Obviously, why can I continue to "dazzle" desserts?
Author:China Popular Science Expo Time:2022.09.26
I do n’t know if you have experienced such an experience. After a meal, I feel that I ca n’t eat it anymore, but after seeing the dessert, I can still be happy. Just like a Crayon Shin -star, it is obviously full, why can the stomach still "freely free up" and continue to eat desserts?

Image source: "Crayon Shin new"
Dessert attracts you not just delicious
When eating, there are not many types of making or buying themselves. Usually concentrated on two or three kinds of food. When the same food is eaten more, the happiness obtained from it will decrease. This is a phenomenon called Sensory-Specific Satiety (SSS). It is a sensory pleasure, which was proposed by French physiologist Jacques Le Magnen in 1956. Usually when you eat the same food to reach a certain amount, the satisfaction of this kind of food will decrease, which will produce a sense of satiety. The happiness obtained from this kind of food will also decrease.
For example, when you hear a nice song, keep circulating, after listening for a while, you will feel that this song is not so attractive. When we eat, we feel that this large table of food is delicious, but over time, the brain will eventually become "tired" of the food and then feel full. If you change your dessert at this time, because the dessert is a new flavor food in this meal, it will cause the update of appetite, so that the stomach can still make room for desserts, even if you have felt full before.
A study published on Brain in 2001 further proves this phenomenon. Scientists recruit volunteers to participate in chocolate experiments and observe the brain activities of volunteers. After each one after eating a piece of chocolate, volunteers are asked to give themselves happiness and whether they want to eat. Although volunteers eat the same chocolate (volunteers themselves have not been told), their scores have gradually declined. By observing the brain activity, scientists found that when they were more willing to eat chocolate at first, the brain's 胼胝 (pián zhī) below area, the inner orbital cortex (love/reward) of the tail on the tail was more active. However, when they were full, they were full. , Back to the hippocampus and the outer orbital cortex (dislike/punishment), etc., are more active.
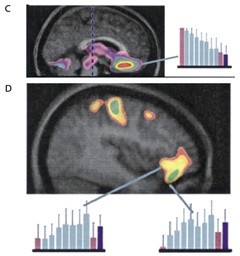
Eating chocolate status from left to right. The C picture shows that the RCBF of the lower area, the hill brain, and the middle brain decreased. The D picture shows the increase in RCBF in the outer orbital cortex of the tail. Picture source: Literature [2]
The researchers also experimented with different types of chocolate and got the same results. So even if the attractiveness of the meal to your brain has been reduced, when encountering other foods, such as desserts, your brain will respond differently.
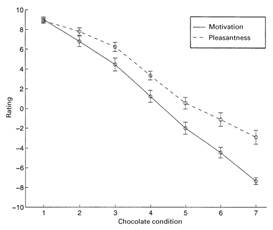
Eat the degree of pleasure (dotted line) and solid (motivation) in different states of chocolate. The more you eat, the degree of joy decreases, and the power to eat chocolate also decreases. Picture source: Literature [2]
Sugar is not strong enough
For those who love sweets and do not want to gain weight, there is also a bad place: dessert (mainly sugar) will not make people have a strong sense of fullness.
When we are hungry, the stomach releases a hormone called hunger hormonal, which stimulates the nerve transmission signal to tell the brain that it needs to eat. When eating, complex carbohydrates, protein, and cellulose can lead to a significant decline in the content of hunger hormones, thereby alleviating hunger and enhancing satiety.
But I have to admit that eating sugar and drinking water will not last long. The intake of sugar will quickly decompose to monopolic sugar into the blood, and the blood glucose level will rise. At this time, it will feel full. The abdomen disappears. This process is relatively fast, and the stomach secreted by hunger hormones is still empty, so there will still be hunger.
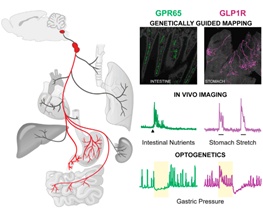
How does the brain feel full? Picture source: Literature [3]
Of course, eating desserts in the real world will still feel full. This is because although the dessert has a high sugar content, it also contains other nutrients, so it is not the same as eating only sugar. In addition, the stomach pulls will increase also increases. These stimuli will also tell the brain to be full. But because its ingredients are mainly sugar, the feeling of fullness will be weaker.
In summary, after eating full meal, desserts are attractive to the brain under the influence of the SSS mechanism, and eating desserts is not strong enough, so after eating full meal, we can continue to "dazzle" desserts ~
Why does the brain respond like this
In some people who want to lose weight, it is very distressed to see this, but from the perspective of evolution, this is actually an advantage. This mechanism allows us to not be limited to some foods when eating food, but tend to choose more types of food. This expands the nutritional range to a certain extent and achieves the purpose of a balanced diet. And eating more types of foods can ensure that our bodies will not lack certain key nutrients. Such brain response also makes us have a better survival advantage.
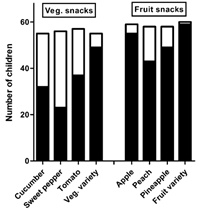
We can also use this mechanism in turn. For example, preschool children are generally low in intake of vegetables and fruits. Scientists have found that if vegetables and fruits are made into snack foods and expanded the types, it will significantly increase the proportion of children to eat a variety of vegetables and fruits. This result shows that preschool children may quickly reach "tired" to a food. In order to make children's nutrition balance, they should prepare a variety of fruits and vegetables as much as possible. Children's selection of vegetables and fruits is higher than a single type in mixed types. The four pillars on the left are vegetables, the first three are single vegetables, and the fourth mixed vegetables; the four pillars on the right are fruits, the first three are single fruits, and the fourth mixed fruit. Black indicates the number of children who choose vegetables or fruits. Picture source: Literature [4]
In short, although you know why you can eat desserts after meals, we cannot help us restrain and eat desserts, but we can help us eat better through the brain response mechanism. For example, add more types of foods when cooking, which can contain what we usually don't like to eat.
Produced: Popular Science China
Production: lunch (Peking University Sciences)
Producer: China Science Popularization Expo
references:
[1] Wilkinson LL, Branstrom JM. Sensory Special Satiety: More than 'Just' Habituation ?. Appetite. 2016; 103: 221-228. Doi: 10.1016/J.APPET.2016.04.0199
[2] Small DM, Zatorre RJ, Dagher A, Evans AC, Jones-Gotman M. Changes in Brain Activity Related to Eating Chocolate: From Pleason to Aversion. Brain. 2001; 124 (PT 9): 1720-1733. Doi:: 10.1093/brand/124.9.1720
[3] Williams Ek, Chang Rb, Strochlic de, Umans BD, Lowell Bb, Liberles SD. Sensory Neurons Thatct Stretch and Nutries. j.cell.2016.05.011
[4] Roe LS, Meengs JS, Birch LL, Rolls BJ. Serving a variety of vegetables and fruit as a snack increased intake in preschool children. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):693-699. doi:10.3945 /ajcn.113.062901
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/sensory-specific_satiety
[6] https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%A5%B1%E8%8%B9%E6%8:4%E6F/3846800?fr=aladdindin
The China Science Popularization Expo is the Science Popular Science Platform of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is sponsored by the Computer Network Information Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Relying on the high -end scientific resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, it is committed to spreading cutting -edge scientific knowledge and providing fun science and education services.

