What geological disasters can climate warming?
Author:Institute of Physics of the Ch Time:2022.09.16
Although the autumn has arrived, the friends who are reading this article may be impressed by this year's high temperature weather, and some are still suffering from high temperatures. Although the news of "the coolest in the next ten years" has been rumored, in the context of global warming, the global temperature continues to rise year by year but it is an indisputable fact (Figure 1). In the face of high temperature, we can still choose to live in the air -conditioned room to enjoy cooling, and the rivers, lakes, mountains and rivers of nature have to be exposed to the scorching sun. What geological disasters can climate warming?
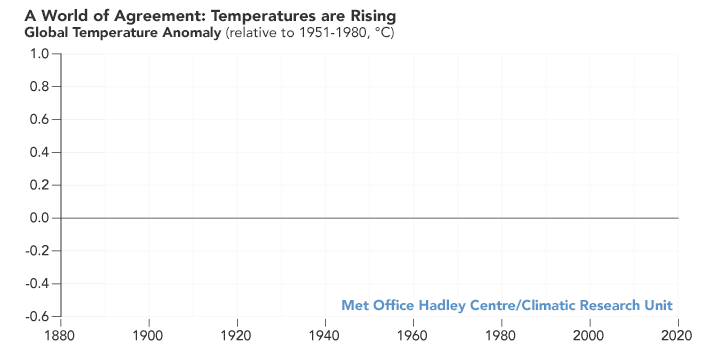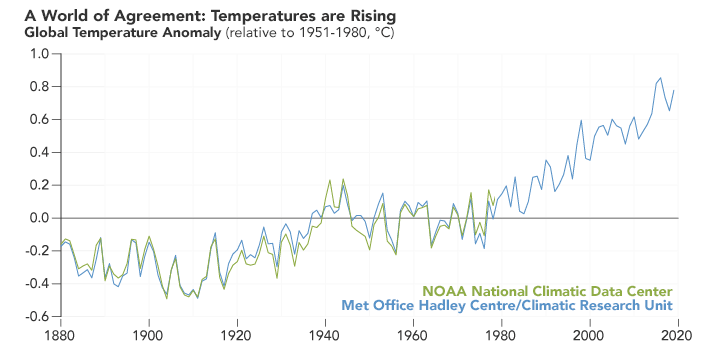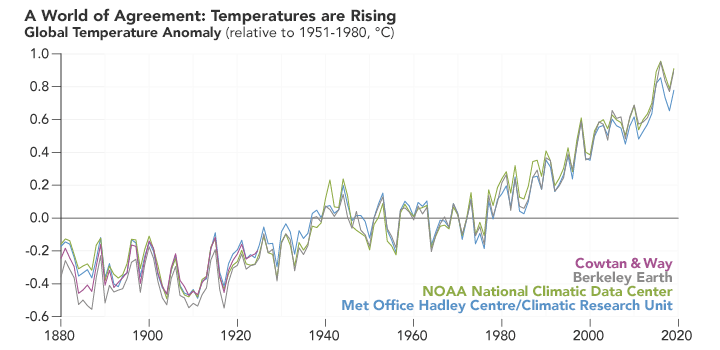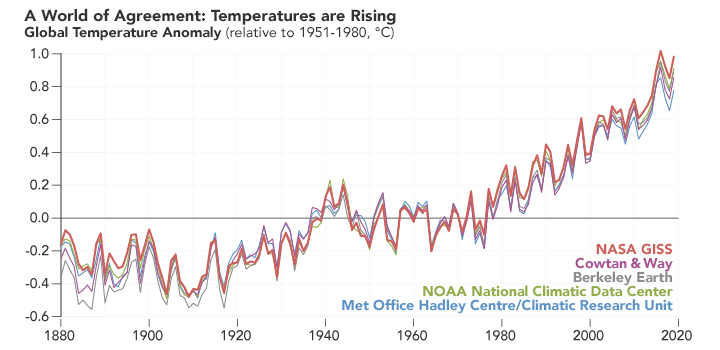
Figure 1 Global temperature change map measured by multiple institutions
(Picture source: NASA)
Glacier Melting
Under the influence of global warming, glaciers are the first. It can be seen through the global temperature change map that the temperature changes in high -cold regions such as polar, Greenland, and my country in Qinghai -Tibet. And this is the area of glaciers.

Figure 2 Comparison of global temperature and average value of 1951-1980 from 2021.
It can be seen that the polar areas are the most affected by global warming.
(Picture source: NASA)
Under the influence of global warming, glaciers show a trend of accelerated retreat. According to satellite images, 75%of the world's glaciers are shrinking, and only 8%of the area increase. NASA's satellite monitoring data shows that in the four years of 2003-2007, the land glaciers on the earth, North American Alaska and Arctic Greenland melted more than 2 trillion tons.
Oak Glat, located in Iceland's capital Reykjavik, was formed about 700 years ago, but in just more than 100 years, the area was reduced from 16 square kilometers to less than 0.7 square kilometers. It was officially declared in 2014 that "Death" became the first glacier to be declared death. On August 18, 2019, the main officials and scientists of Iceland went to the original site of the glacier to hold a "funeral" for glaciers. It is engraved with "a letter to the future" on its tombstone, hoping to call on the impact of global attention to the impact of climate warming on glaciers.

Figure 3 comparison before and after Okjokull
(Picture source: NASA)

Figure 4 On August 18, 2019, people held a "funeral" for Oak Glacier.
(Image source: https://viaggi.corriere.it/eventi/islanda-funerale-ghiacciaio-Okjokull-seva-project/))))))
In China, the problem of glacier ablation is equally severe. China is the world's glacier resources. According to statistics from China's first glacier catalog (carried out from 1978-2002), a total of 46,377 glaciers in China, with a total area of 59425km; and the "China Second Glacier Video" released in 2014 shows that the area of China exceeds 0.01km more than 0.01km There are 48,571 glaciers, with a total area of 51766km. In just two or three decades, the glacier in China has decreased by about 20%.

Figure 5 is located in the Hailugou Glacier of Gongga Shandong Slope, Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
(Picture source: Hailuogou Scenic Area official website)
The rapid melting of glaciers will bring many catastrophic consequences. The most serious of which is the rise of the sea level. According to NASA data, the global sea level has increased by 20 cm from 1870, and the speed of the sea level rising is also accelerating From 2.5 mm/year in the 1990s, it increased to the current 3.4 mm/year. The report issued by the Antarctic Science Research Committee (SCAR) shows that the melting acceleration of the western Glacier in the Antarctic Antarctica is expected to rise by 1.4 meters by the global sea level meeting in 2100, and more than 10%of the world's population will lose the land that survives.

