Anwen Ling et al.
Author:Institute of Geological Earth Time:2022.09.08


The Yangtze River is the largest river in my country, accounting for about 36%of the total runoffs of the country, and has raised nearly one -third of the country's population. Most of the water energy resources in the Yangtze River Basin are concentrated in upstream areas. Under the background of global warming, extreme hydrological events in upstream areas have frequently occurred, which has an important impact on social production and people's life and property in upstream and middle and lower reaches. However, the upper reaches of the Yangtze River and the water station are sparse, and the measured materials of most stations are less than 60 years, which limits people's understanding of the rules of the characteristics of extreme hydrological events in the area. The upper reaches of the Yangtze River is mainly influenced by the Indian summer season. Most extreme hydrological events also occur in summer. Therefore, it is necessary to find a record of high -resolution, accurate annual accurate annual accuracy, and accurately reflect the changes in the summer runoff of the area.
With the characteristics of a wide range of spatial distribution, accuracy, high resolution, and good replica volume, the annual trees are becoming one of the preferred information on the preferred ones of climate change in the past. Compared with the traditional tree wheel width index, tree wheel oxygen isotope is affected by the "age effect" of the tree, which can retain more climate low -frequency signals. The trees in the monsoon area are affected by region evaporation and precipitation oxygen isotope, which are closely related to the summer (tree growth season) precipitation. At the same time, changes in river runoff are also mainly affected by summer precipitation. Therefore, tree -wheel oxygen isotonophyllin can be used for reconstruction of changes in the changes in rivers in the summer of rivers.
In order to understand the changes in extreme hydrological events upstream of the Yangtze River and its response to global warming, the Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Geology and Earth Physics Research Institute of Geological and Environmental Academy Key Laboratory Research Researcher An Wenling and other researchers in China The Chengdu Plateau Meteorological Research Institute was held in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River (Baiyu County, Ganzi Prefecture, Sichuan) in 2017 (Figure 1).
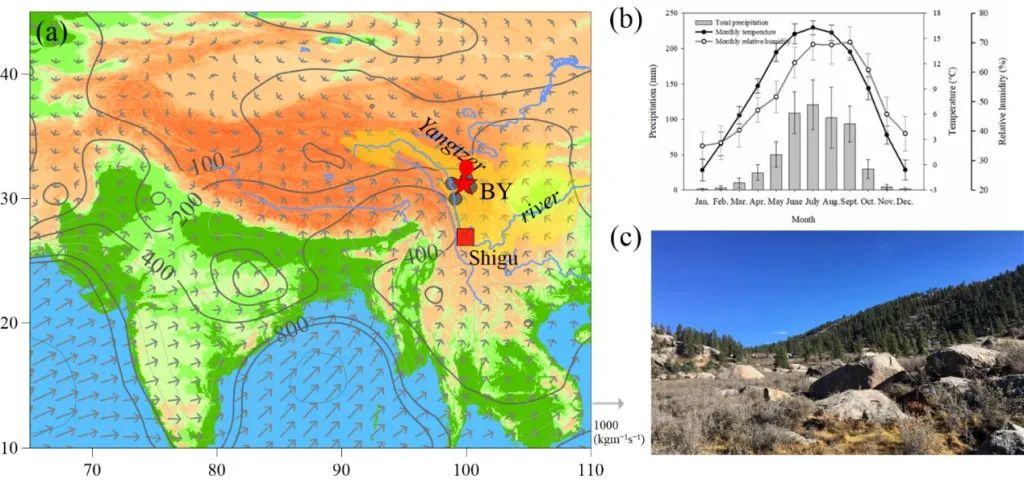
Figure 1 Study regional geographical location (A) and regional climate characteristics (B), sampling environment (C)
Through the measurement of 3067 samples of 6 cords, the research team established a tree-oxygenotor sequence in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River over the past 700 years (1260-2017).根据树轮氧同位素与夏季(6-8月)径流量的高度相关关系(相关系数为-0.72,自由度为67),他们重建了长江上游过去700多年来的夏季(6-8月)径Flow changes, the interpretation variance is 51.3%(Figure 2).