- END -
[Scientific Research Progress] New understanding of the background of the old constructor in the southeast edge of the southeast of the South China sector
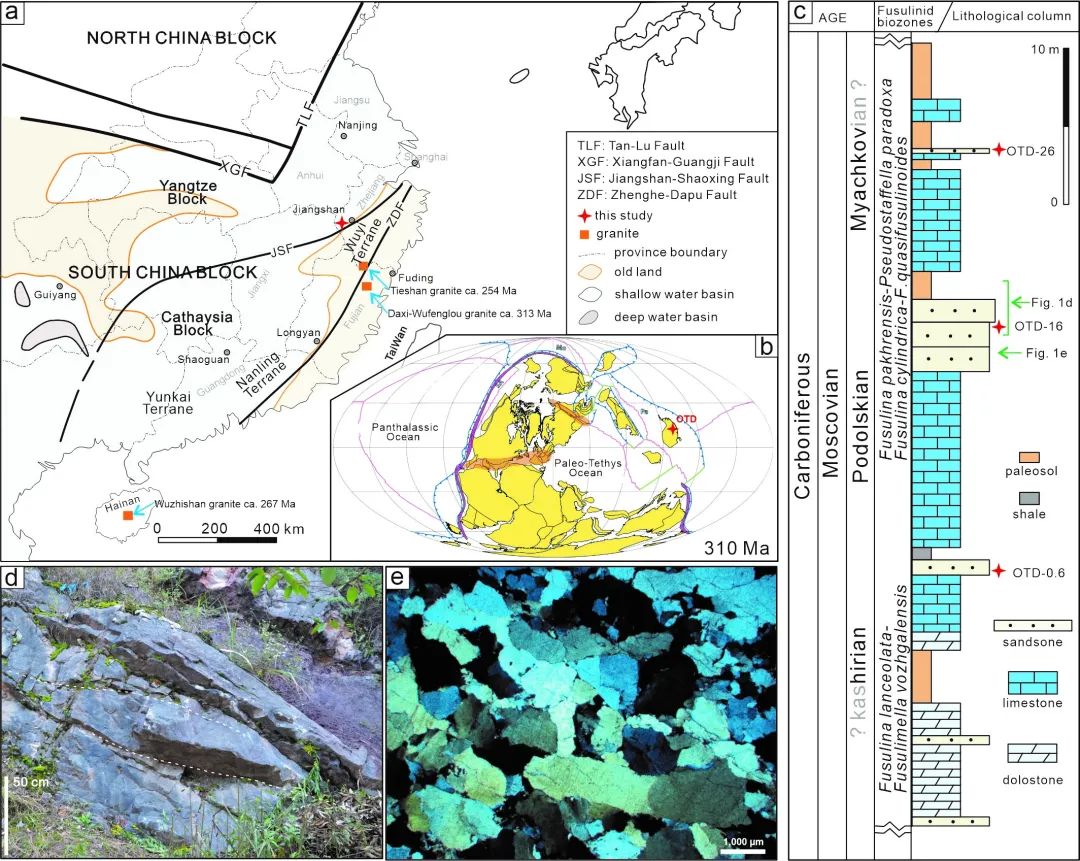
The South China sector was made up of the Yangtze Plate and the Huaxia sector in t...
[Scientific Research Progress] The joint team of Shanghai Observatory and Shanghai Jiaotong University of China and Shanghai Jiaotong University has made important progress in the structural research of the fairy landline (M31)

Recently, the joint research team of the Shanghai Astronomical Station of the Chin...