Chuanguan Scientific Examination Team 高 | "Plateau Doctor" puts the pulse high cold and wetland
Author:Chuanguan News Time:2022.09.19
Chuanguan News reporter Xu Lisha Photography Li Qiang edited Guo Yuhe
Scientific examination point: Sichuan Johgai Gaoshan Wetland Ecosystem National Field Scientific Observation Research Station (hereinafter referred to as Ruergai Station)
Scientific examination task: Carry out a variety of scientific research and observation work, "diagnose the pulse" of the high -cold wetland ecosystem
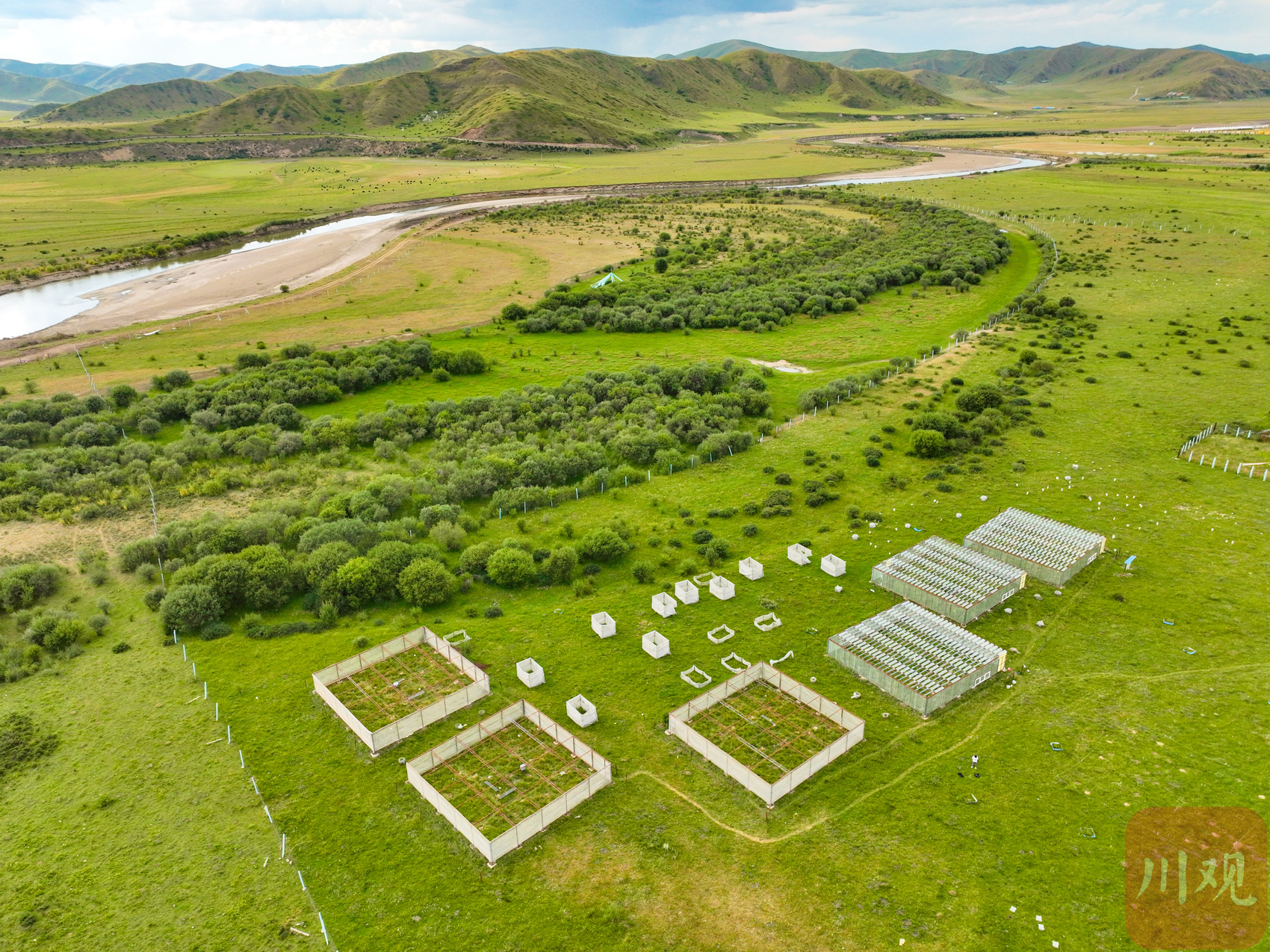
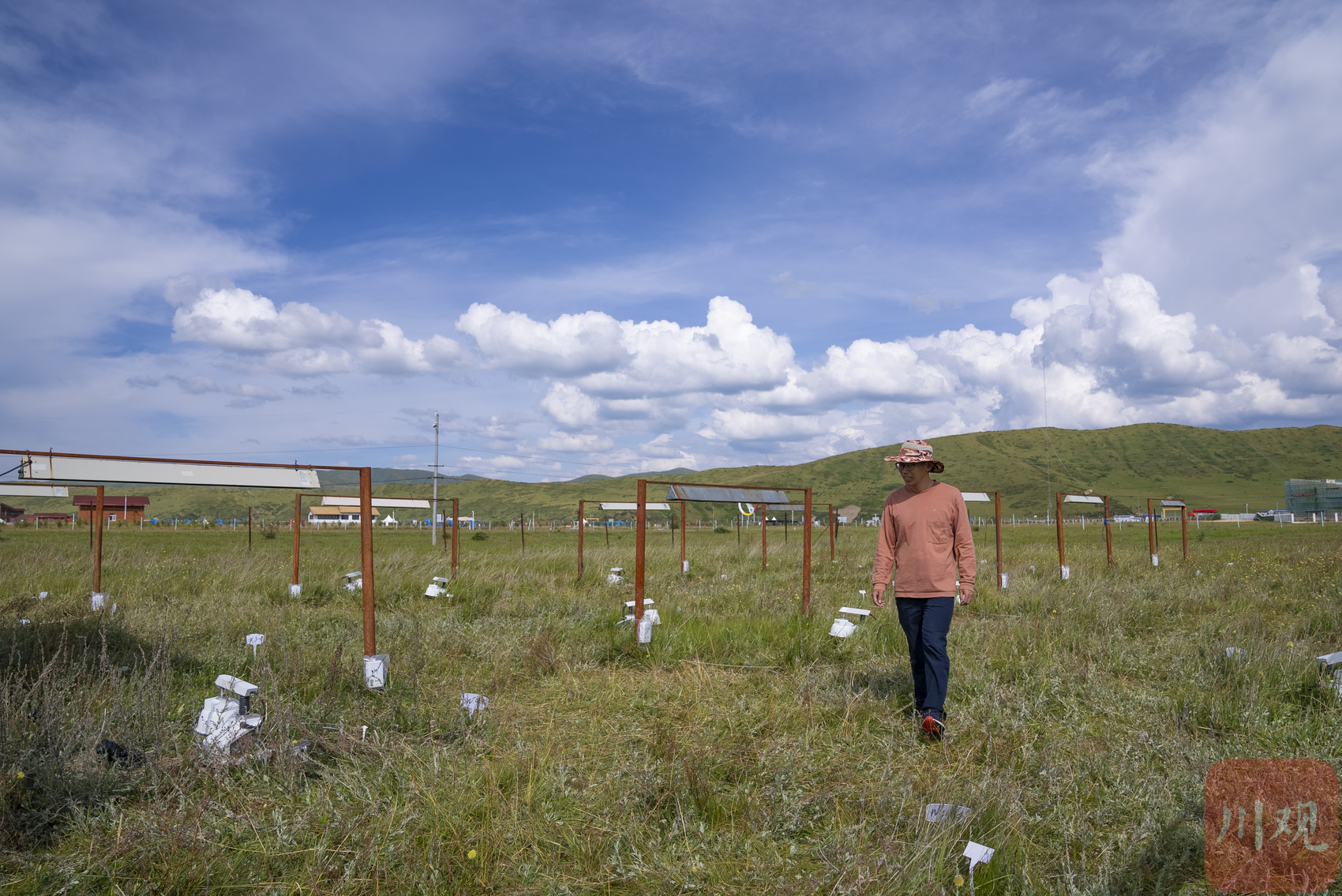
In the northern part of Warche Town, Hongyuan County, Aba Tibetan Qiang Autonomous Prefecture, which is more than 3,600 meters above sea level, the "Red Army Crossing Monument" stands in the Grand Marsh in Japan. Looking at it from a distance, the empty swamp land, grass and blue sky are integrated. Hu Jian, assistant to the station director of Ruo Ergai, is carrying technical staff in planning and observation.
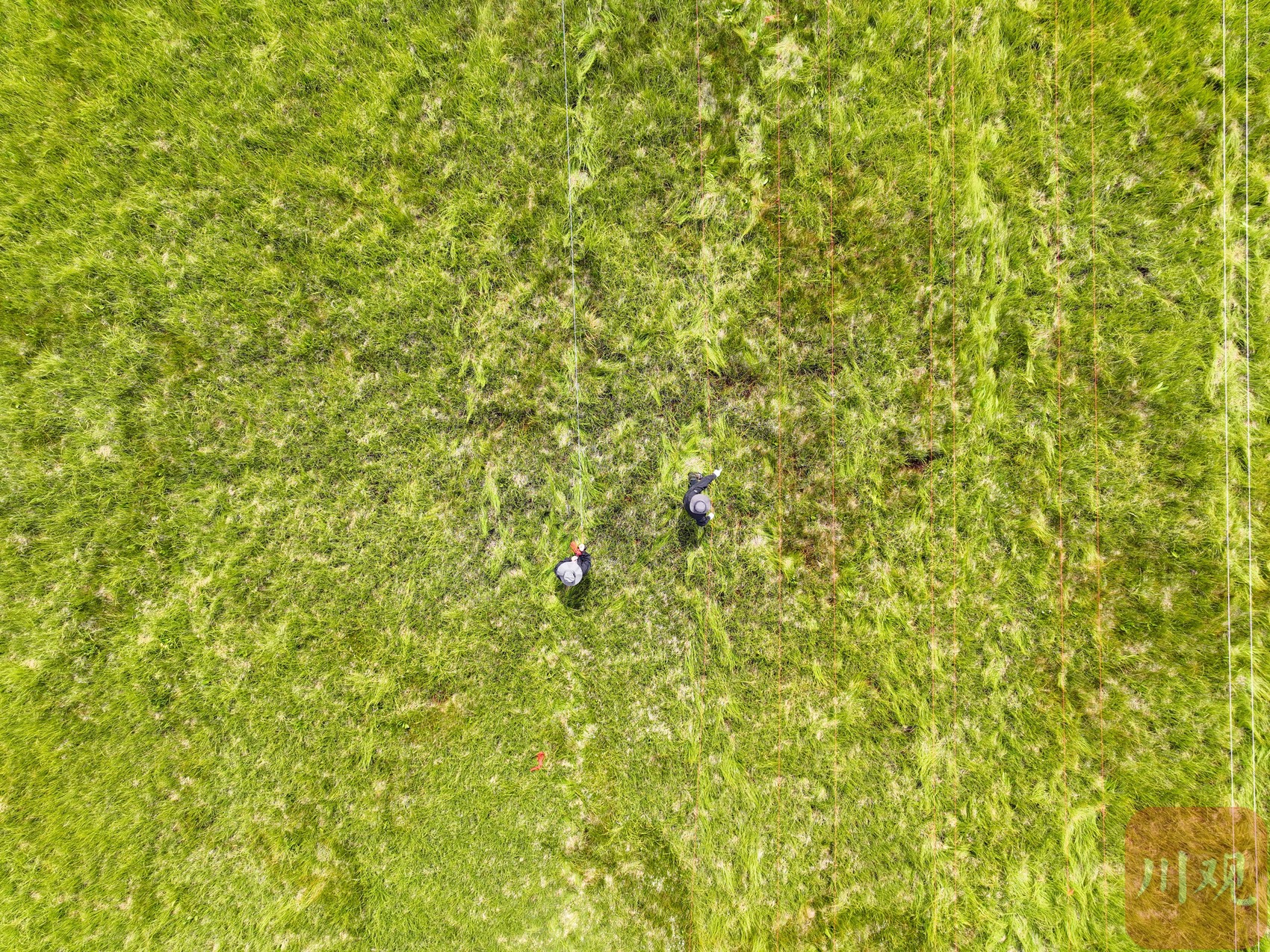

