Cao Yang and others found the liver-heart interaction new molecules: coagulation factor XI
Author:Bioart biological art Time:2022.09.27

The interaction between small molecules such as secretion of protein -mediated organs is essential for maintaining the steady state of the body. The functions of the heart and the liver are closely linked and influenced each other. For example, patients with non -alcoholic fatty liver increase the risk of heart failure; at the same time, patients with heart failure will also be accompanied by acute or chronic liver disease. Therefore, understanding the interaction between other organs and the heart is very important for diagnosis and treatment of heart disease.
Hemorrhoids retaining heart failure (HFPEF) is a type of heart failure, accounting for about half of the number of patients with heart failure. Compared to studying more ejaculation scores reduced heart failure (HFREF), the risk factors of HFPEF are closely related to metabolic conditions, including obesity and diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and women's gender. HFPEF's inflammation and metabolic disorders involve multiple organs outside the heart, including liver, lung and kidney. The cause and treatment of HFPEF are complicated. Many drugs that are effective for HFREF have no significant effect on HFPEF. Except for the recently proposed SGLT2 inhibitors (blood glucose drugs), there is no effective drug treatment HFPEF. Therefore, at present, it is urgent to understand the mechanism of HFPEF and find effective treatment methods.

Recently, the Aldons Jake Lusis team from the University of California, Los Angeles, published an article entitled Liver-Heart Cross-Talk Mediated By CoACTOR XI Protector Against Heart Failure in Science. The article found that the coagulation factors secreted by the liver to regulate the heart effect and protect the dirty relaxation function of the HFPEF center.

In order to systematically screen the factors that media the liver-heart interaction, the author uses about 100 near-handed mouse products with about 100 different genetic backgrounds, namely Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel (HMDP). The author conducts high-throughput RNA-SEQ on the liver and cardiac tissue of about 100 mouse products in HMDP, and establishes the HMDP database. The author screens the secretion protein expressed in the liver, and calculates the correlation between these proteins and the cardiac transcription group, predicts that the secretion protein related to the heart transcription group is predicted and sorted according to the strong and weakness of the heart. There are some liver secretion factors in this list. Studies have found that it has a regulation of the heart, indicating the accuracy of this method prediction. The author found that the coagulation factor XI (FXI) can mediate the heart through further verification and analyze the new molecular pathway.
In the mice HFPEF model, the level of FXI in the blood is significantly negatively related to heart relaxation function damage. The author further adopts AAV and KO mice to express and knock out FXI in the liver, and establish the HFPEF model to evaluate the changes in the heart relaxation function. Studies have found that the heart relaxation function of the mice expressed by FXI becomes better, while the heart relaxation function of the mice knocked by FXI has deteriorated. FXI is a factor of endogenous coagulation pathway. After activation, it promotes the activation of coagulation factor IX and then promotes coagulation. Expressing FXI in the HFPEF mice model, the coagulation function has not changed significantly, indicating that FXI expresses other functions except coagulation.
FXI expresses the activation of the BMP7-SMAD1/5 pathway in the heart, that is, FXI promotes the shear maturity of BMP7, thereby promoting SMAD1/5 phosphate. The phosphorylated SMAD1/5 and SMAD4 are combined in the nucleus and the expression of inflammatory and fibrosis related genes, thereby weakening the inflammatory and fibrosis of the heart, and improving the heart relaxation function. After mutation of FXI's protein hydrolysis area, the regulation of SMAD1/5 phosphate disappears, indicating that FXI's regulation of BMP7-SMAD1/5 relies on its protein hydrolysis activity. Among HFPEF patients, the level of FXI in the blood is significantly negatively related to heart relaxation function damage, indicating that FXI also has similar effects among HFPEF patients.
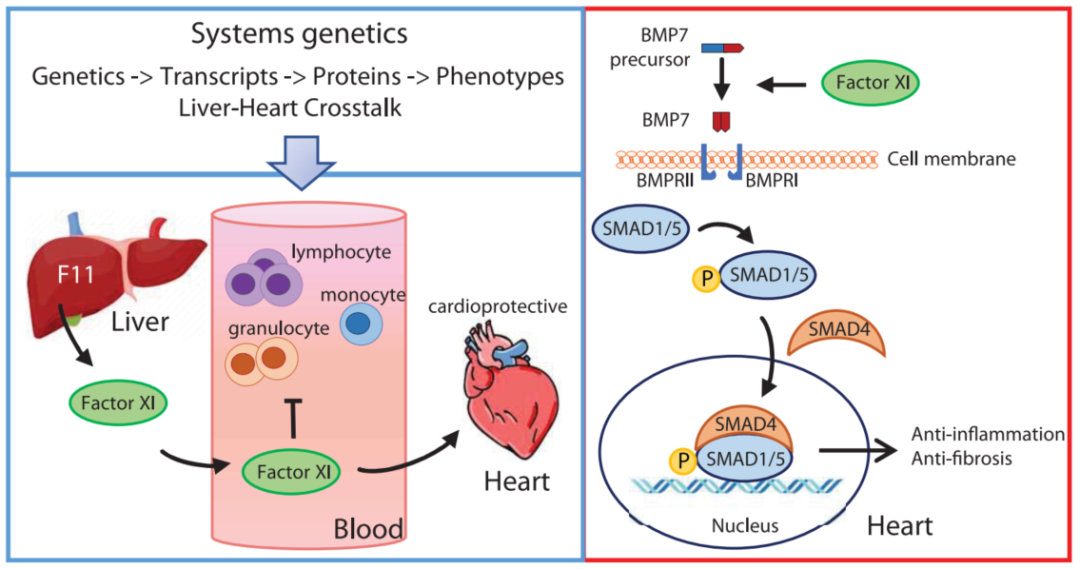
This study reveals that FXI has the function of protecting the dirty relaxation function of the HFPEF center, which is independent of the coagulation path of traditional discovery. In view of the early discovery of FXI participating in regulatory coagulation and thrombosis, the risk of cardiovascular diseases, FXI should be used in HFPEF treatment. More research should be required. However, its downstream BMP7-SMAD1/5 pathway may be a key target for research and treatment methods.
During the same period, Science published a special comment: a coagulation factor moonLights in the heart. Comments pointed out the exchanges and regulation of the work disclosure of Cao Yang and others. Studies have important clinical significance: BMP7-SMAD channel regulation can be used as the treatment target of HFPEF. With the launch of anti -FXI clinical experiments, Cao Yang's work reminded FXI that FXI caused possible trouble in myocardial muscle, and clinical evaluation needs more detailed development.

Original link:
http: //doi/org/10.1126/sclence.abn0910


Want to know more exciting content, come and pay attention to BIOART biological art
- END -
One day | If you love something in your heart, you will be worth it in the world

The shaving is scattered like wavesDisappear at the end of HaitianWood grain like ...
State Grid Xiangtan Power Supply Company: Help the "Supervisor" of the Summer Discipline Inspection "Supervisor"
We must do a good job of supervising the power supply of the peak summer and summer, and cooperate with various professional departments to move the supervision of the supervision, strengthen on -sit