Affiliated to Ruijin Hospital and Renji Hospital achievements "Liu Ye Dao" and "Nature" sub -journals
Author:Shanghai Jiaotong University Time:2022.09.25
Shanghai Jiaotong University Medical College has always insisted on writing scientific research on the forefront of world science and technology, writing scientific research papers on the chapter of people's health, and constantly exploring more efficient treatment methods to help patients benefit. Recently, the scientific research team of Ruijin Hospital and Renji Hospital affiliated to the Affiliated Ruijin Hospital and the Renji Hospital have the courage to innovate and dare to break through, and release the latest research results to bring patients with new treatment and treatment of treatment.
Explain the importance of protecting the elderly during the new crown epidemic
"Liuye Knife" published the heavy results of Ruijin Hospital affiliated to the Affiliated Hospital
Recently, Professor Wang Weiqing, the Department of Endocrine metabolic metabolic metabolic metabolism of the Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, the Shanghai Institute of Endocrine metabolism, and the National Metabolic Disease Clinical Medicine Research Center. Protecting Older People: A High Priority During the Covid-19 Pandemic. The importance and feasibility strategy of protecting the elderly during the new crown epidemic were explained.
Recently, the new crown Omikon outbreak has affected in many areas of China. In Shanghai, the new crown -related mortality rate is low, which may be due to the high vaccination rate. However, the vaccination rate of the elderly is low. The investigation by the research team conducted a survey conducted by the Metabolic Management Center (MMC) in Shanghai. Among the 39,498 diabetic patients, the vaccination rate of vaccine enhanced needles over 60 years old was less than 60 or less (36.6%vs.45.0%). In the country and other countries, the vaccination rate among the elderly is also low. In addition, during the epidemic period, more than 90%of Shanghai's new crown -related deaths occurred among the elderly who did not vaccine, and 84.6%of Hong Kong's related deaths occurred in the elderly who vaccinated 0 to 1 vaccine. These all show the importance of vaccination for the elderly.
At present, the aging population has become a worldwide issue. In 2021, the results of our population census suggest that this problem is more severe in China. Population aging is accompanied by rapid increase in age -related diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. Therefore, in the face of the double burden of population aging and the new crown epidemic, how to take measures to protect the elderly from the new crown infection not only to China, but also for many medium -income countries that face the same problems during the epidemic. Matters.
Based on this, the research team first used the traditional culture of my country's traditional culture and early new crown epidemic prevention and control. At the same time, combined with Shanghai MMC survey data, it focused on analyzing the potential causes of relatively low vaccination rates of early elderly people.
On this basis, the feasible strategies and thinking of protecting the elderly in the elderly are further proposed:
How to alleviate public concerns and promote vaccination of the elderly; how to combine the slow disease management center in the hospital such as MMC and long -term care services to provide better slow disease management and continuous care for the elderly; The vaccine of the plant is developed, and the clinical approval process is simplified to cope with the rapid mutation of the new coronary virus; and for the elderly who have the contraindications of vaccination, how to find other methods to establish a protective barrier.
As a result, the article provides a Chinese perspective for the global response to the new crown epidemic through the comprehensive thinking of protecting the elderly during the epidemic period, and provides a reference strategy for fully realizing healthy aging during the epidemic.
For the first time, the new Pan -based research method is used for human tumor genome research
"Nature" sub -publication published the latest research results of Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Ruijin Hospital
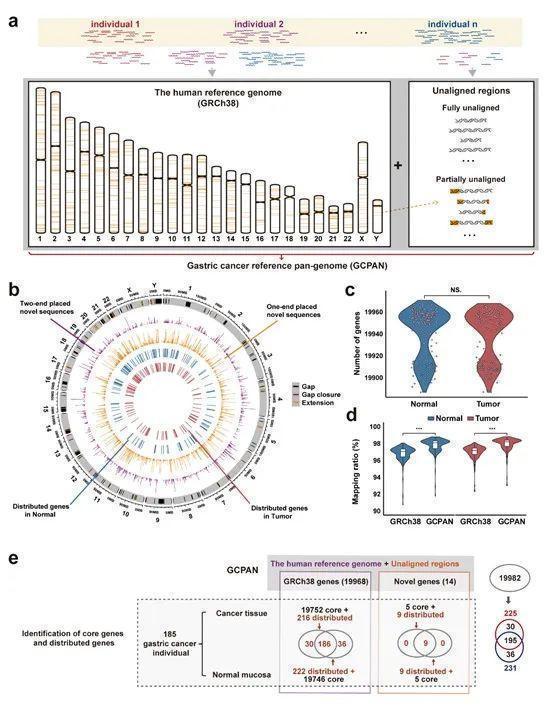
Recently, Yu Yingyan and Zhu Zhenggang, Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, published an entitled "Pangenomic Analysis of Chinese Gastric Cancer (DOI: 10.1038/S41467-022-33073-7) in the international authoritative journal" Nature Communications "online. (Analysis of the Pan -Bersene Study of Chinese Stomach Cancer). For the first time, the study used a new pan -based research method for human tumor genome research. By constructing a pan-genes in the gastric cancer crowd, and then using the pan-genes as a reference to compare the sequencing data of each whole genome, the existence of the gastric cancer individual genome-missing new mutations. In the sequences that cannot match the reference genome, there is a set of new genes missed in the genome of human reference genomes. Research results provide important references for analysis of the molecular genetic background of the high incidence of Chinese gastric cancer.