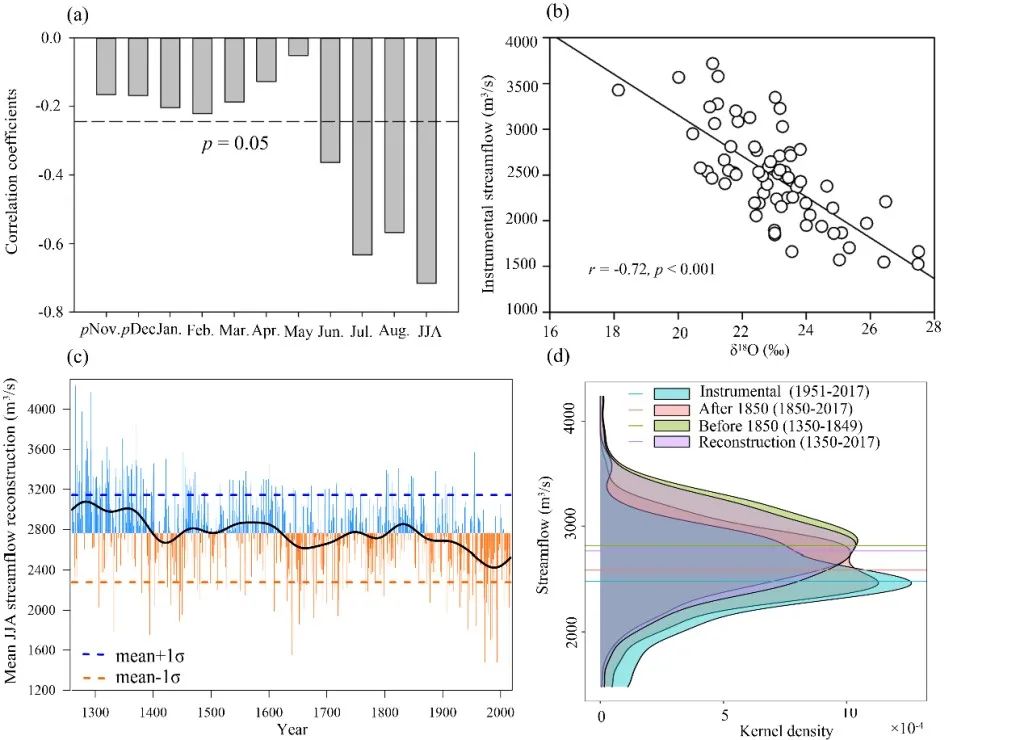
Figure 2 The reconstruction of the summer of the Yangtze River in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River based on tree wheel oxygen isotope sequence. (A) Analysis of tree wheel oxygen isotope and monthly flow flow; (b) reconstruction equation; (C) reconstruction sequence); (D) the probability density analysis of reconstruction sequence
The reconstruction sequence shows that the summer of the upper reaches of the Yangtze River has declined, especially the runoffs in recent decades have the lowest value in the past 700 years. Based on the reconstruction sequence, the reappearance period of extreme drought and extreme floods (average ± 1 standard deviation) was analyzed in the four periods: reconstruction period, before 1850, and after 1850, and the test period. Studies have found that the reproduction period of extreme drought events has been significantly shortened since 1850, and the reappearance period of flood incidents is relatively stable (Figure 3). At the same time, with 30 years as a window, the time change sequence of extreme drought and flooding incidents (Figure 4). The results showed that extreme drought incidents showed the characteristics of many ages, and the extreme drought incidents have increased significantly in more than 100 years. This shows that in the context of global warming, the frequency of extreme drought in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River has increased significantly, and in recent decades, it has been the most incidental incident in the past 700 years.
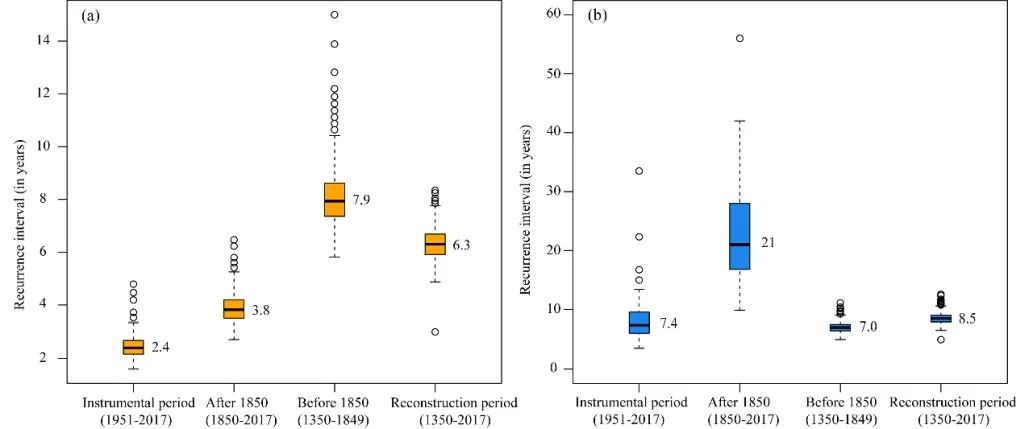
Figure 3 Extreme drought (A) and flood incident (b) Reapped period analysis
Further analysis found that at the age of the age to the age, extreme drought and floods were mainly controlled by the Indian summer season (Figure 4). In the context of the global temperature increase, the temperature difference between sea and land decreases, and the summer wind in India has weakened, resulting in a decrease in water vapor conversion, resulting in an increase in extreme drought incidents, and decreased in extreme floods. At the same time, the increase in regional evaporation may also lead The reason for the increase.
