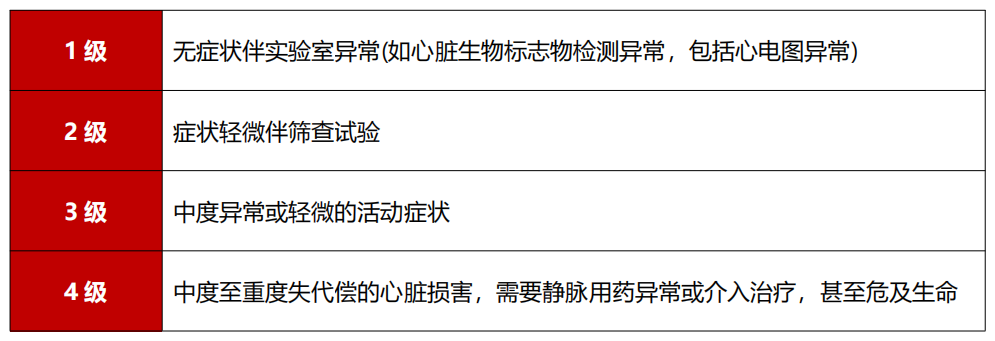
Cardiac damage to ICI correlation needs to be determined and evaluated the severity of cardiac toxicity [5]. At present, the severity of ICI -related heart toxicity can be divided into level 4 (see Table 1). In addition to oncology experts, the clinical team of the oncology department should also include a cardiovascular system expert to detect cardiovascular diseases early before the start of tumor treatment, in order to provide the best treatment plan for patients with tumor patients.
Table 1 ICI related heart toxicity severity
For patients with suspected ICI -related heart toxicity, it is recommended to conduct relevant diagnosis and examination, including ECG, chest X -ray, ultrasonic heart -motion, cardiac biomarkers (including creatine kinases and myolatamin), inflammatory indicators (including ESR, CRP, and WBC count) and BNP, NT Pro-BNP and anti-horizontal muscle antibody levels. In addition, heart f FDG PET/CT also helps to detect myocarditis. In cases that are not clear or uncertain, the endometrial myocardial biopsy is necessary.
2.ici -related heart toxic treatment strategy:
The treatment strategy of ICI -related cardiovascular complications is divided into three aspects:
① Stop using ICI to prevent further toxicity;
② Supportive treatment of cardiac complications;
③ Application of excessive inflammation of inflammation. Because ICI's functional half -life is long, stopping ICIS may not immediately reverse its heart toxicity. Deciding whether to stop ICI treatment requires comprehensive discussions between oncology experts and cardiovascular experts. At present, some guidelines are recommended to stop ICI treatment when patients with level 3 or level 4 ICI -related toxicity.
If necessary, patients with ICI cardiac injury can receive effective support treatment. Patients with heart failure should receive drug treatment recommended including β-receptor blockers and guidelines such as ACEI/ARB.
For excessive active T cell reactions, immunosuppressive therapy can also be used. At present, it is believed that the first -line immunoscopic drugs of ICI -related myocarditis are corticosteroids. At present, ASCO guidelines recommend oral or venous injection of large dose of cortexyl steroids.
summary:
ICI treatment has expanded to covering a variety of cancer types, and more patients have benefited from new immunotherapy. But they also experience serious Irae, which usually forces them to give up treatment or cause death.
Although ICI -related heart toxicity is relatively rare, it is often severe and fatal once it occurs. Due to the incomplete and controversial interpretation of cardiac toxicity caused by excessive activation of T cells, this greatly limits the modification of clinical treatment solutions and the development of new therapy. With the continuous and in -depth research on the pathological mechanism of ICI -related heart toxicity, it may provide new theoretical basis for early discovery and intervention of ICI cardiac toxicity.
references:
[1] Lyon AR, YouSaf N, Battisti N, Moslehi J, Larkin J.immune Checkpoint Inchibitors and Cardiovascular Toxicity.lancet oncol.2018.19 (9): e447-e458..
[2] han d, do, li h, ma t, yu w, song l.cardiac adverse events of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in Cancer Protocol for a Systematic metWork Meta-Analysis: a Protocolol Review.Medicine (Baltimore) .2020.99 (5): E18701.
[5]Zhou YW,Zhu YJ,Wang MN,et al.Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Cardiotoxicity:Current Understanding on Its Mechanism,Diagnosis and Management.Front Pharmacol.2019.10:1350.
The first release of this article: the medical world tumor channel
Author of this article: Wei Jia
Editor in charge: Sweet
- END -
Donghu High -tech Zone 323 Tackling Action Regional Prevention and Control Center settled in this hospital
Wuhan Evening News July 14th (Correspondent Jiang Hongying Li Yan) On the 14th, the licensed ceremony of the 323 Institute of Action Regional Prevention and Control Center of Donghu High -tech Zone wa
Diet, not pay attention to the heart of the heart, cause the upper body
There is a kind of human and animal disease, fever, sweating, muscle pain, fatigue ... this is a disease, also known as lazy disease. In the first seven months of 2022, Luoyang found 432 patients wi