Figure 6 NASA's global sea level change from 1992-2014 based on satellite data analysis. (Picture source: NASA)
At the same time, glacier melting is also a huge resource loss. On the earth, 85 % of the freshwater resources that humans live in about 2825 × 10km are stored in glaciers. Glacier ablation will greatly affect the hydrological and ecological environment. At the same time, the melting of glaciers will also greatly increase the instability of glaciers, which will cause a series of disasters.
Ice Avalanche/Glacier Collapse
Like the collapse of the rock body, the ice collapse refers to the large ice body and even the whole glacier on the slope with a large slope. Phenomenon is the most intense form of glacier disaster. Historically, the ice -lavexture disaster has occurred many times, but often smaller and low frequency. In recent years, the ice -collapsed disaster has frequently occurred, the scale has also been large, and the cause is closely related to climate warming. On the one hand, the melting of glaciers itself will increase the instability of the ice body. On the other hand, the melting water into the crack will also cause pressure on the ice body and lubricate, which greatly increases the risk of collapse.
Table 1 As of 2016, there are records of large ice -collapsed disaster records in history

On July 17, 2016, the Glacier 53 Glacier in the Ali District of the Ayu District of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau my country was broken from about 5,800 meters above sea level. When 9.4 square kilometers, 9 people were killed. Two months later, the No. 50 glaciers on the south side also occurred. Such a large -scale ice collapse occurred in the northwestern region of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau, which has always been stable in glacier activities, which is rare, which has caused great response at home and abroad. Figure 7 Remote sensing map of Glacier Ice Light, 53, Tibet.
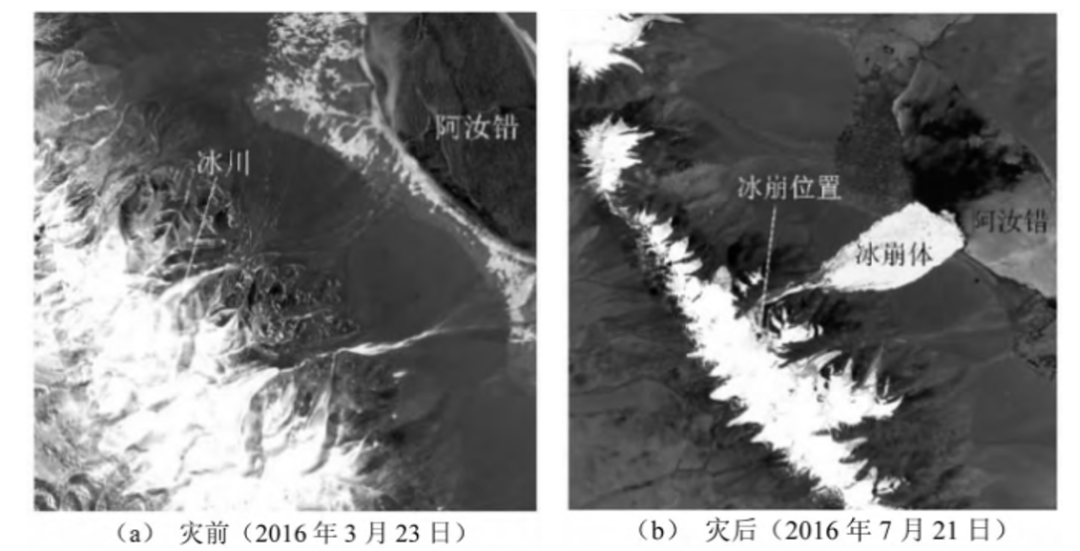

(Picture source: Literature)
Figure 8 After the Ali Binglu, the rescue team was implementing rescue.
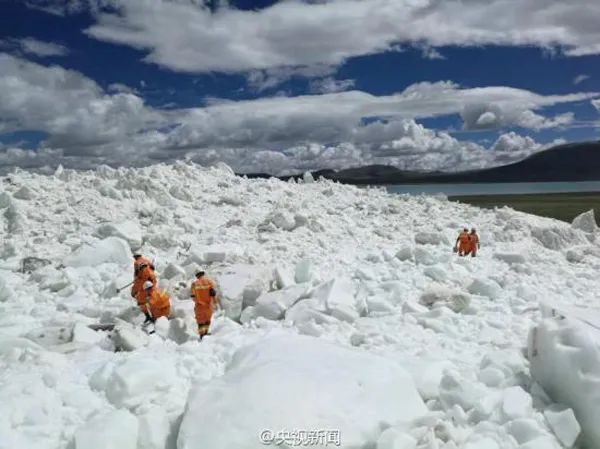

(Picture source: CCTV News)
On February 7, 2021, the glacier collapse of the Chamoli region of Chamoli, India, caused the large -scale floods of Alaknanda and Dhauli Ganga, which caused it. The houses and two hydropower stations along the coastal residents caused thousands of people in the surrounding areas to be forced to evacuate, and more than 200 people died or disappeared.
Figure 9 Bingnu caused floods and caused huge disasters.
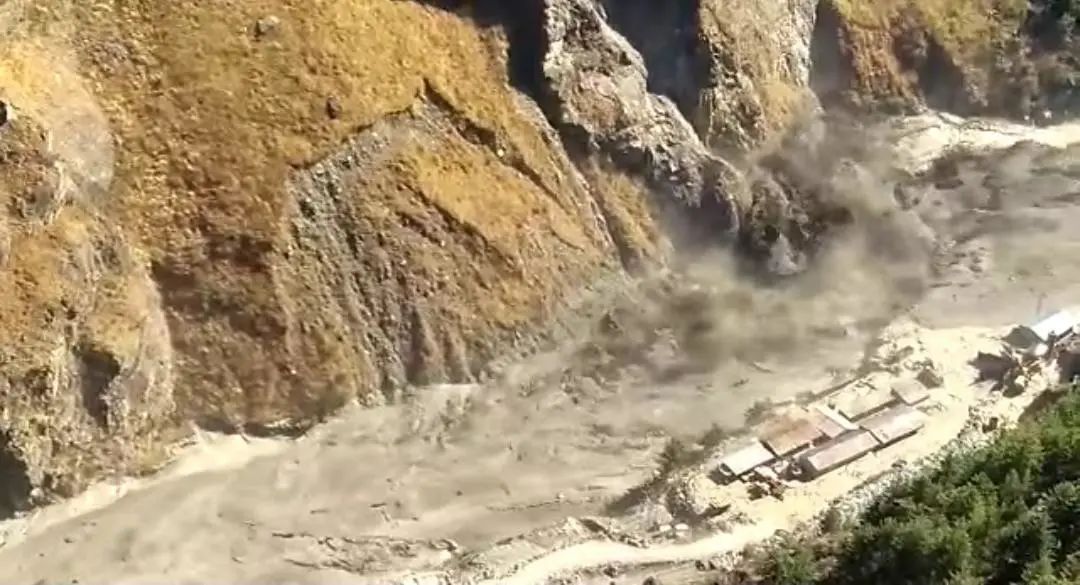