In the comprehensive observation site of Ruergai Station, the staff is planning to observe.
After the field observation instrument equipment is installed, it will be used to monitor the natural evolution of the high -cold wetland ecosystem and response to climate change. "The wetland observation field that flooded all year round showed a relatively dry state this year, and this year can be used as an extreme event year." Hu Jian said.
Jorgi Station is a national -level field observation station approved in 2021 and officially unveiled in July this year. Construction was jointly constructed by the Institute of Geographical Sciences and Resources of the School of Geography and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Institute of Geographical Sciences and Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Sichuan University.
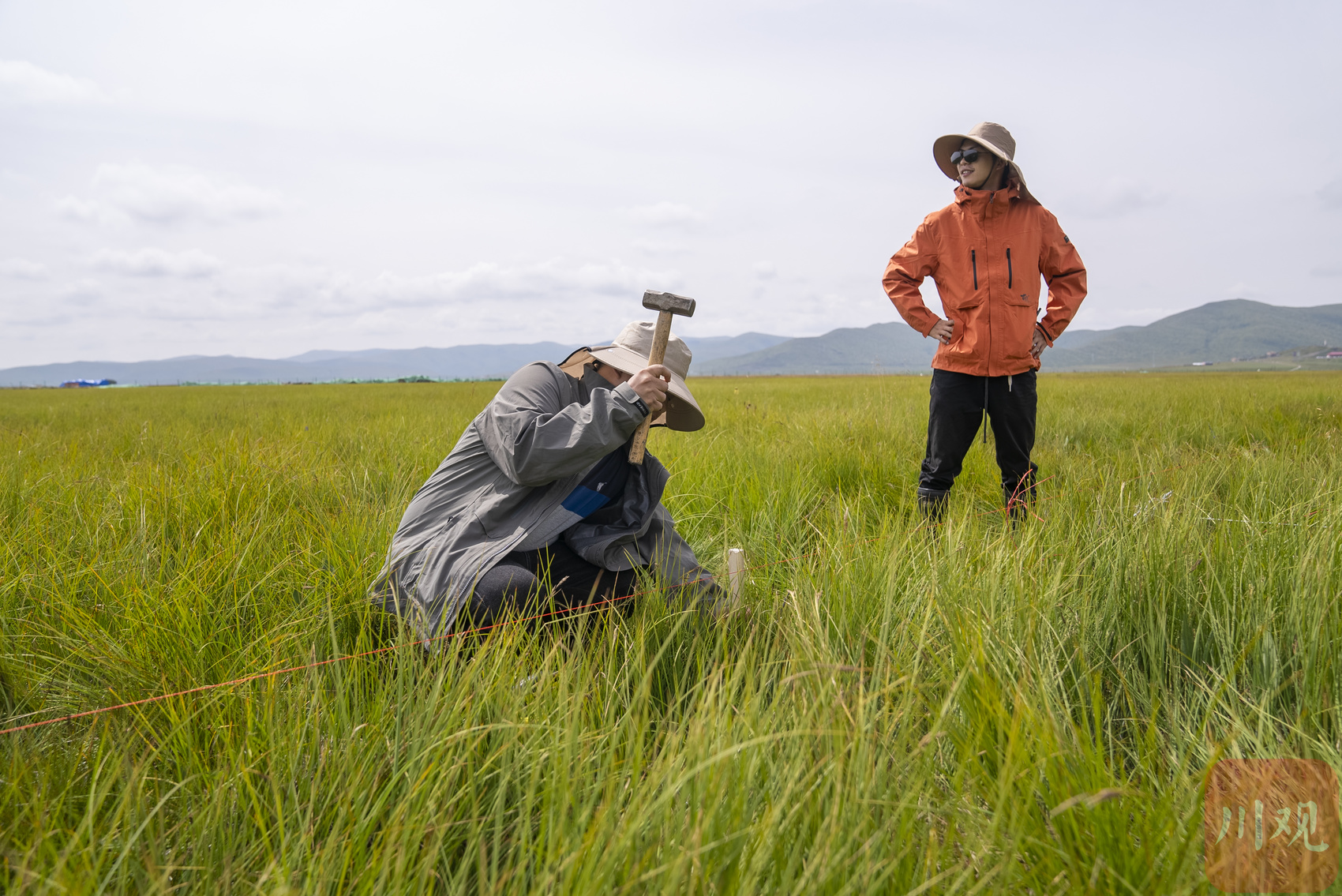