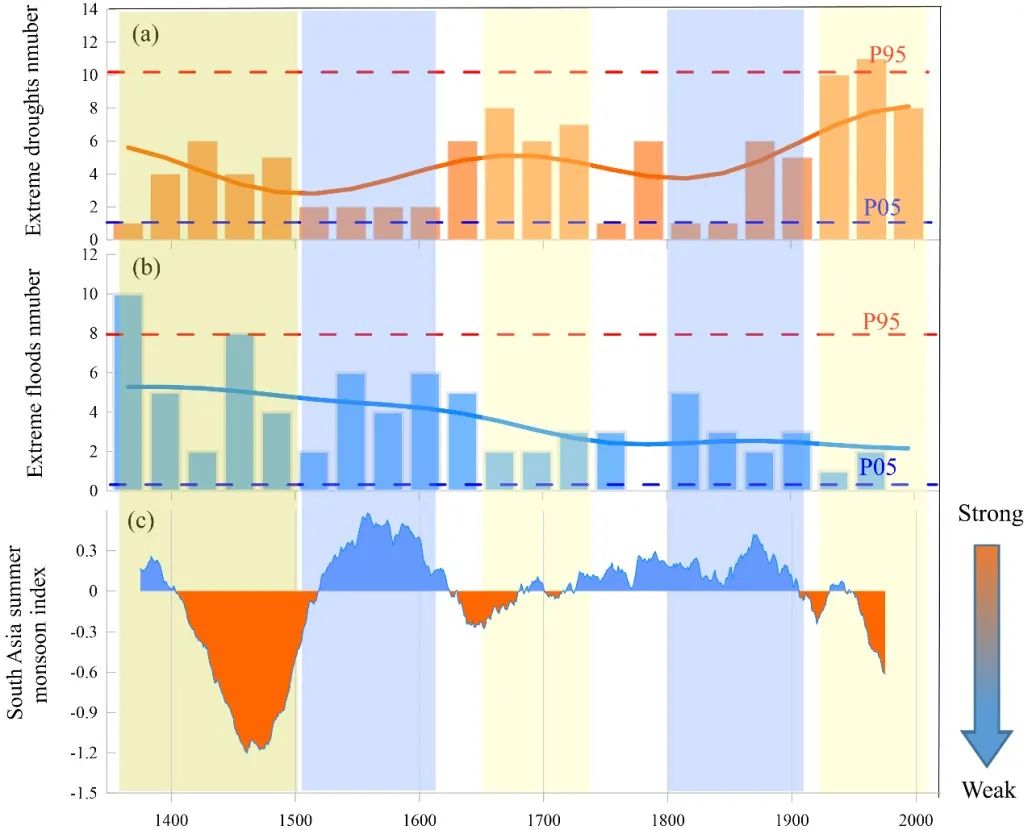
Figure 4 The relationship between extreme drought (A) and flood incident (B) and its relationship with Indian summer monsoon (C)
The above results revealed that the global warming caused extreme drought in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River frequently. According to the recent model results, in the context of rising temperatures, India's monsoon changes will increase and regional evaporation will also be enhanced. In the future, this area may face more extreme events.
The research results were published in the international academic journal JGR-ATMOSPHERE (An Wenling, Li Jinjian, Wang Yan, Xu Chenxi*, Shao Xuemei, Qin Ningsheng*, Guo Zhengtang. Hydrology Extremes in the Upper yangtze river over the passRecord [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 127, E2021JD036109. Doi: 10.1029/2021jd036109).Studies have been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41772173, 41888101, 42022059, 41630529, 41877457).Beautiful editor: Chen Feifei

School pair: Wanpeng
- END -
@, The problem you care about here are here!

Ask the people's voice and ask, dare to askAnswer the promise, do not push or avoi...
Tunchang: All medical institutions shall not refuse the diagnosis without nucleic acid negative proof and health code "yellow code" personnel
In order to effectively protect the demand and order of medical treatment during the prevention and control of the epidemic prevention and control, and the health code yellow code personnel for medi