(Picture source: Internetal Business Times)
And on July 3, 2022, a mountain glacier in the Marmolada area in northern Italy also collapsed. After the ice cover on the top of the mountain collapsed, the stones were mixed with stones pouring down the mountains at an altitude of more than 3,300 meters. Essence He killed 11 people and 8 people were injured.
Figure 10 Rescue helicopter is emergency rescue
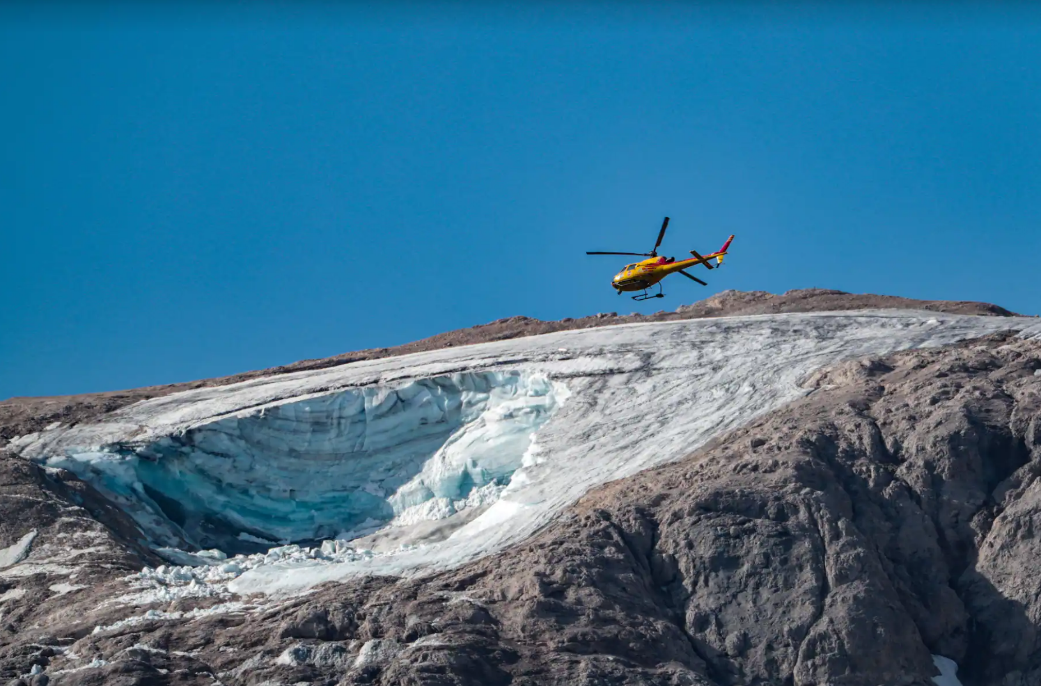

(Picture source: Washington Post)
The occurrence of the Bingpai disaster sounded the alarm for us, not only the catastrophe of itself, but also that it could lead to a series of disasters. If the altitude of the ice collapse is higher, it can further induce secondary disasters such as ice crickets, glacier mudslides, and ice lakes.
Glacier Surge
Glacier is not static, but under the influence of gravity or lower base rock deformation, slow exercise occurs at all times, ranging from a few meters to hundreds of meters a year. The glacier jump is a special glacier movement phenomenon. It refers to the rapid movement of glaciers at a speed of dozens of times or even hundreds of times or even more than hundreds of times or more than dozens of days. form.
Figure 11. The Malaspina Glacier (Alaska) in Alaska overflowed from steep valley to the plain.
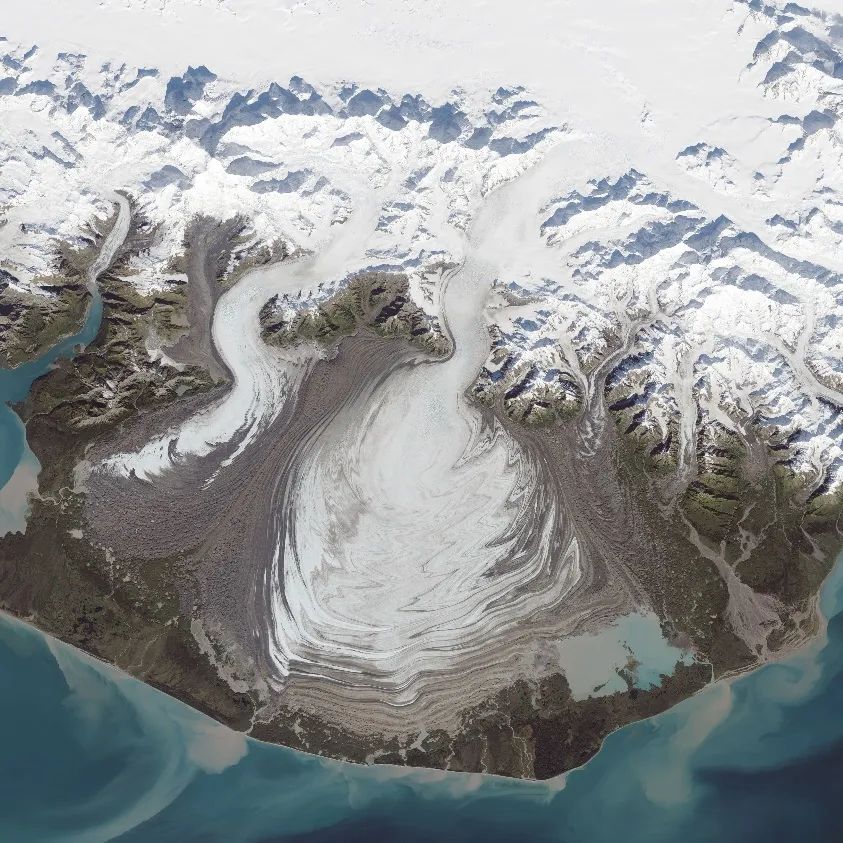