In the comprehensive observation site of Ruergai Station, the staff is planning to observe.
The wild platform station is like a "listener" installed on the earth. The researchers at the wild station are "plateau doctors", which changes the veins with the changes in the ecosystem. From May to October each year, it is the growing season of Jorgei wetland plants, and it is also the best period for wild surgery examinations. During the peak period, more than 200 people in Jorgi Station carried out a variety of scientific research observations at the same time.
Recently, the reporter came to Jorgi Station and followed the group of "plateau doctors" to "consult the pulse" to the Gahan Wetland Ecosystem.
Study pastoral grass, let the yak eat well when protecting the grass field
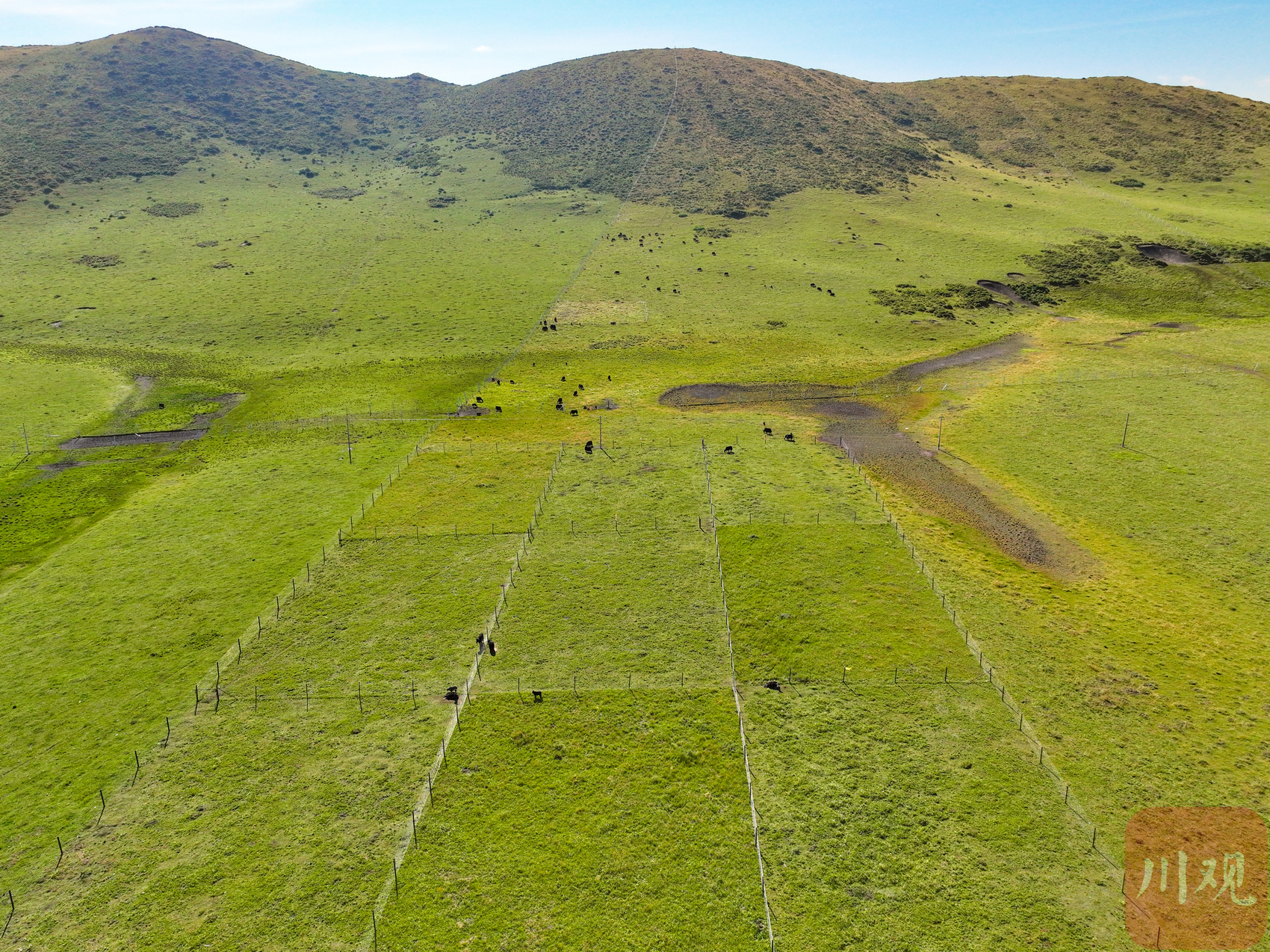
After the afternoon, the breeze was blowing, and the pastoral grass was like the waves of the waves. From the air overlooking the pastoral germplasm resource garden at the air, more than 100 acres of resource gardens are divided into several blocks, with different color depth. Because the types of pasture grown in each block are different, the color, height, shape, and output are different.
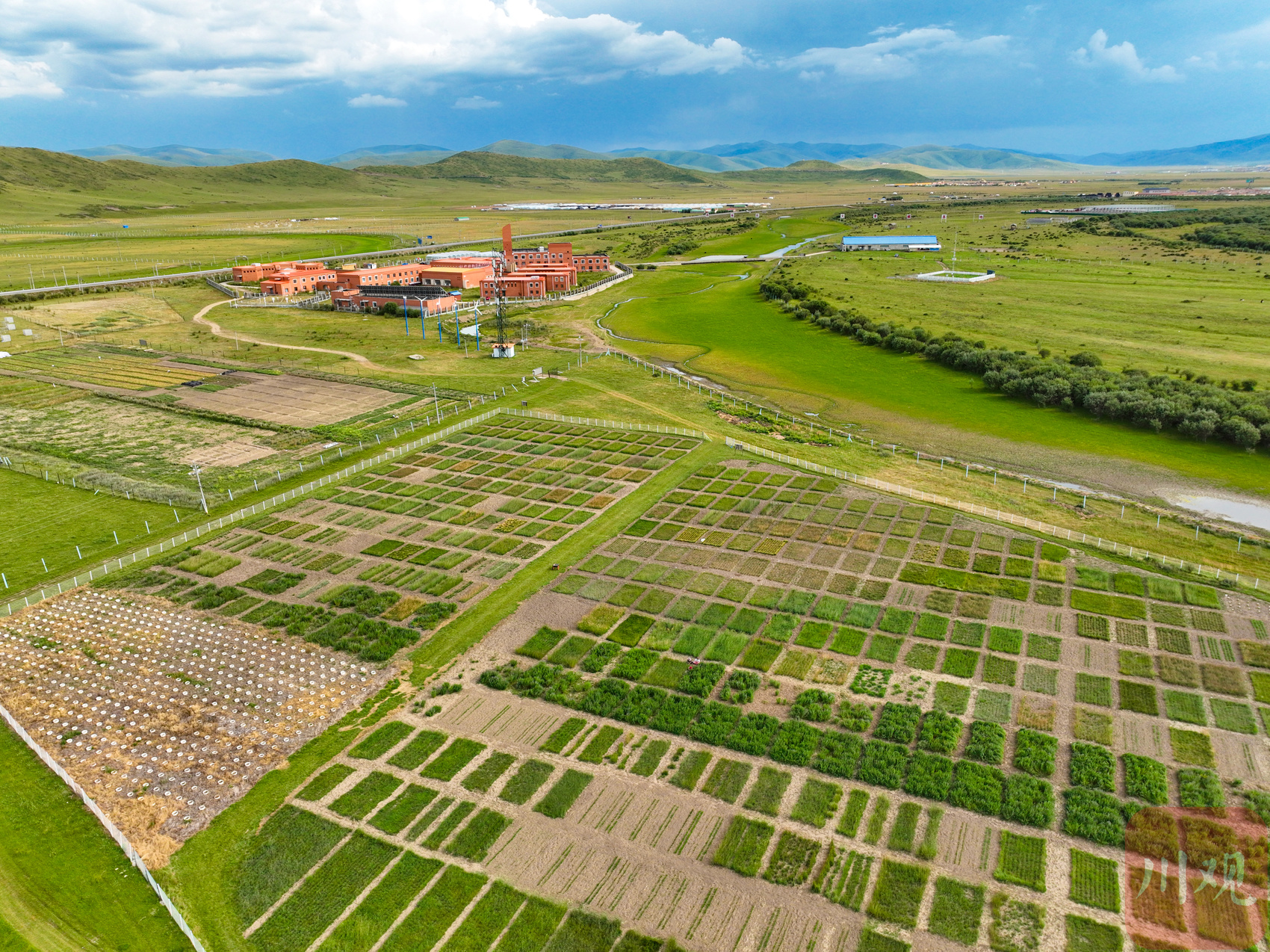

