Immunotherapy Real World Report is released!Effective efficacy and quality of survival
Author:Cancer Channel of the Medical Time:2022.09.06
*For medical professionals for reading reference
Today, the combined chemotherapy of immunotherapy has gradually become a standard treatment plan, how the immunotherapy affects the quality of survival of cancer patients, a high -quality system evaluation and a contribution analysis to you.
Summary:
1. The use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIS) is related to the improvement of the patient's report ending (PROS) score.
2. Multi -drug combined therapy containing ICIS does not show the improvement of the health -related survival quality (HRQOL) related to it, but it will not cause the quality of the patient to worsen.
3. Immunotherapy helps to improve the quality of survival in patients.
ICIS changed the treatment of tumors. Although the treatment effect of ICIS has been widely studied in the past few years, compared with other anti -cancer treatment, the relationship between the quality of life with patients is rare.
A systematic evaluation and fate analysis published in Jama Network Open on August 16, 2022. Based on multiple clinical trials (RCT) based on a number of patients with advanced physical tumors that are incorporated or not received for immunotherapy, the researchers analyze The assessment of the patient's report ending (PROS) to explore the relationship between the quality of life of ICIS and physical tumor patients.

Official website screenshot
Researchers retrieve all RCT -related research related to ICIS and PROS in PUBMED, Medline, Embase, and Scopus database. The deadlined date is June 1, 2021, and a total of 2259 studies are retrieved. Researchers stipulate that the experimental group is: patients with ICIS as a single therapy or combined with chemotherapy or combined with another ICIS and/or targeted therapy; the control group is: patients with advanced physical tumors who do not include immunotherapy.
Research methods
Research search and retrieval of 34 immunotherapy related research documents, including 18,709 patients, research involved ICIS includes PD-1 inhibitors, PD-L1 inhibitors, and CTLA-4 inhibitors. Based on the global health status (GHS) scale (QLQ-C30) of the core life of European Cancer Research and Treatment (EORTC), or EUROQOL health-related quality of life, 5-dimensional 3L (EQ-5D-3L) visual simulation table (VAS), evaluate PROS. Researchers reported the quality assessment of the test using the cochrane deviation risk tool.
Ending
(1) The difference between the PRO scores assessment of the QLQ-C30 GHS or EQ-5D-3L VAS between the treatment group is different from the average changes from baseline to 12 and 24 weeks;
(2) The difference between the deterioration time (TTD) between the treatment group in the PRO score (TTD) is defined as the first time from the patient's randomization to the clinical correlation. A main measure of treatment effect.
Research result
Among the 19 RCTs that are treated as a single medicine treatment, the difference between the PROS score from the baseline to the average change of the 12 -week follow -up is 4.6 (95%CI, 2.8 ~ 6.4), and the average change from the baseline to the 24 weeks to 6.1 (95%CI, 4.2 ~ 8.1), the change of PROS has significantly supporting ICIS to improve the quality of life.
Among the 8 RCTs that apply ICIS combined chemotherapy, the total differences between the PROS scores of 12 weeks and 24 weeks are 1.4 (95%CI: −0.4 ~ 3.2) and 2.5 (95%CI: −0.8 ~ 5.9).
Among the 8 RCTs containing other ICIS treatment combinations, the total differences between the PROS scores of 12 weeks and 24 weeks are 2.1 (95%CI: −0.8 ~ 5.0) and 2.1 (95%CI, −0.4 ~ 4.5).
In all 3 groups of evaluation RCT, compared with the control group, the deterioration time of the treatment group containing ICIS is significantly longer. The risk ratio is 0.89 (95%CI: 0.78 ~ 1.00), and the risk ratio of other combinations containing ICIS is 0.78 (95%CI: 0.63 ~ 0.96)].