(Picture source: wikipedia common)
Glacier leaps, one is that under the cold weather conditions, the increased pressure of the ice occurs and the lubricating glacier causes the glacier; the other is that under the warm weather conditions, the mellow water from the glacier migrates down the water. The pressure is rising and lubricating has a jump. Glacier jumping will overwhelm the grassland, farmland, houses, and cause damage to infrastructure.
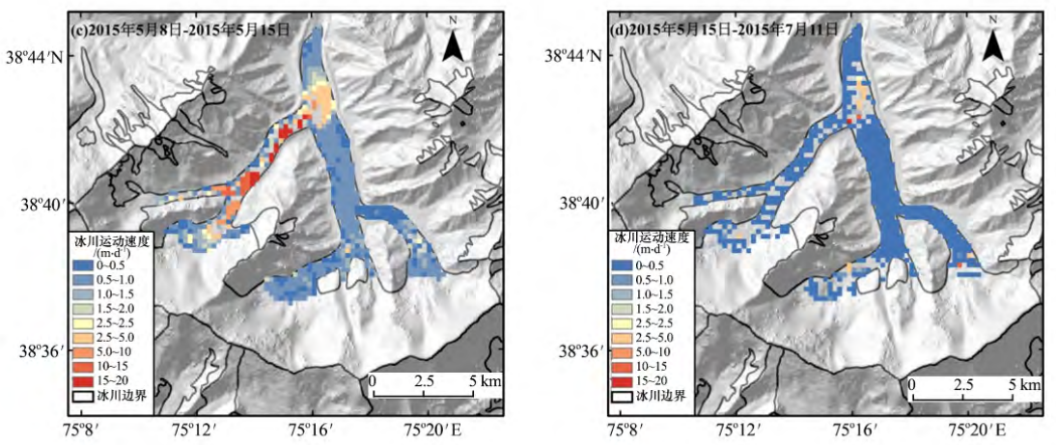
Figure 12 In May 2015, the Claritian Irak glaciers stopped after a jump in Xinjiang, and the movement speed of the red part of the red part of the figure changed significantly. This jumper caused the grassland and some houses to be flooded. (Picture source: Literature)
Binghu collapse
(GLACIAL LAKE OUURTBURST FLOOD, GLOF)
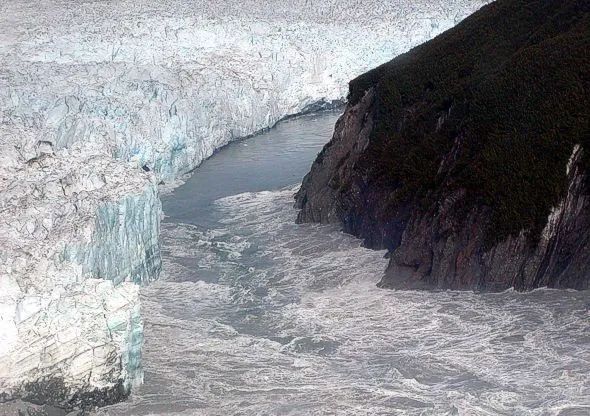
Ice Lake is a natural water body formed by modern glacier melting water or the water body formed in the ice of the ice.
Binghu collapsed floods refers to sudden floods formed by collapsed by the ice lake dam and a large amount of drainage. There are many reasons for the collapse of the ice lake dam. The melting of ice bodies caused by warm climate and high temperature weather has also become one of the important reasons for the collapse of ice lakes in recent years.
Figure 13 On August 14, 2002, The Hubbard Glacier (Alaska) in Alaska was flooded by the second largest ice lake in history. (Picture source: wikipedia)