The pastoral germplasm resource garden in Ruergai Station.
Here we can be called the "living museum" of pastoral grass grass grass. According to Wang Hui, director of the office office of Ruierga Station, the plant resources of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau are very rich, accounting for one -third of the plant resources of the country. Among them, plant with feed value There are about 3,000 kinds. Zhou Qingping, a professor of Southwest University for Nationalities, has gone through major typical areas of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau and brought back more than 4,000 pasture resources. Among them, more than 800 copies are planted here, including 22 forage wild germinated resources including alkaline grass, cinema, and early maturity.
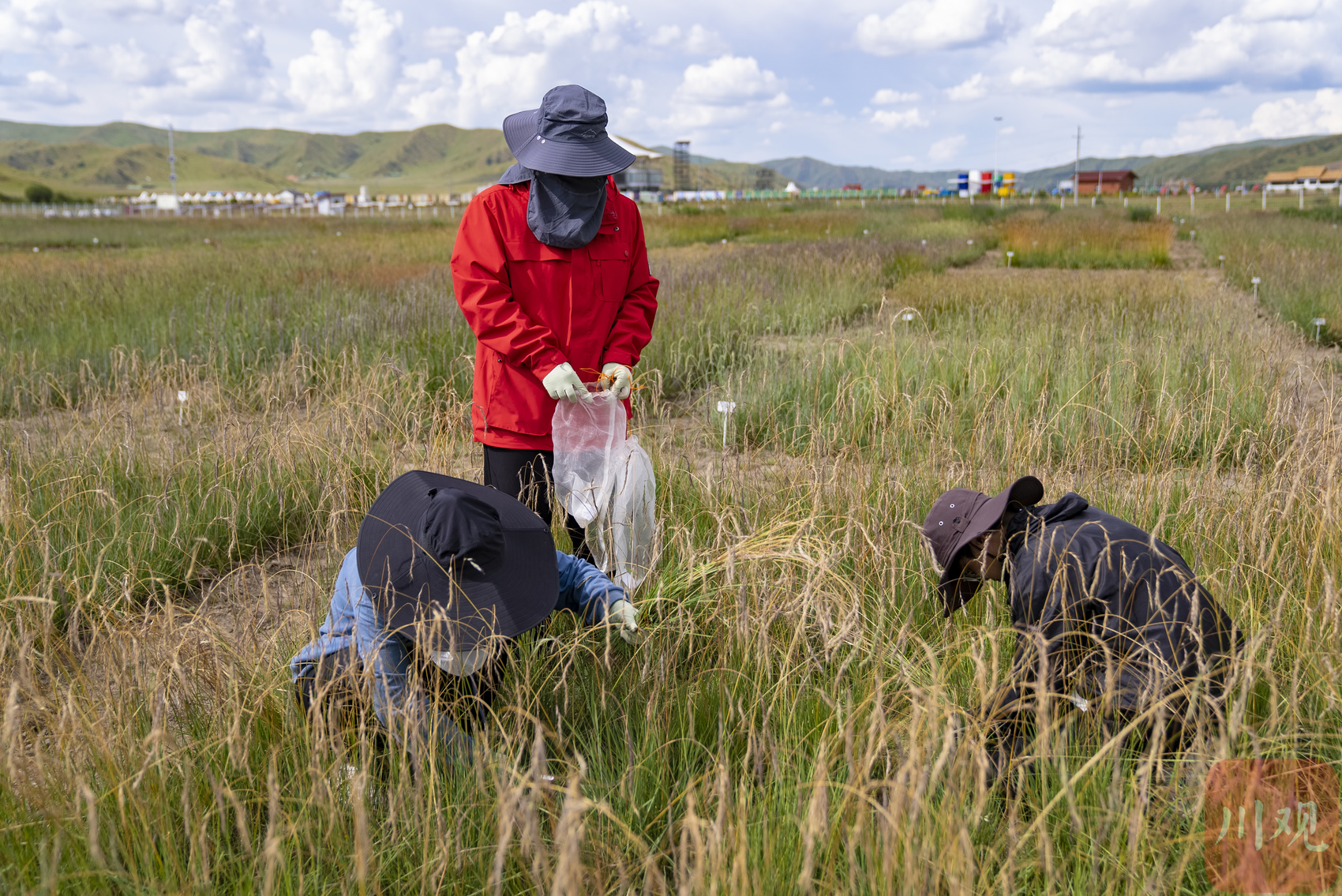

Researchers collect samples in the pastoral germplasm resource garden.
The graduate students of the team are collecting samples to carry out the evaluation of pasture species of pasture. Lao Muchi and other pastoral grass have a large amount of bioscope and rich nutrition. They have a good momentum here and straighten to more than 1.3 meters. When taking samples, use the sample box to be placed in the roots of the pastoral grass, and the number of branches in the statistical sample box to understand its ability to divide. After the sampling, put in the oven to dry it to measure the production of dried grass. In addition, they must focus on the morphological characteristics and production performance of the leaves and stems of various pastoral resources, longitudinal spikes, height, seed yield and other morphological performance.
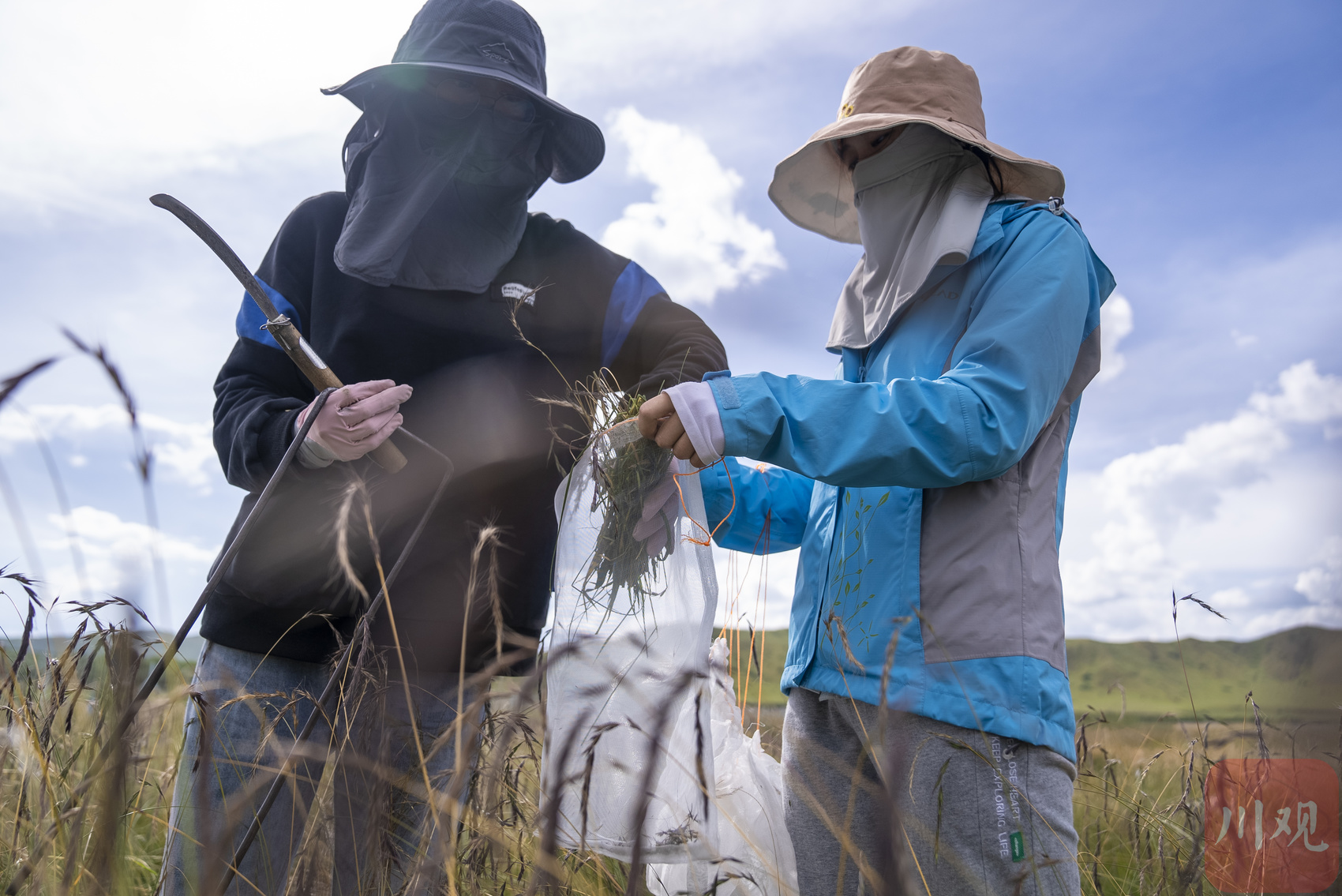

Researchers collect pastoral samples in the pasture germplasm resources.
This is the largest and largest number of pastoral germinated resource gardens in high -cold regions in China. With the goal of breeding high -quality, high -quality, precocious Qinghai -Tibet Plateau, they will carry out the collection, appraisal, protection, evaluation and innovation utilization of excellent pasture species of pasta, from resources to high -tech, from resources to varieties, from resources to varieties, from resources to varieties, from resources to varieties. It continues to make breakthroughs in the theory and technical methods of pastoral breeding, the innovation and utilization of gear resources, and efficient cultivation.
Through the support of the national pastoral industry technology system and the project support of Jessa Station, the Zhou Qingping team has cultivated new varieties such as old menus, Chinese cinema, and oats based on this pasture. The varieties cultivated by Zhou Qingping's team are currently dominant varieties of the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau. The promotion effect is very good, the promotion area is large, and it contributes to the high -quality development of the ecological grass animal husbandry industry in the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau.