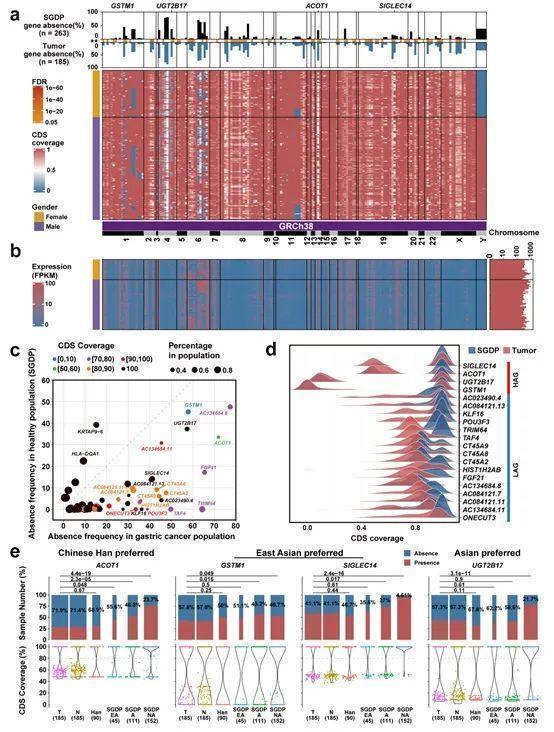
The "sketch" of the human reference genome released in 2001 is a major research result of the international human genome program, which greatly promotes the research of disease genome and cancer genome. Because DNA samples that build human reference genes are taken from a few donors, there are genomes of genome in different regions and different races in different regions and race. Pan -based group refers to the sum of all individual genomes in a group. Compared with a single human reference genome, it can reflect genetic diversity. It may be more appropriate to use Pan -based genetically as a reference in human disease -related genome research. Stomach Cancer Research Team of Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine and the School of Life Science and Technology of Shanghai Jiaotong University together with the Genomics Research Team of Life Sciences and Technology of Life Sciences and Technology, and a number of research teams including Fudan University Affiliated Cancer Hospital and Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine University. Scientific and technological research has independently established the application research on the application samples of the Genome Biology, 2019, 20: 149) and this gastric cancer genome (2022, 13: 5412). In this study, Hupan analyzed the depth sequencing data of 185 gastric cancer and cancer tissue (370 samples), and constructed the gastric pan -based gastric cancer pan -based gastric cancer pan -based gastric cancer pan -based gastric cancer in the human reference genome (GRCH38) and 80.88 MBP. Among them, the new sequence contains at least 14 new genes. The individual genome is compared with a pan-genes as a reference to identify the new type of genetic mutation of the individual of the gastric cancer-the presence-absence variations (PAVS). A total of 261 non -essential genes were found among the gastric cancer crowd, of which 195 non -essential genes belonged to cancer and cancer tissue coexistence (186 person reference genome genes and 9 new serial genes). Comparing these genes with different racial health groups in public databases in the public database, it is found that some non -essential genes can increase gastric cancer sensuality. For example, non -essential gene ACOT1, GSTM1, SIGLEC14, and UGT2B17 are significantly higher than that of other people.
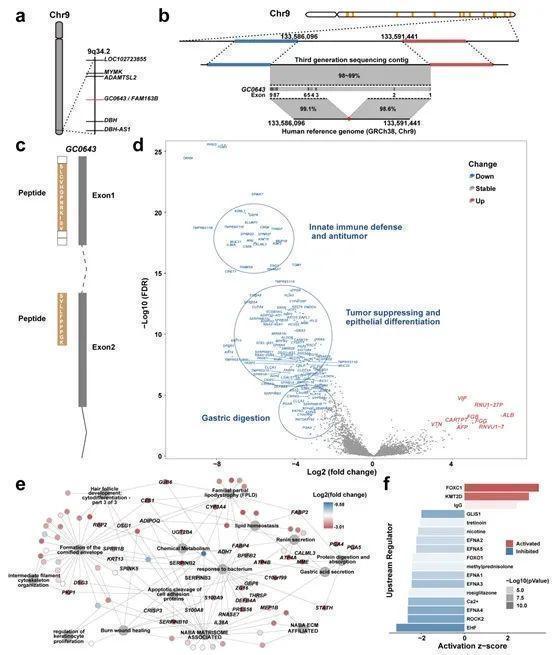
For new genes predicted by sequences outside the genome of humans, the research team uses three -generation long -reading long -reading sequence to conduct chromosomal positioning research, and successfully positions the new gene GC0643 to 9Q34.2 sites.