The Qinghai -Tibet Plateau region in my country is a high -incidence area of ice lakes. The ground is high, the climate is cold, and the glacier is wide. Glacier melts water into the river, making it the birthplace of several large rivers such as the Yangtze River and the Yellow River. Therefore, it is known as the "Asian Water Tower", and Rongshui has also converged into many ice lakes. According to statistics from scholars, the Tianshan Mountains, Karakolon Mountains, Himalayas, Nianqing Tang Gula Mountain, Hengduan Mountain and other places are rushing frequently, among which the Himalayan region is the most. Since the 1980s, the Himalayas and Nianqing Tang Gula Mountains have occurred an average of 1.3 collapse each year. The ice collapse, glacier sliding, and upstream water are the main reasons for the collapse of the ice lake, and these are not inseparable from the climate warming.
Figure 14 The distribution of the Binghu Crown Flood in the Gaoshan District of Asia
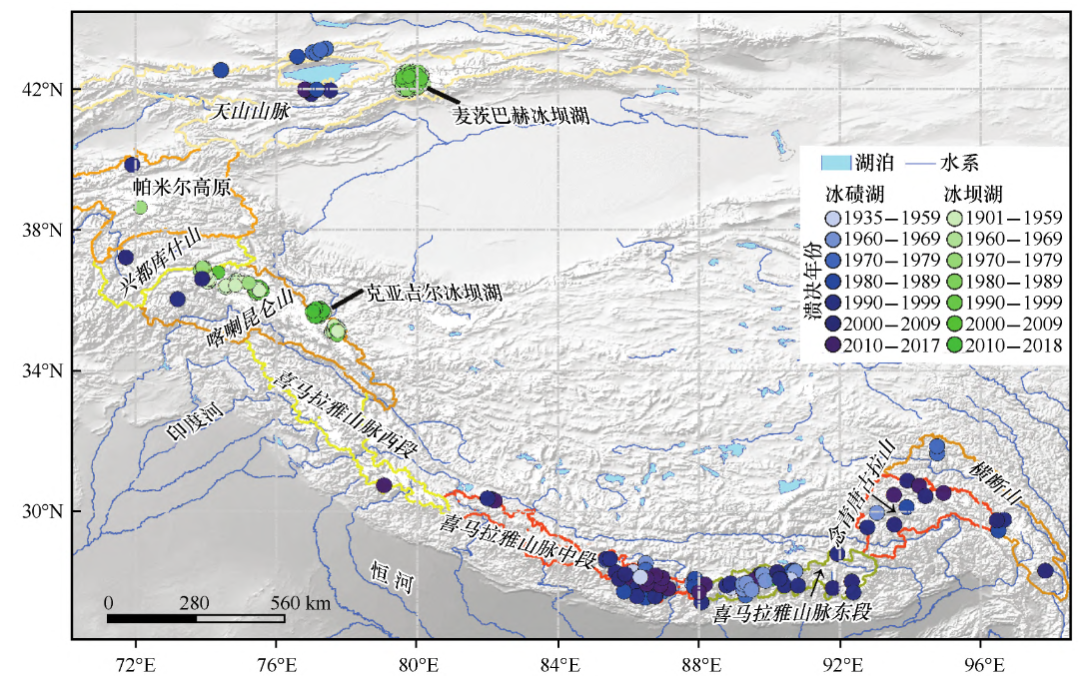
(Picture source: Literature)
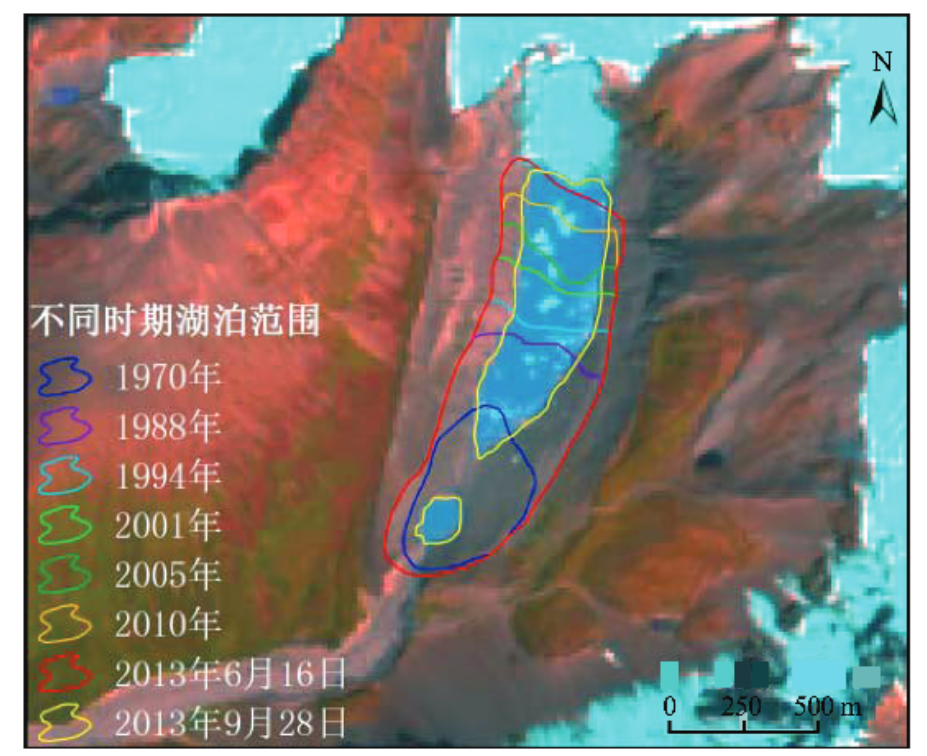
Binghu collapse is strong, and it often causes catastrophic erosion and destruction to downstream. For example, on July 5, 2013, Ran Ran, located in Jiali County, Tibet Autonomous Region, decided that the affected population reached 1,160, 49 houses were destroyed, a large number of farmland and bridges were destroyed. Yuan. Figure 15 The changing chart of Ranzi Lake in Jiali County, Tibet. The lake increased from 0.16km² to 0.58km² from 1970-June 16, 2013, and was separated into two small lakes after the collapse. The avalanche and ice lambling caused by the continuous precipitation and temperature recovery caused this disaster. (Picture source: Literature)
Glacial Debris Flow
Glacier mudslides refer to the sediment formed by the glacier flood and glacier or glaciers or other cold weathering sediments in the high mountain glacier environment. It is characterized by dozens of kilometers) and a large scale (volume up to one million cubic meters). Like ordinary mudslides, it also requires energy (steep terrain provides gravity potential energy), material (rich loose stacking objects such as ice crickets, ice water sediments) and water sources (ice and snow melted water or ice lake collapsed floods. ) These three conditions. Depending on its causes, it can be divided into glacier melted mudslides, ice -collapsed snowproofed mudslides and ice lake collapse mudslides.
Figure 16 Glacier ablation type mudslides. This type of mudslides is generally small and the flow velocity is low. Often, the slopes of muddy streams with a gentle slope are often formed in front of the mountain.
(Picture source: Literature)
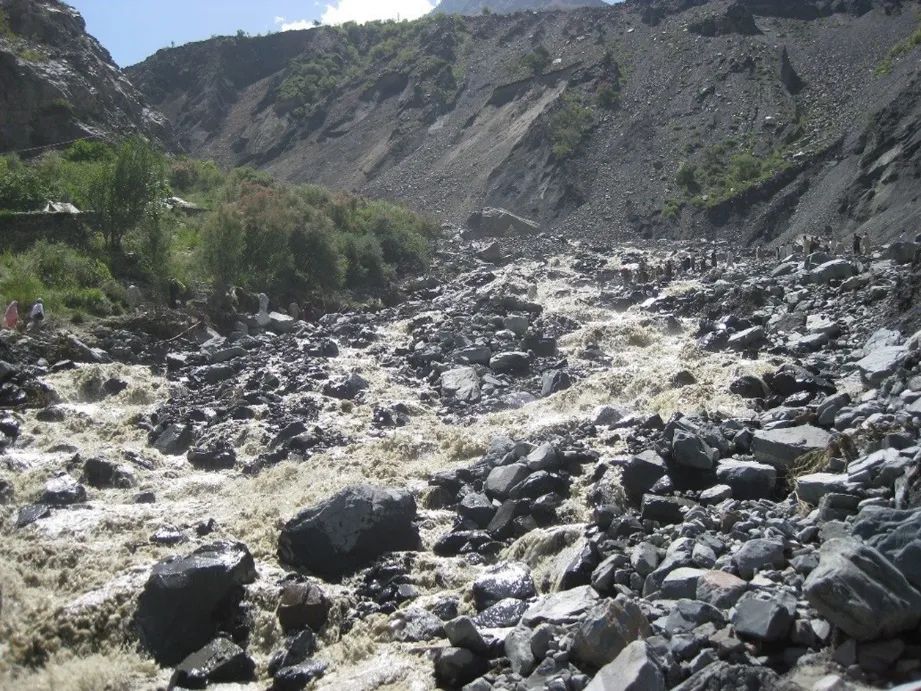