Ze Rang Dongke's yak grazing feed test platform set up in Jorgi Station.
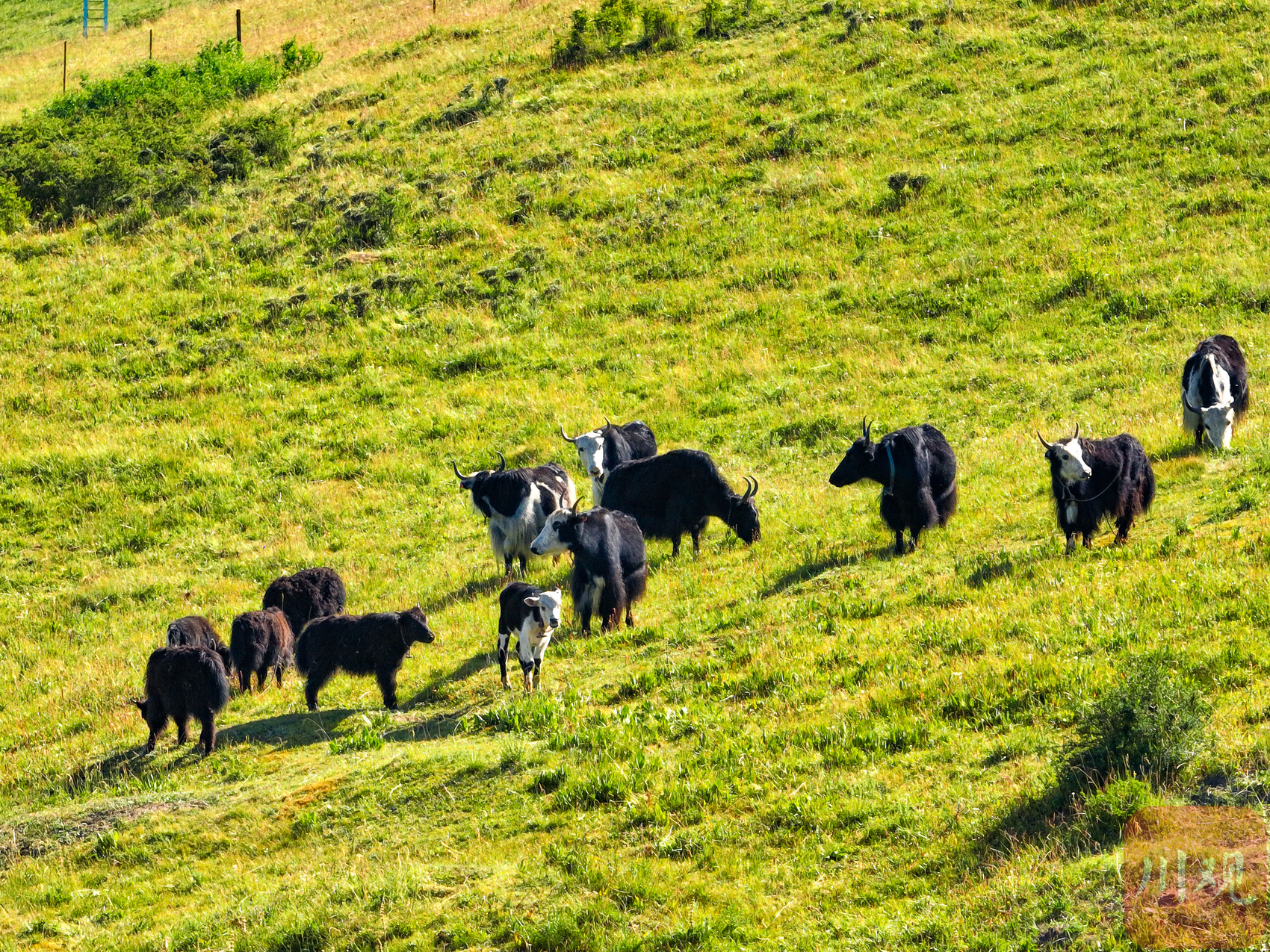
In addition to studying what Niu Yang eats, Ze Ring, an associate researcher at Southwest University for Nationalities, is still studying where the yak eats, how much to eat, and how to protect the yak better when protecting the grassland. The tall Ze made Dongke the local natives. Here, he set up a mullet of mulberry fodder feeding test platform. The so -called supplementary feed refers to feeding yaks in the morning and evening in addition to natural grazing.
Ze Rang Dongke's yak grazing feed test platform set up in Jorgi Station.

Yak is a precious species on the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau. There are more than 17.6 million yaks around the world, and the number of yaks in Sichuan reaches one million levels. In the past few decades, the Qinghai -Tibet Plateau has been traditional grazing. The degeneration of the grassland caused by severe grazing has promoted supplementary or house feeding in recent years to reduce the intensity of the grassland bellfunding.
"We commonly believe that summer supplementation can improve the productivity of the grass, but there is no quantitative control research support. Therefore, we have established a comparison test platform for severe granting, supplementary feeding (mild grazing), and not grazing to study summer supplementary feed to grassland. The impact of the ecosystem is to achieve grass and livestock balance and improve the productivity of grassland. "Ze Lang Dongke said.
Ze Rang Dongke studied pastoral grass in the yak gratitude supplementary feed test platform set up in Jorgi Station.

Every year from May to the end of September is the growing season of the grassland. The team compares the productivity of the three types of grassland through the observations of plant diversity, bi quantity, community changes, and insectic limbs animals, soil and so on.
After four years of research, they initially discovered that the amount of grassland biological in the supplement was more than traditional severe grazing. Among them, the proportion of the grades and shuttlecocks of the yak's preferences was rising, and supplementing was more conducive to the development of yak breeding.
Studying insects, the largest opening temperature increase device in the world
Behind the base of Ruo Ergai Station, the winding white river flows quietly. On the side of the river, there are 6 2.5 -meter -high opening heating boxes standing on the grass.
This is the world's largest opening temperature increase device, 15 meters long and width, and a single area of 225 square meters. The box is an independent ecosystem. Among them, the three surroundings are 8 mm thick tempered glass for temperature increase; three only fence mesh is used as a control. The recorder hidden in the grass in each opening box is recorded every 60 minutes, a temperature and humidity of 30 cm, surface, underground, and 10 cm underground.
Sun Shucun, a professor of Nanjing University, led the world's largest opening temperature increase device in the world.

In the box, the post -doctoral Hu Xiaoli and doctoral student Zhang Yuxia of Nanjing University "fully armed", hats, sunscreen masks, sunscreen arm collisions were neatly worn, holding the insect catheter, walking according to the "field" shape route, waved the arm to sweep the net insect. Facing cicada, real flies, aphids, bees, blindness, moths, mosquito, mosquito, and crickets are the objects they capture.
Dr. Zhang Yuxia of Nanjing University is capturing insects.
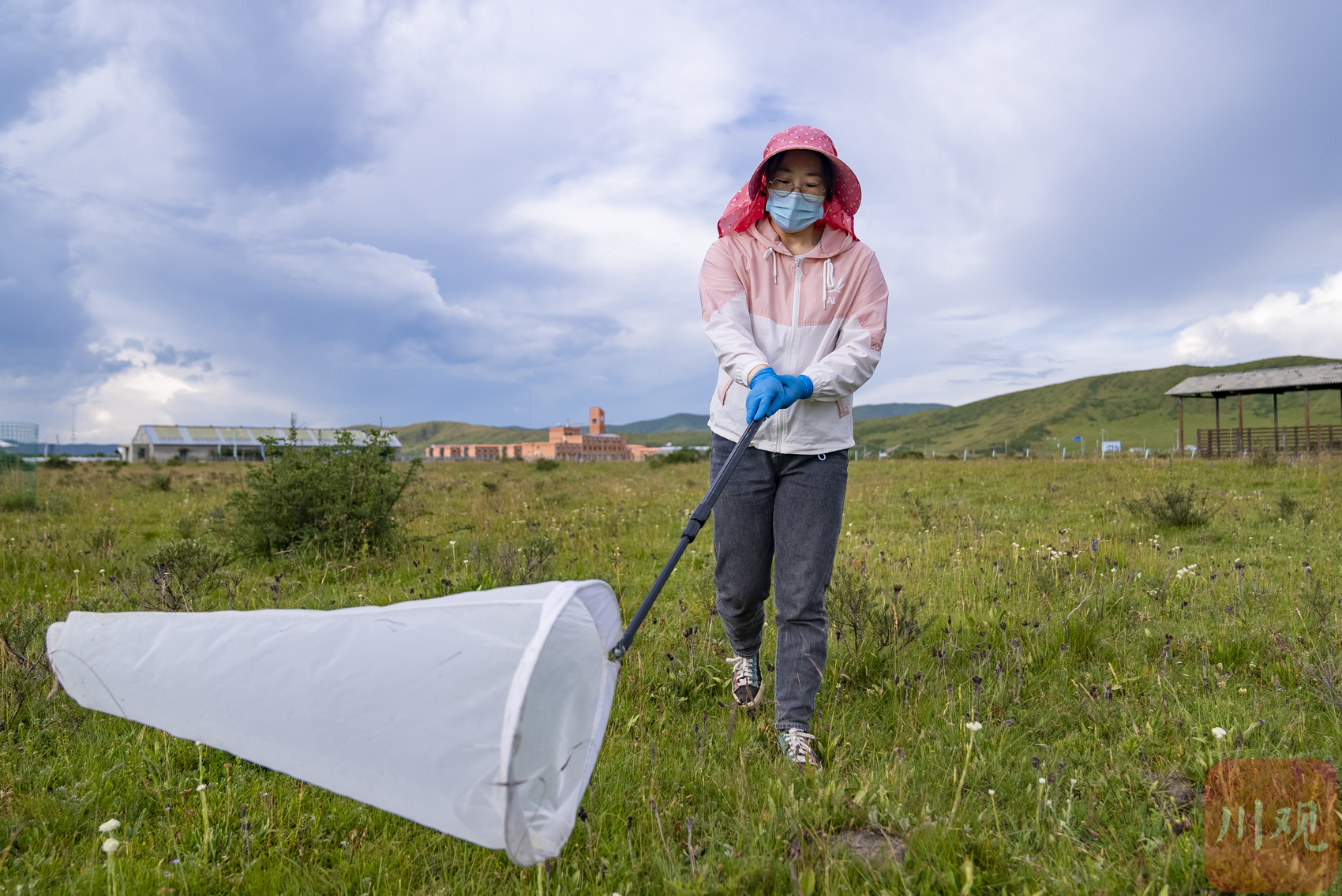

