Analysis of how symbiosis suppress metabolic syndrome
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.09.25

Written article | Xueyue
##And metabolic syndrome is a very complicated pathological state, which can lead to a variety of diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, stroke and II diabetes. Change of diet is the main factor of increasing incidence of obesity and metabolic syndrome. High-Fat Diet (HFD) of Western-style high-fat diet can cause obesity and related metabolic complications. There are many studies on the advanced pathology of these diseases, but it has not yet been fully clarified for its starting mechanism. In addition, there is still controversy in the role of non -fat components in diet. It has not been determined whether the sugar content in food is metabolic syndrome is not determined.
The intestine is the largest immune organs of the body and will contact the food antigen. The intestinal immune system has become an important regulatory factor for metabolic steady state. HFD can increase intestinal inflammation and cause inflammation of toxin ledin and fat tissue. However, HFD has increased the mechanism of intestinal inflammation and the diet that mediated these changes has not yet been determined. And it is unclear how to regulate the metabolic syndrome about intestinal microorganisms.
Recently, the Ivaylo I. Ivanov team from Columbia University published an article entitled Microbiota Imborance Industry Indic Sugar Disrupts IMMUNE-MediaTABOLIC SYNDROME. This analysis found that bacteria induced TH17 can prevent or treat metabolic syndrome and II diabetes by regulating small intestinal lipid absorption.
In order to study the starting mechanism of metabolic syndrome, the author first detected mice around the HFD diet. Inflammation changes have not yet occurred during the surrounding area. Compared with mice with a normal diet, the author found that HFD mice have characteristics of metabolism syndrome, including weight gain, insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. In the inherent layer of the small intestine, the RORGT+ Foxp3-Th17 cells are significantly reduced, but the Rorgt-or RORGT+ Foxp3+ Tregs has not changed significantly, and the RORGT of RorGT+ TH17 cells has decreased. This shows that TH17 cell function is destroyed. Cyclical detection found that IL-17+TH17 was significantly reduced. However, other cell groups expressing IL-17 are not affected. However, the proportion of TH1 cells in the inherent layer of small intestine increases, and CCR6+ ILC3 (can produce IL-22) cells is enriched. Detecting other inflammatory immune cell sub -groups, the author did not find significant changes. The main bacteria SFB that induced TH17 cells found that the abundance of SFB in the intestine decreased significantly, and the ability of SFB specific TH17 to express IL-17 also decreased significantly. This shows that HFD will quickly cause bacterial loss induced TH17, causing TH17 cells to be destroyed, which occurs before the emergence of metabolic syndrome. The author also detects this phenomenon in human samples.
The author then uses Rorg-Stop-Flox (STOP) mice to detect the role of ILC3 and TH17 on metabolic syndrome. The author found that the protective effect of microorganisms requires TH17 cells. TH17 cells such as SFB are necessary for protecting and preventing and preventing obesity and preliminary phenotypes in diabetes. The author also treats SFB mice. When the abundance of SFB recovers, the author found that the intestinal T cells were corrected, TH17 cells rose, TH1 cells decreased, and dietary diabetes and metabolic syndrome improved.
The author also studied the impact of each component on SFB and TH17 cells. The author found that the sugar in the dietary ingredients will cause the abundance of SFB and the decrease in the proportion of TH17 cells, not fat ingredients or cellulose. And if the sugar in the diet is not enough to provide the treatment effect, it also needs the help of TH17 cells. Therefore, the combination of diet intervention and immunotherapy may achieve the expected treatment effect.
The author compared the composition of HFD and sugar diet mice and the intestinal flora in the control group. The sugar can increase the abundance of ErysiPelotrichiaceae in the intestine, especially Frod, which in turn replaces SFB and reduces intestinal protection. Sex cell TH17. Finally, the author found that the IL-17 secreted by TH17 cells can regulate the expression of CD36 of fatty acid transport protein in the epithelium, thereby regulating the intake and absorption of small bowel lipids to prevent metabolic syndrome.
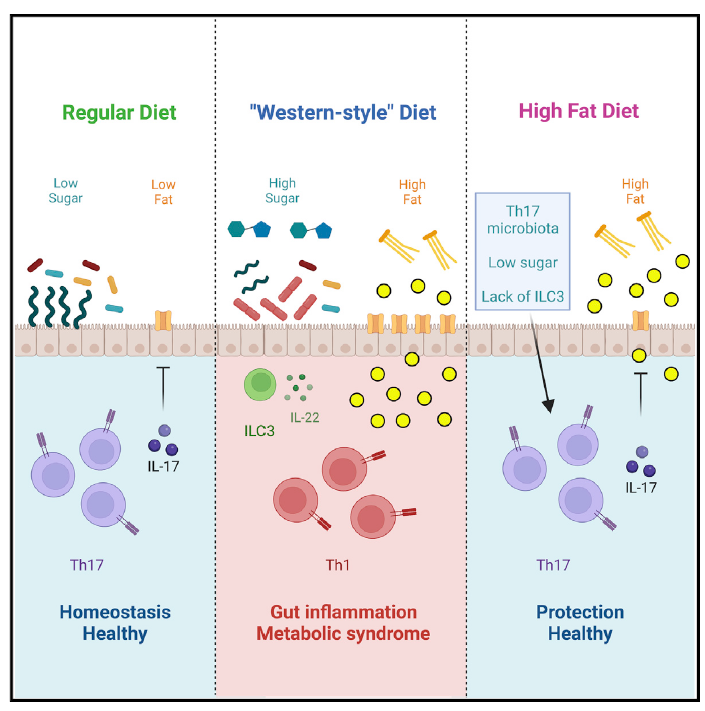
This study provides a protective role for the intestinal flora to regulate the intestinal immune system to prevent and treat metabolic syndrome. It is a key potential treatment target for metabolic syndrome and type II diabetes.
Original link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.20222.08.005


Want to know more exciting content, come and pay attention to BIOART biological art
- END -
Sichuan Tianquan carried out the environment and product testing of specialty agricultural products in 2022

In order to promote the establishment of the provincial Bamboo Sea Fishing Townshi...
Exit: In -depth promotion of the "Double Hundred" action to maintain the stability of traffic safety in the jurisdiction
Huanghe News Network Luliangxun (Wen Jing) Tao Hongpo squadron of the traffic police brigade of Jiaotou County strictly implemented the Double Hundred action plan and the arrangement of superior arr