Fig
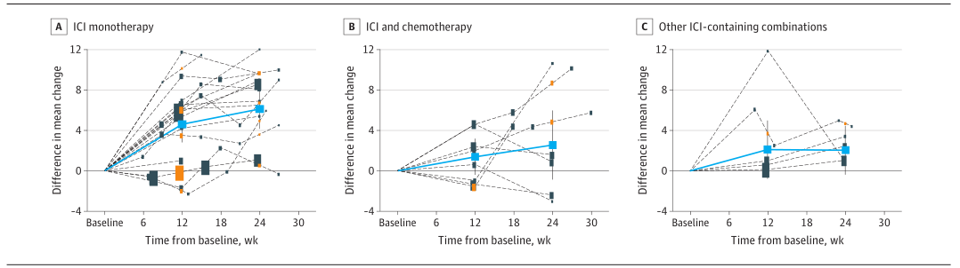
Figure 2 Different group differences between the group changes in the PROS change over time with the trend chart
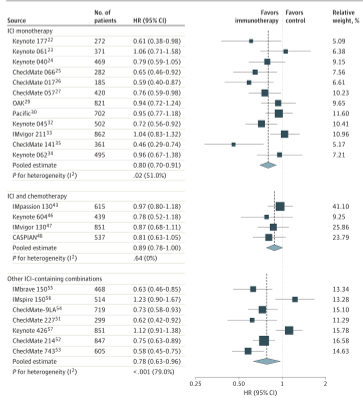
Figure 3 The danger ratio of deterioration time
The results of the study show that in the ICIS single -drug treatment RCT, with the push of time, the difference between PROS supports immunotherapy is beneficial to improve the quality of patients' survival. However, in RCT, which is combined with ICIS and other drugs, the degree of improvement of PRO at 12 or 24 weeks is limited and below the clinical -related critical value. Although this result cannot be concluded that there is a better health -related survival therapy (HRQOL) in patients receiving ICIS combined therapy, it supports such a conclusion: that is, compared with the control group, the multi -drug combination does not deteriorate patients who deteriorate patients. Quality of Life. Considering that in some random control trials, patients received up to 3 different categories of drugs, which is worth noting.
Analysis conclusion
ICIS seems to have a good correlation with the quality of life reported by the patient as a single drug, and can be used with other categories of anticancer drugs without reducing the quality of life. Study discussion
As immunotherapy combined chemotherapy is becoming a standard treatment for multiple solid tumors, this assessment of a variety of impact analysis of physical tumor treatment schemes including immunotherapy on PROS shows far -reaching clinical significance.
However, researchers point out that an important observation result appearing in the process of completing this system is that none of the incorporated RCTs use HRQOL as the main end point, and usually only mentioned Pros in the secondary end and delay reports in the secondary end and delay reports. Essence The results of this observation show that the importance of HRQOL in the field of anti -cancer immunotherapy is underestimated.
In this regard, the researchers made some suggestions. First, the evaluation of HRQOL should be included in the main goals of RCT detection immunotherapy. Second, we should consider the combination endpoint of joint evaluation, toxicity and HRQOL, such as the time-free or toxic symptoms (Q-TWIST) of the survival quality adjustment, and incorporate the Pros into the main analysis of the test results to achieve the new for the new The risk of treatment-a fair assessment of the income ratio. In addition, in most cases, the HRQOL assessment in the random control test stops after 24 weeks. Because ICIS significantly increases the percentage of long -term survival patients, the plan to extend the ICIS test should be extended to improve the HRQOL collection. Finally, the currently used tools used to evaluate PRO are limited. Due to the lack of special development and verification, these tools may not completely capture the tolerance characteristics of some new therapy. Therefore, researchers suggest that related scientific associations focusing on the quality of survival should speed up the development, verification and promotion of new HRQOL assessment tools for immunotherapy tests.
In addition, the researchers pointed out some limitations of this study. First of all, this analysis is only included in the published research, not META analysis of individual case data (IPD). Secondly, although the researchers have discovered heterogeneity related to different tumor tissue types that may be included in RCT. Potential differences between patients with different tumor tissue types are worth more detailed research in the future. Third, since only a few RCTs have reported the results of testing ICIS in the new fabric or fabric environment, the researchers have not incorporated these studies into this analysis.
Research expansion
At present, the application of immunotherapy in the field of tumor therapy is increasingly valued by the majority of clinicians and researchers. Immunotherapy drugs have long been a hot spot for drug research and development and clinical trials. Related RCTs have emerged endlessly. Accompanied by immune is immune. The treatment -related META analysis continues to emerge.
Among them, in addition to the efficacy of immunotherapy in different types of cancer, it has received widespread attention from researchers. It is also a considerable number of related studies.
In 2018, a META analysis evaluated the fatal toxic effect related to the immune checkpoint inhibitor. As a result, the fatal toxic effect of the immune examination point inhibitor is rare It occurred in the early stage of treatment [2]. In the same year, some researchers would see the problem of the related endocrine dysfunction of the immune examination point inhibitor. This META analysis report pointed out that the risk of thyroid dysfunction and pituitary inflammation in patients with PD-1 plus CTLA-4 inhibitors increased [3].
A META analysis in 2021 evaluates the heart toxicity of immune examination point inhibitors. Researchers pointed out that although the incidence of heart immune -related adverse events (Iraes) is low, the mortality rate is high, which is worthy of attention. [4]. In the same year, another META analysis also paid attention to Iraes related Iraes (CV), and found that the use of ICI is related to the increase in the risk of 6 CV-Irae, including myocarditis, cardiac percental failure, abnormal blood lipids, myocardial infarction and cerebral artery cerebral artery Ischemia [5].
Some researchers have paid attention to the relationship between side effects and efficacy and benefits in immunotherapy. This META analysis in 2021 shows that among the patients who receive ICI treatment, Iraes and Objective Relief (ORR) and no progressive survival (PFS (PFS) There is a positive correlation between the development of the period and the total survival period (OS), regardless of the disease parts, ICIS types, and Iraes. Level 3 or higher toxicity leads to more ideal orr, but worse OS [6].
references:
[1]Pala,L.Association of Anticancer Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors With Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed in Randomized Clinical Trials:A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA network open,5(8),e2226252.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.26252[2]Wang,D.Y.Fatal Toxic Effects Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors:A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA oncology,4(12),1721–1728.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3923
[3]Barroso-Sousa.Incidence of Endocrine Dysfunction Following the Use of Different Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Regimens:A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA oncology,4(2),173–182.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3064
[4] Rubio-Infantiotoxicity Association with Immune Checkpoint Inchibitor: A Meta-analysis.european Journal of Heart Failure, 23 (10), 1739–1747.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.2289
[5] Dolladille, C.Cardiovascular Immunotoxicities Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inchibitors: A Safety Meta-Analysis Heart Journal, 42 (48), 4964-4977497749774977497497497497497497497497497497497497497497497497497497497
https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab618
[6]Hussaini,S.Association between immune-related side effects and efficacy and benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitors-A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer treatment reviews,92,102134.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102134
The first release of this article: the medical world tumor channel
Author of this article: Sonia
Editor in charge: Sweet
- END -
New PD-L1 inhibitor, ADC ... New strategy of first-line lung cancer treatment | 2022WCLC

*For medical professionals for reading referenceDirectly hit WCLC, the medical ind...