Don't look at it just a simple movement. Each box must be swept 96 times. Each action should be kept as much as possible as possible, and at the same time, it is necessary to reduce interference with plant communities.
Sweeping the net should also choose as sunny and windy weather as much as possible. It is carried out at 10 o'clock to 16 o'clock per day. This is the most active period of insect activities. At the end of the sweeping net, they should count the types and numbers of insects in the statistics, observe their size and body temperature in turn day and night, observe their behavior, and put it back after the end.
Global warming is an indisputable fact, and it is also profoundly affecting the structure and functions of the ecosystem. Earlier research on the impact of global warming on biological communities is mainly concentrated in plant community. It rarely discusses the response process of animals to increased temperature from community levels, especially the lack of research on control experiments.
In 2014, Sun Shucun team of Nanjing University professor led the average quality sample of about 20 hectares of about 20 hectares in Hongyuan County to build 6 such large -scale opening boxes to carry out the research on the relationship between the relationship between animals and plants and global changes.
In the third year, Hu Xiaoli, a doctoral student, came here and began the study of global warming on the impact of active animals and plants and its relationships. It takes several months every year for samples and experiments.
Hu Xiaoli, a postdoctoral of Nanjing University, and members of the team collected insect samples.
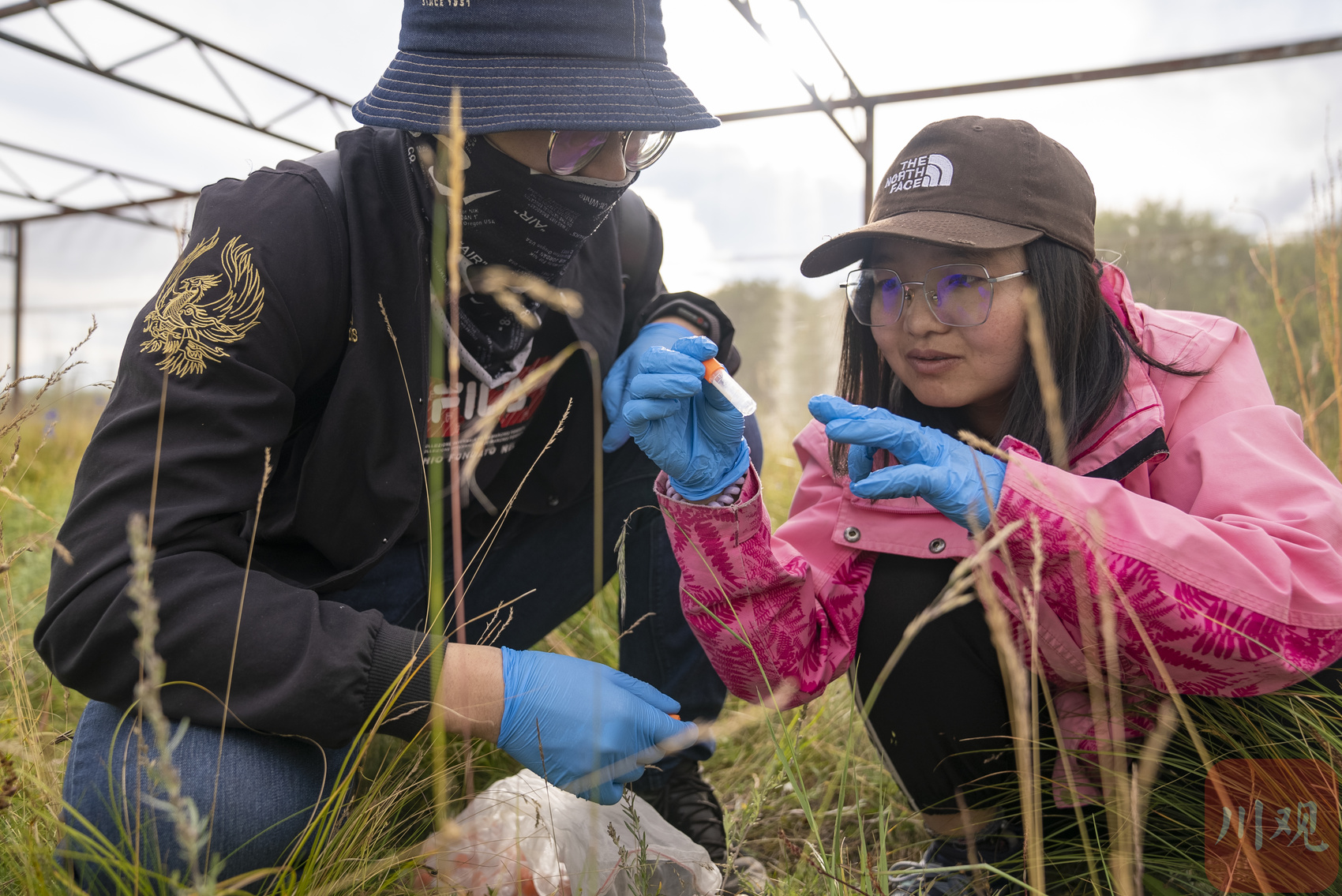