The use of the cell system to express the GC0643 gene in the body to significantly inhibit tumor cell growth, migration invasion, cell cycle progress, and promoting the apoptosis of cells. This tumor inhibitory effect can be reversed through genes. GC0643 new gene has been certified by the International NCBI database (Genbank: MW194843.1).
The first item is completely targeted at the Chinese crowd
The clinical study of the development of Ilidic acid hydrochloride combined with 5-FU/LV second-line treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer and obtained positive results
Affiliated to Renji Hospital International Stage International Stage China Plan
One of the world's three top tumor scholars in the 2022 European Cancer Internal Science Society (ESMO) Annual Conference kicked off in Paris, France on September 9, 2022. On September 10th, at the digestive system tumor special "MINI ORAL Session: GI, Upper Digestive", a study brought by Professor Wang Liwei, Director of the Cancer Department of Renji Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine (the summary number number of the conference : LBA61) Dampered on the ESMO International Stage. This study is the first clinical study of the Ilideye Development Lipstick Injection of Ilideyin Dippermine in the Chinese population combined with 5-FU/LV second-line two-line two-line treatment and obtaining positive results.
Obaclar tube adenocarcinoma is one of the common high malignant tumors. The Globocan database of the World Health Organization International Cancer Research Agency (IARC) shows that nearly 500,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer worldwide in 2020 have about 120,000 new cases in China, accounting for about 25%of the world, and to the people The health and life have a huge burden. Due to the concealment of pancreatic cancer, the staging of the diagnosis is often late. Treatment depends mainly on drug treatment. However, the current standard treatment plan for pancreatic cancer is very limited. In addition to choosing the first-line treatment of the unused Jesitabin as the basis or 5-FU Basic solutions, almost facing the dilemma available for use.
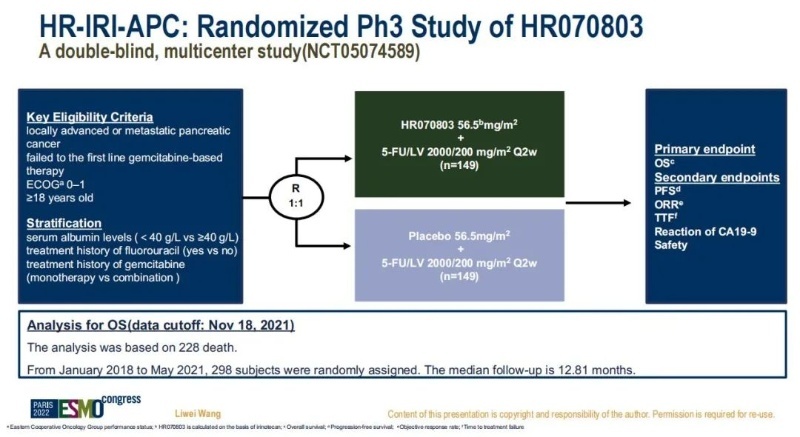
The HR-IRI-APC Studies were led by Professor Qin Shuyi of the Eastern Theater General Hospital and Professor Wang Liwei of Renji Hospital. It is a national multi-centered, random, double-blind, and control phase III clinical study. Study explores HR070803 (Ilideylidine hydrochloride) combined with fluoropicidine (5-FU)/sub-folic acid (LV) scheme for first-line Geshabinbari treatment. ) The efficacy and safety. A total of 298 patients with 298 patients with the failure of the first-line Jesitabin therapy were local advanced or advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Study 1: 1 randomly entered the group and received HR070803+5-FU/LV schemes or placebo+5-FU/LV schemes until until until Development or intolerance. The main research finals are the total survival period (OS), and the secondary research end points include non -progressive survival (PFS), objective relief rate (ORR), safety, etc. The results of the study show that the HR070803 combined with the 5-FU/LV scheme for the first-line Giscitabine treatment fails to remove the LAPC or MPC compared to the comfort group. VS. 1.48 months), significantly reduced the risk of disease death and progress. The choice of second -line treatment of pancreatic cancer is very limited. Domestic drug clinical research is now in the trend of Xinxin. HR070803, as the first Chinese -developed pancreatic cancer second -line treatment, conducts phase III clinical research. Activation and safety are expected to become a standard treatment plan for second -line treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer, bringing new choices to patients with pancreatic cancer in China.
Source: Medical College
Editor on duty: Wang Ning
Editor in charge: Qi Jie
- END -
On August 29th, Gansu newly added local 0+37, specifically here →
August 29, 2022 Gansu Xinguan Pneumonia's epidemic situationThe information inform...
remind!Wearing a mask like this is likely to not wear it!Don't make these mistakes!

In daily lifeMany inadvertent habitsIt may be possible to cause pollution to the m...