Figure 17 The ice lavery mudslides, such mudslides are flushed strong, and the V -shaped slide was flushed along the valley. (Picture source: Literature)
Figure 18 Binghu collapsed mudslides, such mudslides are large and destructive. (Picture source: Literature)
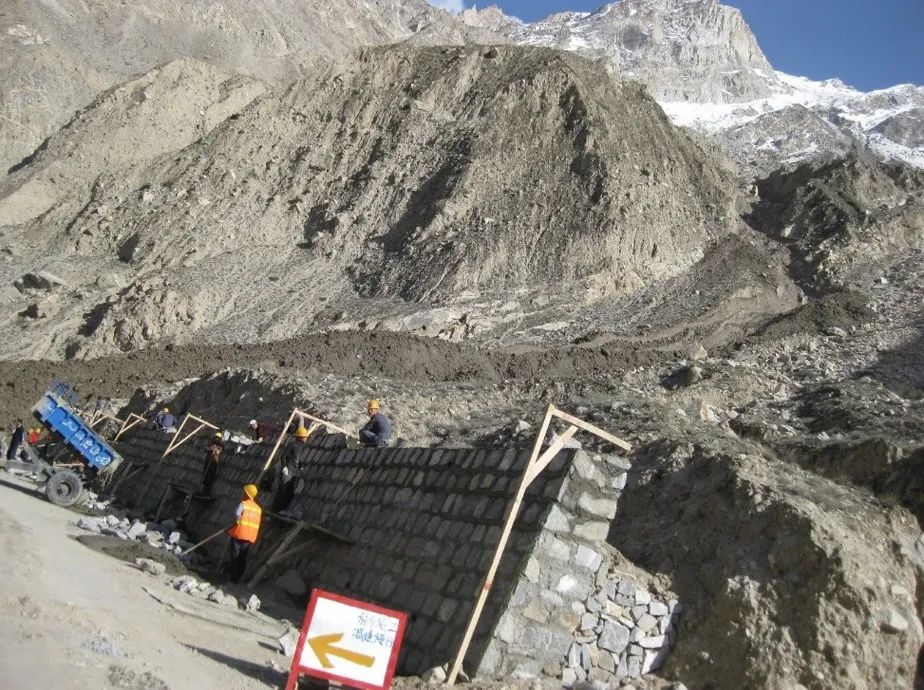

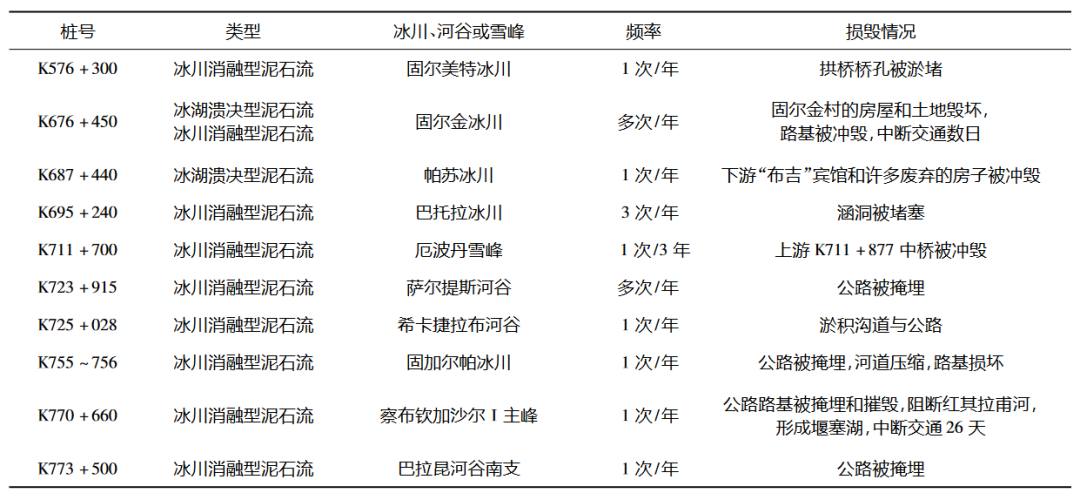
The Central Pakhakara Kunlun Highway connecting China and Pakistan crossed the Karakun-Himalayas. Under the influence of many environmental factors such as the disparity terrain, frequent earthquakes, active glaciers movement, and extreme rainfall, the extreme development of glacier mudslides has made it one of the most dangerous roads in the world.