Analyze the observation data accumulated by the year, and she has some interesting discovery. "Everyone generally believes that in the context of global changes, the biological diversity of animals and plants will decrease, but from our research, the change is not so simple." Hu Xiaoli said, "Research found that temperature increases have different effects on the number of different groups. For example, Increasing the temperature significantly increased the number of foam cicadas and blind crickets, but significantly reduced the number of moths and mosquitoes. Generally speaking, the diversity of plants and insects is declining. "
In addition, as the climate warms, the bugs will not "passively wait for death", and they are also actively adapting. "For example, we will worry that the insects will be reduced, and the spiders with insects will be restricted. In fact, spiders will gradually adapt to the new resource and environment of temperature -increased warming by regulating their predatory behavior. The insect spiders, because the number of big bugs decreases, is to eat small bugs. "
Hu Xiaoli said that the complex food networks composed of dozens of hundreds of animals and plants will change in themselves, can they still be stable, and there are more unknown waiting to be explored.
Study one soil and one leaf to simulate future climate change
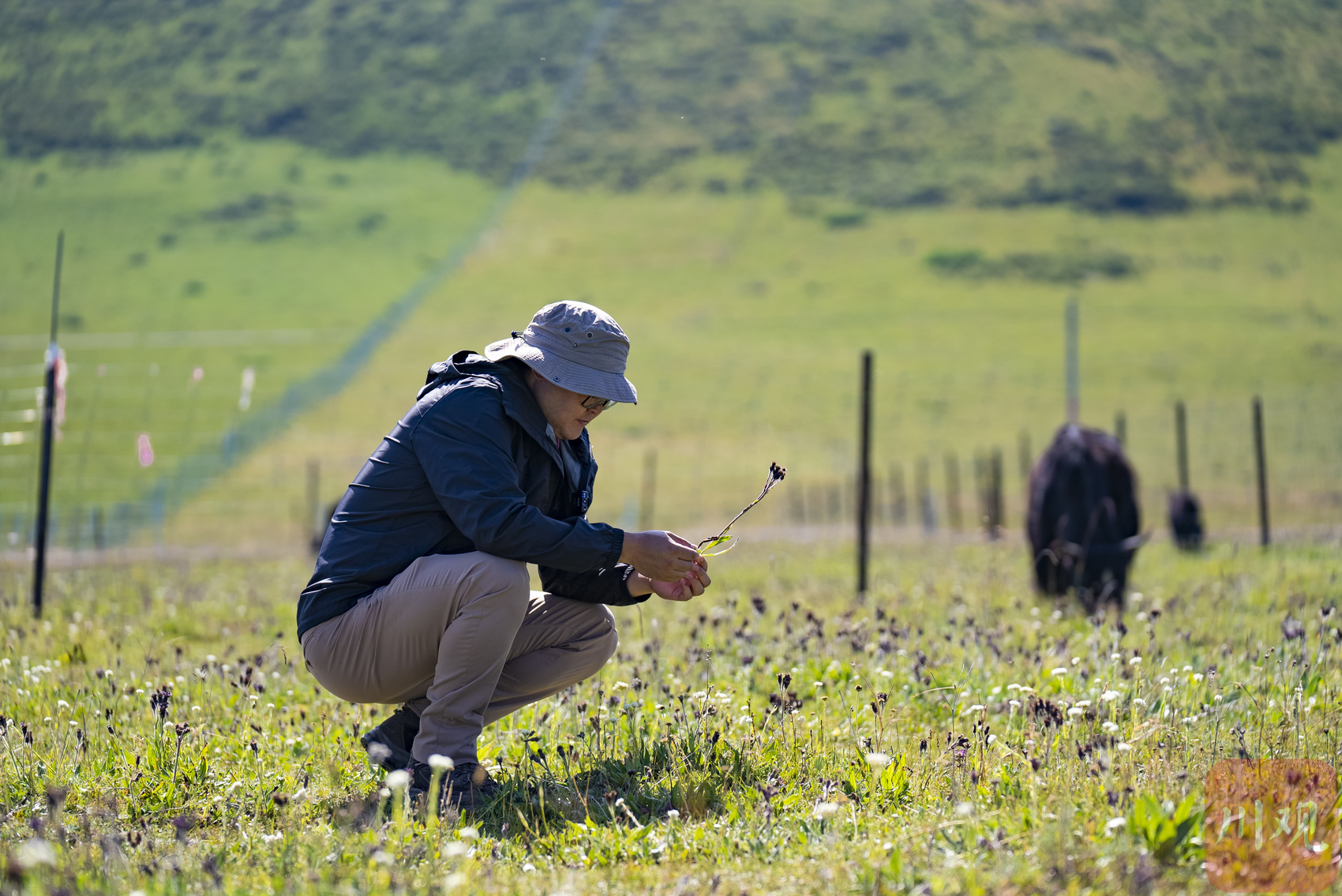
Under the scorching sun, Tian Dajuan, an associate researcher at the Institute of Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, "do medical examinations" for plant leaves with students. He carefully placed a grass in the sample into the leaf chamber of the portable photochemical instrument, and its photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate and other indicators appeared in real time on the screen. Aerial High Curchidal and Global Change Test Platform.
This is the high -cold meadow and global change test platform of Jorgi Station. It was co -built by the Southwest People's University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Here, the grassland is divided into several places. Some of the sites are erected on the surface, and the lamps that are radiated with infrared rays are hung to achieve the heating of about 1.5 degrees to 2.5 degrees to the surface to simulate the scene of future climate warming. Some sites on the surface have set up a series of canopy to change the rainfall received in the sample to study the response to the changes in the rainfall of the plants and microorganisms in the ecosystem.
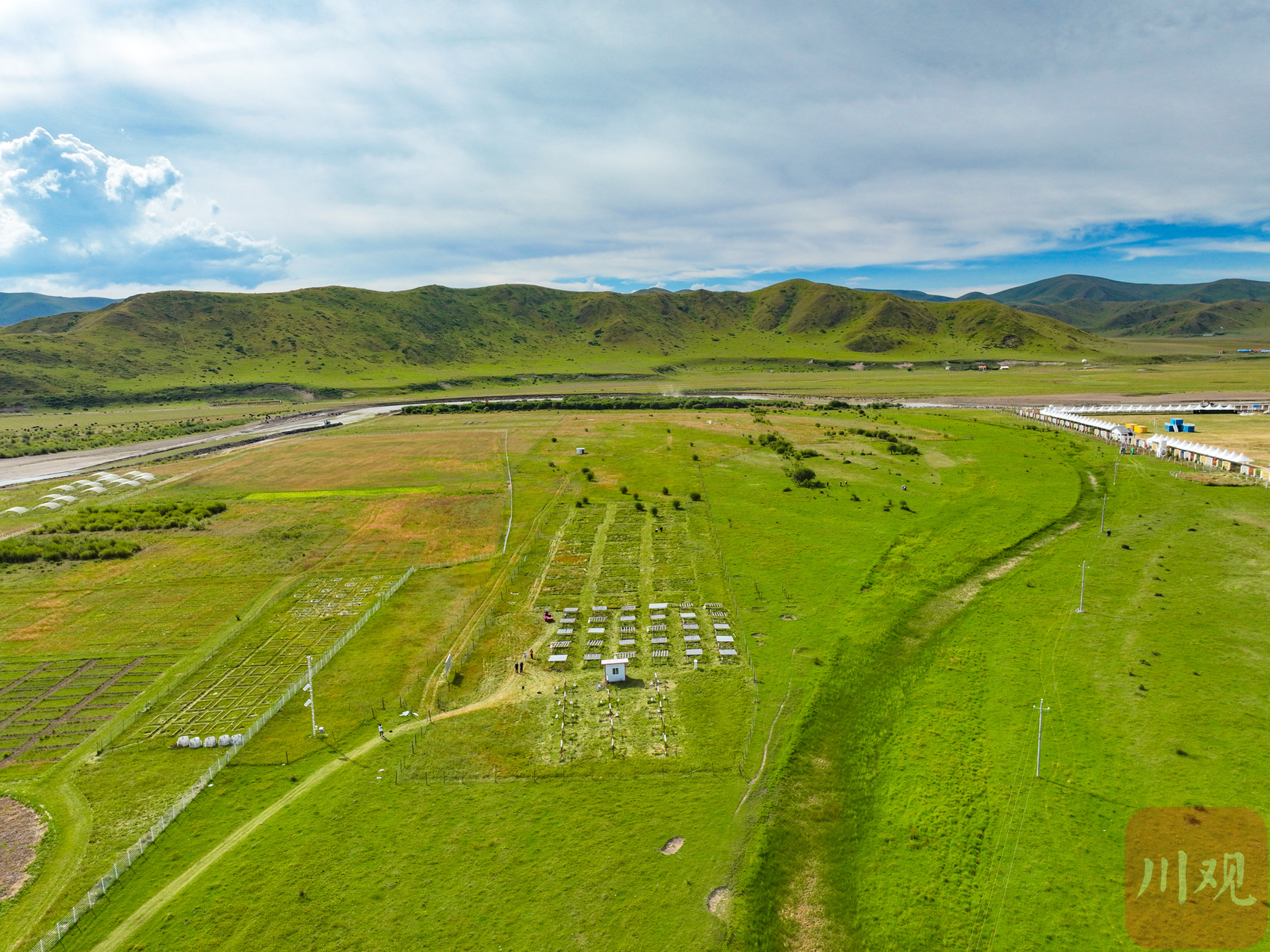

Tian Dajuan, an associate researcher at the Institute of Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced the grass heating gradient experimental device.
Why do you have to do these tasks, you have to start with global changes. Continuously intensified global changes, such as rising carbon dioxide concentration, climate warming, and changes in rainfall. The Qinghai -Tibet Plateau is a "natural laboratory" of biological evolution. It has a high climate sensitivity, and it is also an important area that affects the global carbon exchange function.

In order to study how the carbon exchange capacity of the Gahan Wetland ecosystem responds to global changes, in 2014, Niu Shuli, the headmaster of the Johga Station and the Researcher Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, established a series of control experiments of simulated climate change.
The staff is arranging the full -section of the underground soil.
This is a precise exploration. They are like a doctor, holding the "stethoscope" to capture the response of global changes in the ecosystem. They have continuously monitoring each carbon cycle process and their fine groups. The collected data is finely refined to how much carbon dioxide is exhaled, how much carbon dioxide in the soil is exhaled; how much these carbon dioxide will be solid after entering the soil, what form exist in it, and how to stable and lasting solidarity. Answering these questions is of important scientific significance for the evolution process of studying the Gaohan Caotou ecosystem in the context of global changes.

Research by Niu Shuli's team found that in the context of climate warming, the absorption of the net carbon absorption of the high -cold meadow ecosystem of Johgai has great variants, and the mutation of the breathing release of plants and microorganisms is also large. It is expected that in the context of climate change in the future, the carbon exchange capacity of the high -cold meadow ecosystem has great uncertainty. Combined with global big data, it is found that the carbon revenue and expenditure of the ecosystem responds to the direction and amplitude of global warming. Climate warming generally reduces the clean -carbon absorption capacity in the arid areas, but the impact in the humid area is manifested as a promotional role. These preliminary research results need to be further confirmed in the future.
In the comprehensive observation site of High -Cold Wetland at Ruergai Station, the staff is arranging the test platform.
Niu Shuli said that there are still many problems that the ecosystem responds to the laws and mechanisms of global changes in response to global changes.
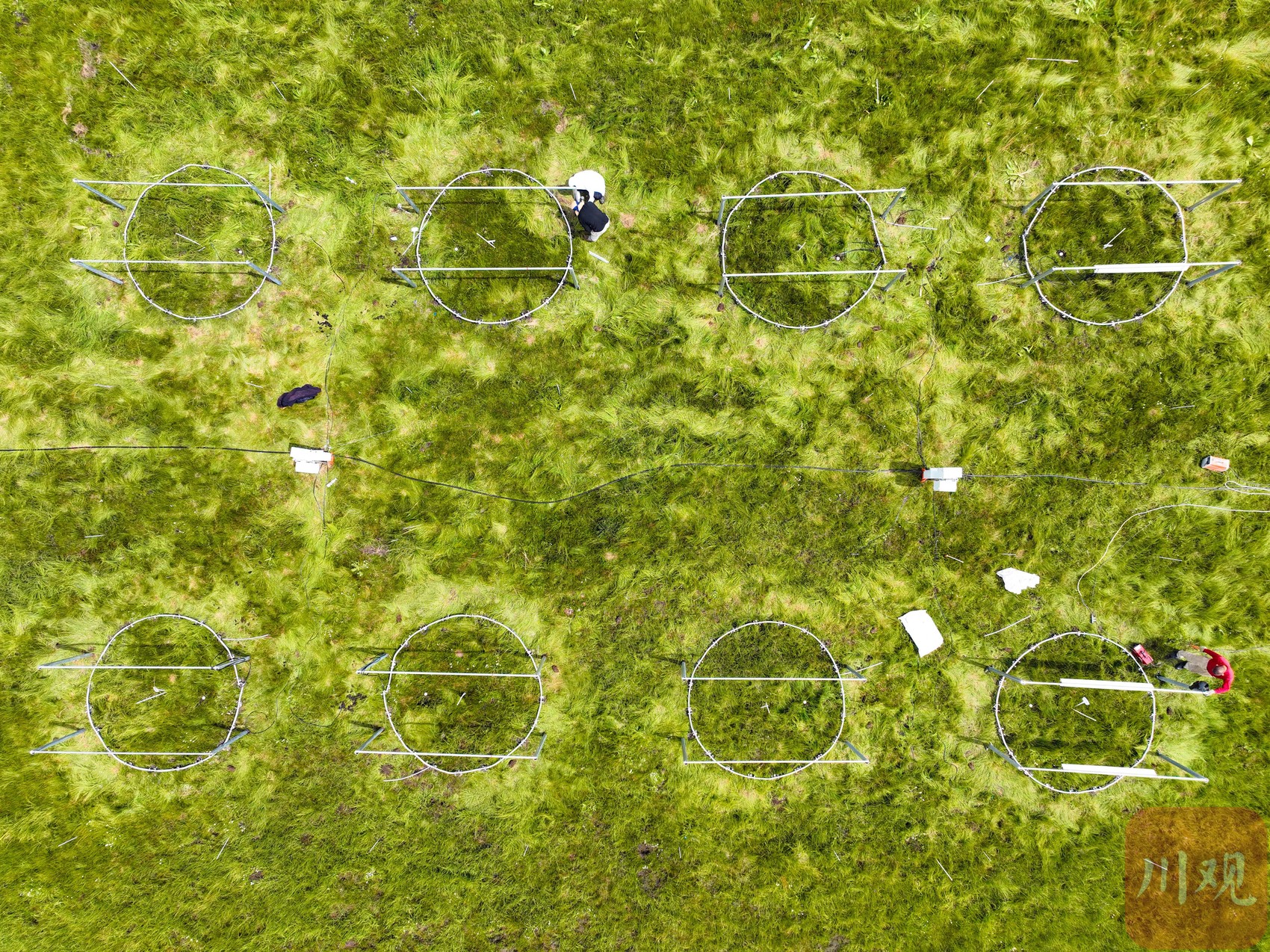

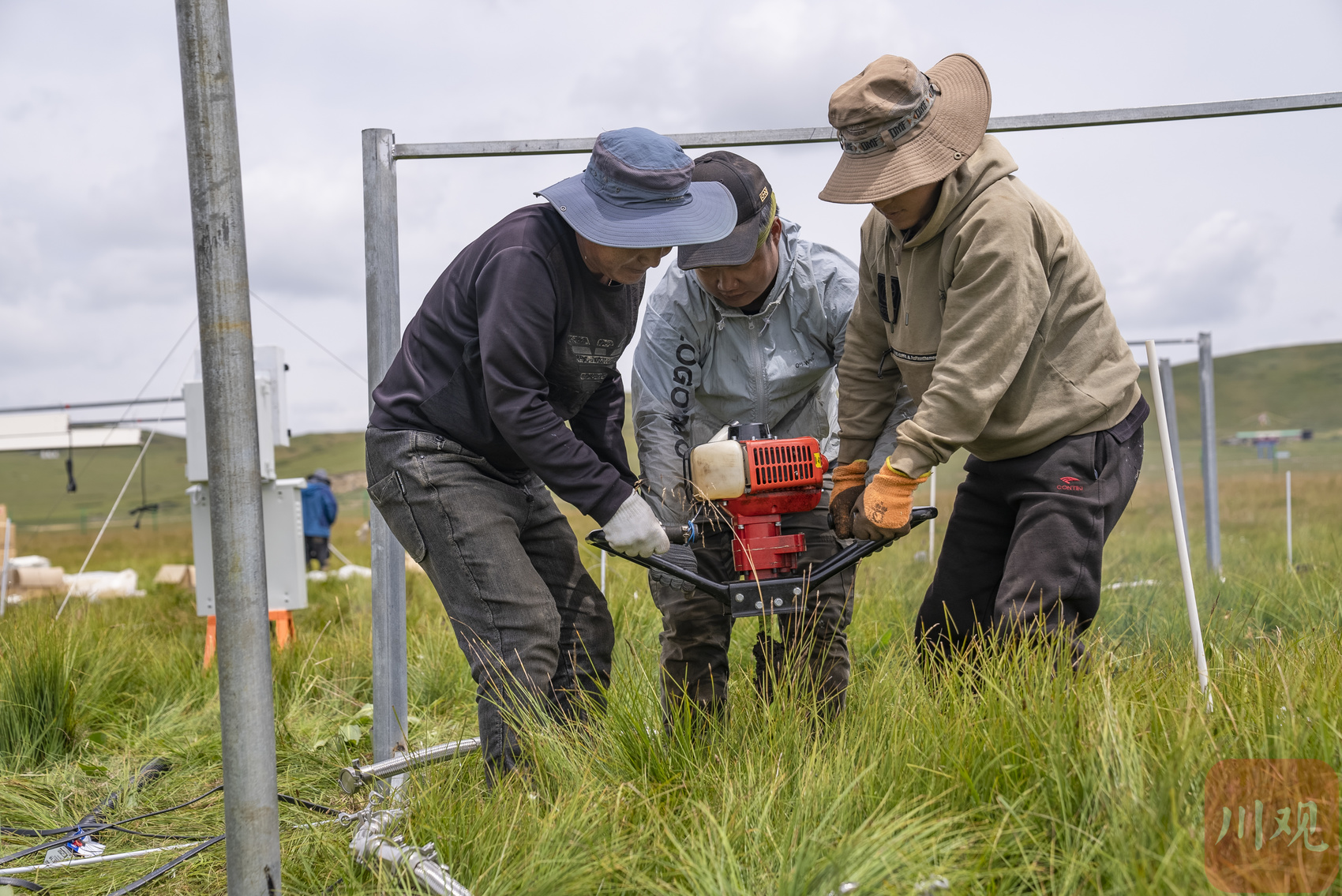
The comprehensive observation site of the Great Cold Wetland of the Great Cold Wetland of the Great Cold Wetland at the Hiroshi Town of Wakche Town, which is half an hour away from Ruergai Station, Pan Junxiao, a assistant researcher at the Institute of Geographic of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, took the students to install a new "auspicious device".
This is an experimental field that combines a variety of temperature increase methods. The experimental treatment is blank control, temperature increase above ground, the temperature increase of the entire underground soil, and the temperature of the ecosystem, and each treatment is 4 repeated. Each treatment is a round -like recipe with a diameter of 3 meters. The heating on the ground is heated with infrared radiator to heat through the lamps that radiate infrared infrared through the steel frame. The horizontal two-circle heating cable buried at the surface of the surface layer is expected to increase the temperature of 0-10 cm soil to the surface layer.
"We monitor the groundwater level, soil temperature and humidity, greenhouse gases, and plants. Monitoring data can be transmitted to Beijing for observation and data analysis in real time, which greatly shortens the work time of the field and improves the efficiency of scientific research." Pan Junxiao said Essence
- END -
Wang Yi: Sino -Malaysia relations set new goals, clarify new focus, and reach a new level
Xinhua News Agency, Kuala Lumpur, July 12th. On July 12, 2022, the State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi met with reporters after talking with Malaysian Foreign Minister in Kuala Lumpur.Wang Yi
Japan officially approves the nuclear sewage discharge plan!
On the morning of the 22nd, local time in Japan, the Japanese Atomic Energy Regula...