Table 2 2008-2011 China-Pakistan Highway Main Glacier Mudslide Incident
(Table source: Literature)
Permafrost Degradation
Frozen soil, as the name suggests, refers to the frozen soil. According to the length of the freezing time, it can be divided into short -term frozen soil, seasonal frozen soil and many years of frozen soil. Among them, many years of frozen soil refers to rocks or soils with a temperature of more than two years and lower than 0 ° C, and they are often called "permanent frozen soil". Generally speaking, soil can be divided into three layers according to temperature differences: the soil close to the surface melts in summer and freezes in winter. Frozen throughout the year, it is "many years of frozen soil layers"; deep soil, due to the impact of geothermal, no longer freezes, is called "unwelling layer".
Figure 19 The schematic diagram of the frozen soil (A) and its vertical section for many years (A) (B)
(Picture source: Literature)
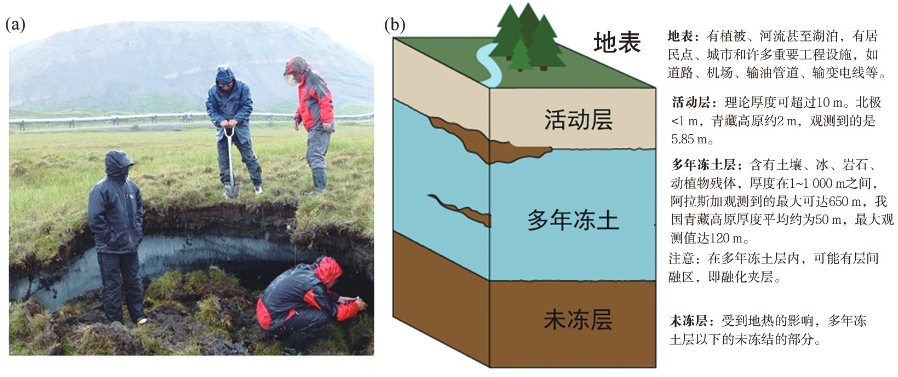
my country has a variety of frozen soil types and a wide distribution area. Especially in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau, the unique high -cold environment has bred more than a million square kilometers of high -altitude frozen soil for many years. It is the most widely distributed area of frozen soil in the world in the world. However, in recent decades, the frozen soil degradation in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau has been extremely serious. In 2000, the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau was 1.40 × 10km² for many years, while in the 2019 survey, it was 1.06 × 10km², and the degraded area exceeded 24%. Some scholars have predicted the decline of frozen soil in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau, and the situation is also not optimistic.
Figure 20 Chinese frozen soil distribution map
(Picture source: National Qinghai -Tibet Plateau Science Data Center)
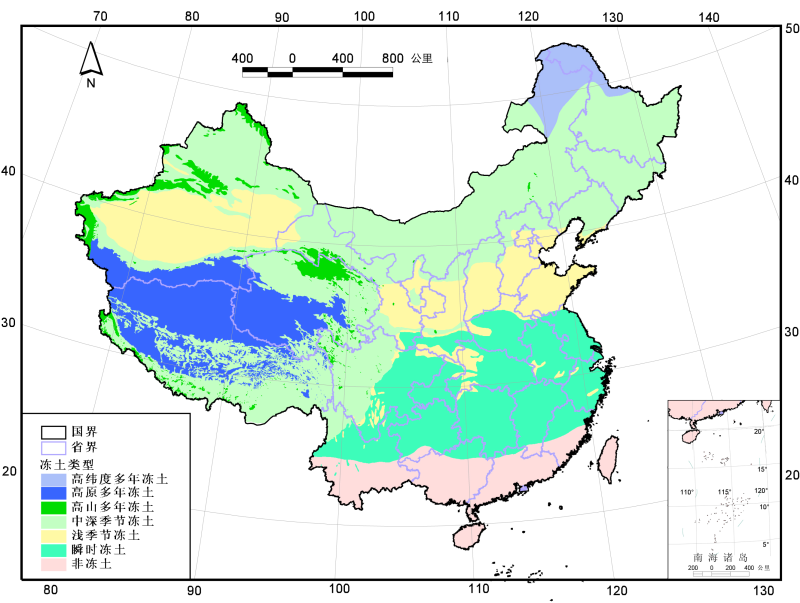
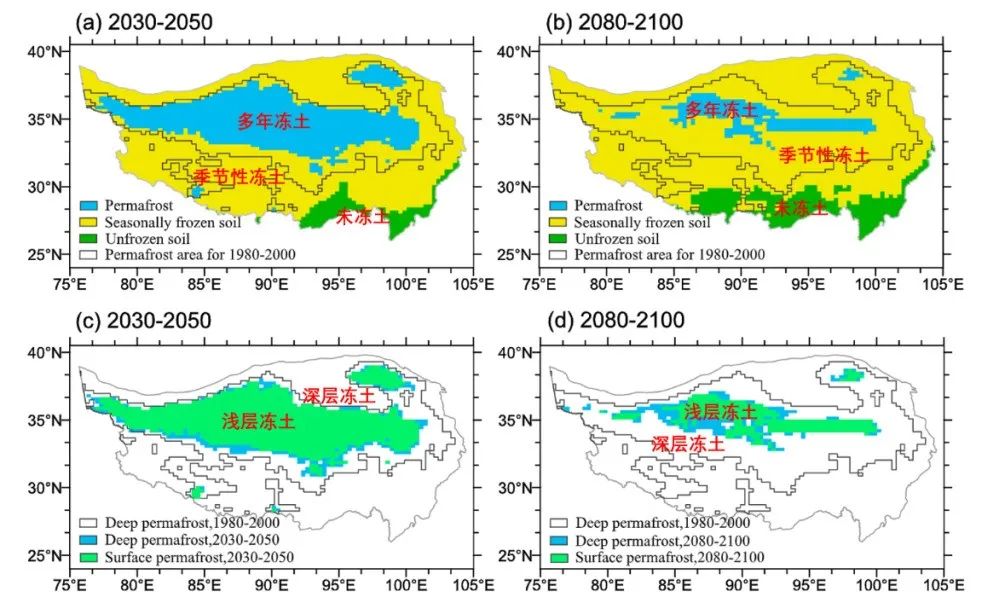
Figure 21 The trend of frozen soil degradation in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau simulated by scholars can see that the area of frozen soil has decreased sharply, the depth of the activity increases, and the shallow frozen soil has almost disappeared.
(Picture source: Literature)
Degeneration of frozen soil will have an important impact on ecological environment and human activities. The melting of frozen soil will affect the water circulation, resulting in uneven distribution of water resources, which will affect vegetation growth. After the melting of the ice in the soil, the volume decreases, which will cause the ground to collapse, forming a hot melt lake pond, hot -melt sliding, etc., which causes the collapse, roadbed, and bridge destruction of houses that were originally built on the frozen soil.
Figure 22 The hot -melt lake pond (A) and the hot melt sliding (B). The hot -melt lake pond is a lake pond formed by the melting of frozen soil and the gathered water after the ground collapse. The hot melting sliding is the sliding collapse after the melting of the frozen soil and the decline of the geotechnical strength. Landscape of the mountains. (Picture source: Literature)
In addition, the frozen substances in frozen soil should not be underestimated. In the long history of ice, a large amount of harmful substances and germs may be sealed. Once melted, it may bring risks to the safety of ecosystems and human life. At the same time, a large amount of organic carbon is stored in the frozen soil layer, and the organic carbon after the melting of the frozen soil is released and released, becoming a greenhouse gas into the atmosphere, which will cause the temperature to further increase.

Figure 23 In October 2016, the anthrax epidemic broke out in Siberia. The epidemic was considered to be caused by the degeneration of frozen soil for many years, and the surface of the surface was exposed to the reindeer infection 75 years ago. (Picture source: ScreenShot Siberian Times) Freeze Thaw Landslide
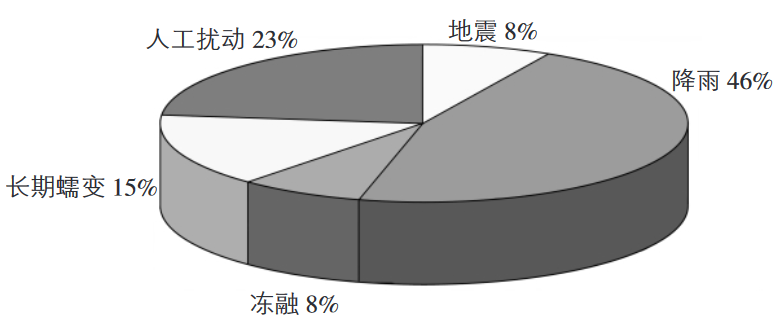
Lirkeys, that is, the influence of factors such as water, earthquakes, and human activities of the slope rocks, and sliding along the weak surface under the action of gravity. In my country, about 8%of the landslides are directly or indirectly induced by the freezing cycle. The warming of the climate will undoubtedly increase the proportion of frozen and sloppy disasters.

Figure 24 The main trigger and induction factors of China's large -scale landslides
The reason why frozen and melting can induce landslides is that it will greatly weaken the intensity of rock and soil. On the one hand, repeated freezing fusion will cause the water inside the soil to continuously exposure and shrink, increase the pores of the soil, and make it loose; on the other hand, a large amount of mellow water penetrates into the rock and soil body The body's self -weight and additional water pressure on the soil will also soften the soil and eventually damage.
Figure 25 On March 29, 2013, a landslide mudslide disaster occurred in Tashigang Township, Mozhu Gongka County, Tibet. A mining area was buried, causing 83 people to die. The accident was a drainage disaster caused by ice and snow frost. (Picture source: CCTV)
Various geological disasters caused by climate warming are the alarm bells that nature sounds. While human beings are pursuing high -speed development, they also need to take into account the protection of nature. Fortunately, reducing the emissions of greenhouse gases and preventing global warming have become a general human general. Although this move will face many difficulties, humans will pay a lot of costs. But with the joint efforts of everyone, they will continue to make breakthroughs, and humans will usher in a better tomorrow.
Reference

[1] Mo Jie and Peng Nana, "World Glacier Deduction and Sea Planes", Science, Volume 70, Phase 05, p. 48–51, 2018.
[2] Wang Zongtai and Su Hongchao, "Glacier Distribution in the World and China and its Water Resources", glacier frozen soil, period 05, p. 498–503, 2003.
[3] Hu Wentao, Yao Tandong, Yu Wusheng, Yang Wei and Gao Yang, "Research Progress of the Bing Laurea Disaster in Gaoma", Glacier Frozen Earth, Volume 40, Phase 06, Phase 1141–1152, 2018.
[4] Shi Lina, borrowing Xuefeng and Wang Xing, "Extraction of the Tibetan Ali Bingpai Scope of SENTINEL-2A data", Inner Mongolia Coal Economy, Period 02, pages 157–160, DOI: 10.13487/J.CNKI .Imce.009400.
[5] Wu Guangjian et al., "Glacier Disaster in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the surrounding areas", published by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Volume 34, Phase 11, p. 1285–1292, 2019, DOI: 10.16418/J.ISSN.1000-3045.2019.11.011.
[6] Zhang Zhen, Liu Shiyin, Wei Junfeng, Jiang Zongli, Xu Junli and Guo Wanqin, "Research on the Monitoring of Glacier Remote Sensing of Glacier in Xinjiang", Glacier Frozen Earth, Volume 38, Phase 01, 11–20, 2016.
[7] G. Veh, O. Korup, S. Von Specht, S. Roessner and A. WALZ, "Unchanged Frequency of Moraine-Dammed Glacial Lake Outburst Flows in the Himalaya", Nat. CLIM. Change, Vol. 5, pages 379–383, May 2019, DOI: 10.1038/S41558-019-0437-5.
[8] Zhang Taogang, Wang Weicai, Gao Tingguang, Anbao Sheng Monk Xuexue, "Review of the Binghu Crown Flood in the Asian Gaoshan District", Glacier Frozen Earth, Volume 43, Phase 06, P. 1673–1692, 2021.
[9] Sun Meiping, Liu Shiyin, Yao Xiaojun and Li Long, "2013 7.5" ice lake in Jiali County, Tibet, the cause of floods and potential harm ", glacier frozen soil, volume 36, period 01, p. 158–165, 2014.
[10] Zhu Yingyan, Pan Junyu, Li Chaoyue, Yang Zhiquan, Liao Liping and M. Waseem, "China Bakkara Kunlun Highway Glacier Mud Stream", Journal of Mountains, Volume 40, Phase 01, 71–83, 2022, DOI: 10.16089/J. CNKI.1008-2786.000656.
[11] Wu Xiaodong and Wu Tonghua, "Many years of frozen soil degradation on the climate and humans,", natural magazines, Volume 42, Phase 05, p. 425–431, 2020.
[12] Cheng Guodong and Zhao Lin, "Frozen Earth Issues in the Development of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau", Fourth Disciplinary Study, Period 06, p. 521–531, 2000. [13] Cheng Guodong, etc. Impact ", scientific report, Volume 64, Phase 27, p. 2783–2795, 2019.
[14] x. Li, R. Jin, X. Pan, T. ZHANG and J. GOO, "Changes in the Near-Surface Soil Freeze –Thaw Cycle on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau", int. J. Appl. Earth OBS. GeoinFormation, Volume 17, pages 33–42, July 2012, Doi: 10.1016/J.JAG.2011.12.002.
[15] Wang Ruiqing and Zhang Chunlei, "Analysis and Research Status of Multi-Factors of Single Landscapes", Shanxi Architecture, Volume 39, Phase 16, pages 82–84, 2013, DOI: 10.13719/J.CNKI.CN1279/TU.2013.16. 003.
[16] Liu Chuanzheng, "Crowding Landscape Disaster on Following Frozen Frozen", Hydrogen Geological Engineering Geology, Volume 41, Phase 02, P. 3, 2014, DOI: 10.16030/J.CNKI.ISSN.1000-3665.2014.02.001.
Other reference materials:
1. SEA Level Rise Is Accelerating, NASA
2. Wikipedia: GLACIAL LAKE OUTBURST FLOOD, GLOF
3. Wikipedia: GLACIAL Debris Flow
Beautiful editor: Han Yatong
School pair: Jiang Shumin Qin Huaqing
Reprinted content only represents the author's point of view
Does not represent the position of the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you need to reprint, please contact the original public account
Source: Address of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Edit: lychee jelly
- END -
Safety and cultural experts talk | Building a good security report culture must be two -pronged from management and personal level

Safety report culture is an important child culture of security culture. Under a g...
The 2022 China Vailiness Day Event Week launched

Leading navigation green and low -carbon intelligent new trend to write a new chap...